User:Asif Hossain/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
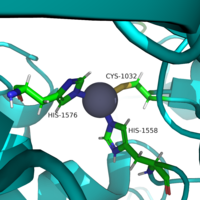
[[Image:Triad.png |200px|left|thumb|Similar to many serine and zinc proteases, HDAC8 uses a mechanism with a "catalytic triad." Instead of the Asp-His-Ser, HDAC8 uses the His to coordinate a H2O nucleophile.]] | [[Image:Triad.png |200px|left|thumb|Similar to many serine and zinc proteases, HDAC8 uses a mechanism with a "catalytic triad." Instead of the Asp-His-Ser, HDAC8 uses the His to coordinate a H2O nucleophile.]] | ||
| - | <scene name='81/811085/Active_site/ | + | <scene name='81/811085/Active_site/5'>Active Site</scene> |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 18:34, 2 April 2019
Contents |
Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8)
Introduction
Histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8) is an enzyme that plays a role in controlling gene expression. Specifically, it catalyzes the removal of an acetyl group off of the ε-amino-lysine sidechain of N-terminal core of Histone proteins. By removing the acetate ion, the reclaimed positive charge on the lysine sidechain is able to interact with the negative charge on the DNA. As a result, DNA will bind more tightly to the histone protein reducing transcription and expression.
Function
Histones
Acetylation
| |||||||||||