This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
RNA polymerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 171: | Line 171: | ||
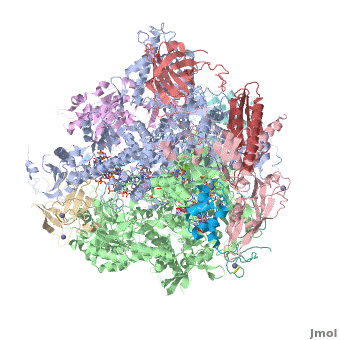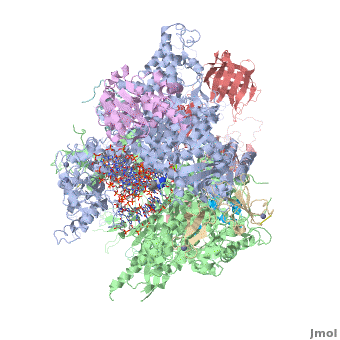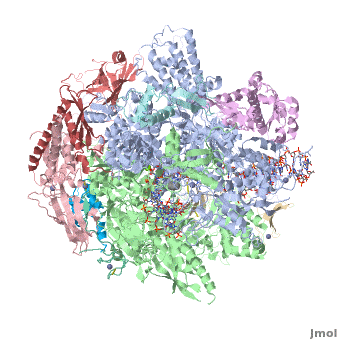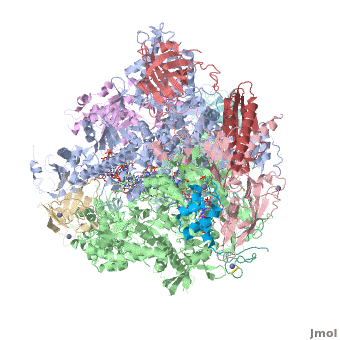
**[[1nik]], [[1nt9]], [[1wcm]], [[2b8k]], [[3fki]], [[3qt1]], [[1i3q]], [[1i50]], [[1dzf]], [[5ip7]], [[5ip9]], [[5u5q]] – yRNAP II<br /> | **[[1nik]], [[1nt9]], [[1wcm]], [[2b8k]], [[3fki]], [[3qt1]], [[1i3q]], [[1i50]], [[1dzf]], [[5ip7]], [[5ip9]], [[5u5q]] – yRNAP II<br /> | ||
**[[4x67]], [[4x6a]], [[4y52]], [[4y7n]], [[5c3e]], [[5c44]], [[5c4a]], [[5c4j]], [[5c4x]], [[6bqf]], [[6bm4]], [[6bm2]], [[6blp]], [[6blo]], [[5w51]], [[5w4u]] – yRNAP II + DNA + RNA<br /> | **[[4x67]], [[4x6a]], [[4y52]], [[4y7n]], [[5c3e]], [[5c44]], [[5c4a]], [[5c4j]], [[5c4x]], [[6bqf]], [[6bm4]], [[6bm2]], [[6blp]], [[6blo]], [[5w51]], [[5w4u]] – yRNAP II + DNA + RNA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6inq]], [[6a5u]], [[6a5t]], [[6a5r]], [[6a5p]], [[6a5o]], [[6a6l]] – yRNAP II + DNA + RNA + histones – Cryo EM<br /> |
**[[3j1n]], [[4v1n]], [[5fmf]], [[5x51]], [[5x50]], [[5x4z]] – yRNAP II – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[3j1n]], [[4v1n]], [[5fmf]], [[5x51]], [[5x50]], [[5x4z]] – yRNAP II – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[1y14]] - yRNAP II subunits RPB4 RPB7<br /> | **[[1y14]] - yRNAP II subunits RPB4 RPB7<br /> | ||
Revision as of 15:08, 3 April 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of RNA polymerase
Updated on 03-April-2019
References
- ↑ Cramer P, Armache KJ, Baumli S, Benkert S, Brueckner F, Buchen C, Damsma GE, Dengl S, Geiger SR, Jasiak AJ, Jawhari A, Jennebach S, Kamenski T, Kettenberger H, Kuhn CD, Lehmann E, Leike K, Sydow JF, Vannini A. Structure of eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biophys. 2008;37:337-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.130008. PMID:18573085 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.130008
- ↑ Comai L. Mechanism of RNA polymerase I transcription. Adv Protein Chem. 2004;67:123-55. PMID:14969726 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3233(04)67005-7
- ↑ Hahn S. Structure and mechanism of the RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004 May;11(5):394-403. PMID:15114340 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb763
- ↑ Longo DL, Herbert V. Radioassay for serum and red cell folate. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jan;87(1):138-51. PMID:1452
- ↑ Frick DN, Richardson CC. DNA primases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:39-80. PMID:11395402 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.39
- ↑ Naue N, Beerbaum M, Bogutzki A, Schmieder P, Curth U. The helicase-binding domain of Escherichia coli DnaG primase interacts with the highly conserved C-terminal region of single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(8):4507-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt107. Epub 2013 Feb, 20. PMID:23430154 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt107
- ↑ Ahlquist P. RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, viruses, and RNA silencing. Science. 2002 May 17;296(5571):1270-3. PMID:12016304 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1069132
- ↑ Fukushi S, Kojima S, Takai R, Hoshino FB, Oka T, Takeda N, Katayama K, Kageyama T. Poly(A)- and primer-independent RNA polymerase of Norovirus. J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(8):3889-96. PMID:15047805
- Created with the participation of Craig T Martin.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Karsten Theis