We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Steve Klimcak/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
===Hydrophobic Pocket=== | ===Hydrophobic Pocket=== | ||
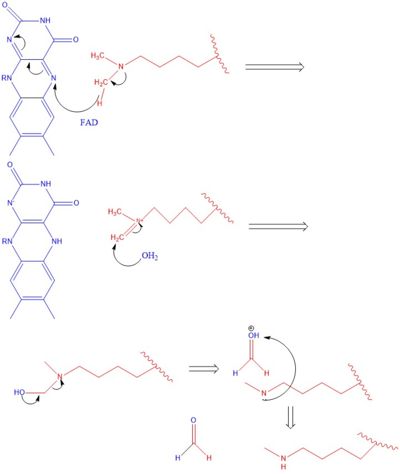
The hydrophobic pocket located in the active site cavity of LSD1, forms a catalytic chamber where the substrate lysine is oriented and positioned to interact with the | The hydrophobic pocket located in the active site cavity of LSD1, forms a catalytic chamber where the substrate lysine is oriented and positioned to interact with the | ||
| - | FAD co-factor to initiate demethylation. The specific residues making up the pocket include valine-317, glycine-330, alanine-331, methionine 332, valine-333, phenylalanine-338, leucine-569, asparagine-660, lysine-661, tryptophan 695, serine 749, serine 760, and tyrosine-761. The <scene name='81/811712/Hydrophobic_pocket/1'>hydrophobic pocket</scene> shown in green surrounds the FAD in a way such that it exposes the <scene name='81/811710/Fad_n5/4'>catalytic nitrogen(N5)</scene> that is responsible for the two electron demethylation. | + | FAD co-factor to initiate demethylation. The specific residues making up the pocket include valine-317, glycine-330, alanine-331, methionine 332, valine-333, phenylalanine-338, leucine-569, asparagine-660, lysine-661, tryptophan 695, serine 749, serine 760, and tyrosine-761. The <scene name='81/811712/Hydrophobic_pocket/1'>hydrophobic pocket</scene> shown in green surrounds the FAD in a way such that it exposes the <scene name='81/811710/Fad_n5/4'>catalytic nitrogen(N5)</scene> that is responsible for the two electron demethylation. Another three seperate pockets help bind the histone tail residues to the substrate lysine which is essential for identifying different modifications of the histone tail. |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 9 April 2019
LSD Demethylase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Khalid MF, Damha MJ, Shuman S, Schwer B. Structure-function analysis of yeast RNA debranching enzyme (Dbr1), a manganese-dependent phosphodiesterase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Nov 7;33(19):6349-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki934. Print, 2005. PMID:16275784 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki934