User:Asif Hossain/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Homology== | ==Homology== | ||
| + | ===Classes=== | ||
| + | ===Sequence Alignment=== | ||
==Structural Highlights== | ==Structural Highlights== | ||
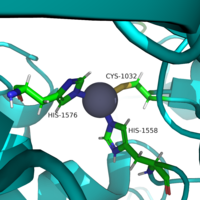
| + | ===Zinc Ion=== | ||
| + | ===Key Residues=== | ||
| + | ===Binding Pocket=== | ||
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 23: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | + | ===Gene Expression=== | |
| - | == | + | ===Disease=== |
| + | ===HDAC Inhibitors=== | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
Revision as of 19:46, 2 April 2019
Contents |
Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8)
Introduction
Histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8) is an enzyme that plays a role in controlling gene expression. Specifically, it catalyzes the removal of an acetyl group off of the ε-amino-lysine sidechain of N-terminal core of Histone proteins. By removing the acetate ion, the reclaimed positive charge on the lysine sidechain is able to interact with the negative charge on the DNA. As a result, DNA will bind more tightly to the histone protein reducing transcription and expression.
Function
Histones
Acetylation
| |||||||||||