We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jordan Finch/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <Structure load='4psw' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Hat1/Hat2 Complex' scene='81/811713/4psw_overview/1'></scene> | ||
| - | |||
==Histone Acetyltransferase HAT1/HAT2 Complex, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''== | ==Histone Acetyltransferase HAT1/HAT2 Complex, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''== | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='4psw' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='HAT1 4PSW' | ||
| + | This is a default text for your page '''Caitlin Marie Gaich/Sandbox1'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
| + | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:Main_bonding_cartoon_3.png|400px|right|thumb|Figure 1]] | [[Image:Main_bonding_cartoon_3.png|400px|right|thumb|Figure 1]] | ||
== Hat1/Hat2 Complex Structure == | == Hat1/Hat2 Complex Structure == | ||
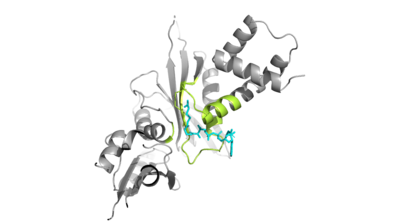
| - | + | Hat1 is not catalytically active until it binds with HAT2 to form the <scene name='81/811718/Hat1_hat2_complex_aco_and_h4/1'>complex</scene>. HAT1 structure includes 317 residues and is identified as <scene name='81/811718/Hat1_protein/1'>chain A</scene>. HAT2 is identified as <scene name='81/811718/Hat2_protein/1'>chain B</scene>, which includes 401 residues. The activated complex acetylates residues in the 38 residue span of <scene name='81/811718/Portion_of_histone_4/1'>Histone 4</scene>. | |
| + | |||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
In this mechanism, the glutamate at residue 255 acts as a general base and deprotonates lysine 12 of histone 4 (the numbering of the modified lysine residue on histone 4 is shifted two residues).The deprotonated lysine then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of acetyl coenzyme A (CoA, forming a tetrahedral intermediate transition state. The negative charge on the oxygen collapses down to for a double bond and the scissle bond between the carbonyl carbon and the sulfur atom of acetyl CoA is broken. The resulting product of this reaction is histone 4 with an acetyl-lysine at residue 12 and CoEnzyme A. | In this mechanism, the glutamate at residue 255 acts as a general base and deprotonates lysine 12 of histone 4 (the numbering of the modified lysine residue on histone 4 is shifted two residues).The deprotonated lysine then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of acetyl coenzyme A (CoA, forming a tetrahedral intermediate transition state. The negative charge on the oxygen collapses down to for a double bond and the scissle bond between the carbonyl carbon and the sulfur atom of acetyl CoA is broken. The resulting product of this reaction is histone 4 with an acetyl-lysine at residue 12 and CoEnzyme A. | ||
| + | |||
== Application == | == Application == | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| - | + | Li, Y. et. al. ''Hat2p recognizes the histone H3 tail to specify the acetylation of the newly synthesized H3/H4 heterodimer by the Hat1p/Hat2p complex.''(2014). ''Genes Dev.''28:1217-1227. DOI:10.1101/gad.240531.114 | |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 18:10, 5 April 2019
Histone Acetyltransferase HAT1/HAT2 Complex, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
| |||||||||||