This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Nicholas Bantz/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
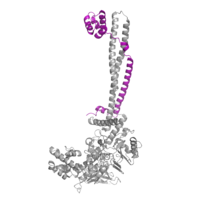
[[Image:COREST.png|200 px|right|thumb|CoRest complex (purple) bound to LSD1 at the Tower domain.]] | [[Image:COREST.png|200 px|right|thumb|CoRest complex (purple) bound to LSD1 at the Tower domain.]] | ||
| - | The <scene name='81/811088/Towerdomain/2'>tower domain</scene> is a protrusion off the main protein body of LSD-1 comprised of 100 residues, which form 2 [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix-helices 𝛂-helices]. The longer helix, T𝛂A, is an LSD-1 specific element that has not been found in any other oxidase proteins. <ref name= | + | The <scene name='81/811088/Towerdomain/2'>tower domain</scene> is a protrusion off the main protein body of LSD-1 comprised of 100 residues, which form 2 [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix-helices 𝛂-helices]. The longer helix, T𝛂A, is an LSD-1 specific element that has not been found in any other oxidase proteins. <ref name=”Stavropoulos”>PMID:16799558</ref> The shorter helix, T𝛂B, is very near to the active site of the oxidase domain. In fact, T𝛂B connects directly to helix 𝛂D of the oxidase domain through a highly conserved connector loop. The exact function of the tower domain is not known, but it is proposed to regulate the size of the active site chamber through this <scene name='81/811090/Allosterictowerdepiction/2'>T𝛂B-𝛂D interaction</scene>. The T𝛂B-𝛂D interaction is responsible for the proper positioning of Phe538, a side chain of 𝛂D that is located in the catalytic chamber. In addition, the T𝛂B-𝛂D interaction positions 𝛂D in the correct manner to provide hydrogen bonding to Tyr761. Tyr761 is positioned in the catalytic chamber very close to the FAD cofactor, and aids in the binding of the lysine substrate <ref name="Stavropoulos"/>. Therefore, the base of the tower domain forms a direct connection to the oxidase domain and plays a crucial role in the shape and catalytic activity of the active site. In fact, removing the tower domain via a mutation resulted in a drastic decrease in catalytic efficiency.(1) The tower domain has also been found to interact with other proteins and complexes, such as CoREST (see Figure 2), as a molecular lever to allosterically regulate the catalytic activity of the active site. (insert other source here) Overall, the exact function of the tower domain has not yet been determined, but it is known to be vital to the catalytic activity of LSD-1. |
=== SWIRM Domain === | === SWIRM Domain === | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 8 April 2019
Human lysine-specific histone demethylase (LSD-l))
| |||||||||||
Student Contributors
- Nicholas Bantz
- Cody Carley
- Michael Thomas