Introduction
Histonesare the key building blocks of chromatin. They are subject to post-translational modifications and play important roles in replication, transcription, heterochromatin maintenance, and DNA repair. Histone acetylation is a common histone modification. This involves the transfer of an acetyl moiety from Acetyl Coenzyme A (AcCoA) to an ε-amino group of the target lysine residue on a histone. This reaction is catalyzed by the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) enzyme families. The specific histone acetylation modification is an important epigenetic marker. It plays a role in RNA synthesis and there a known correlation between gene activity and histone acetylation. Any misregulations of the HAT enzyme can possibly lead to cancer, cardiovascular disease, and HIV.
HAT1 Background
was the first of the HAT enzymes to be identified in yeast. It is lysine specific for newly synthesized histone 4 (H4). One study showed that the deletion of the HAT caused a loss of acetylation on H4K5 and H4K12, leading to the conclusion that HAT1 is the sole enzyme responsible for the evolutionary conserved histone modification. The HAT2 enzyme is identified as a binding partner for HAT1 to help modulate the substrate specificity of HAT1. The complex is highly specific for H4K12.
Hat1/Hat2 Complex Structure
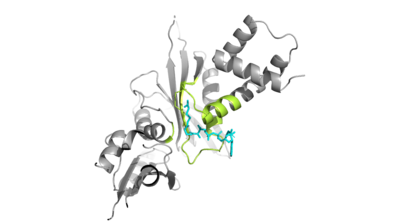
Hat1 is not catalytically active until it binds with HAT2 to form the . HAT1 structure, identified as , includes 317 residues and contains the active site for acetyl-coenzyme A. HAT2 is identified as , which includes 401 residues. The activated complex acetylates residues in the 38 residue span of .
The HAT1 and HAT2 interface is stabilized by hydrogen bonds, , and hydrophobic interactions. Most of these interactions are located in of the HAT1 domain, which forms a well-ordered helix. This LP1 helix is thought to be important for the heterodimer formation as the deletion of LP1 abolished the interaction between HAT1 and HAT2. This suggests that there may be another protein involved such as the N terminus tail of H4 acting as a linker protein interacting with the complex interface. The three major areas where hydrogen bonds are present aids in this complex formation. The side chain atoms of with the main chain nitrogen of Ala202 in HAT1. The side chain of makes hydrogen bonds with Leu288 and Phe205 respectively. The last area of hydrogen bonds between HAT1 and HAT is found between . The at the interface of the complex appears to be critical for the complex formation. This core consists of aromatic amino acids from HAT1 and leucine amino acids from HAT2, however it does not form any obvious ring stacking.
Once the complex has formed, histone 4 and AcetylCoA can begin to interact. The N-terminal segment of H4 that binds with HAT1/HAT2 can be divided into . Similar to 1BOB the N-terminal region of H4 is embedded in a cave between HAT1 and HAT2, though H4 mainly interacts with HAT1. The C-terminal helix of H4 is found inserted into LP2, the N-terminal helix, and C-terminal groove of HAT2. These interactions are strongly stabilized by salt bridge bonds between the histone and the complex. Previous studies suggest that H4K12 inserts into the active site of HAT1 to access AcCoA. The 4PSW structure has H4K12 aligned with the active site and the AcCoA entering the concave groove from the opposite side. This allows the ε-amino group of H4K12 to contact the SH group of CoA.
Active Site
The acetyl-CoA HAT1 active site is parallel to the C-terminal domain of the HAT1 protein. Acetyl-CoA fits structurally into the small binding site due to the kinked pantetheine group giving the molecule a bent confirmation. Once bound, most of the acetyl-CoA molecule is buried in the protein (~60%). Hydrophobic contacts, hydrogen bonds, and salt bridges help to stabilize the protein-ligna interaction. HAT1 protein-ligand contact is concentrated in three areas: C-terminal end of helix alpha 7, C terminal end of strand beta-14/loop Beta15alpha9, and N-terminal half of helix alpha 9.
The beta-methyl of the acetyl group interactions in the hydrophobic pocket formed by the side chain of residues: Ile-217,Pro-257, Phe-261. (ref) The carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl group hydrogen bonds with the aminde of the main chain Phe-220 and the sulfur of the acetyl-group interactions, as a hydrogen bond, with Asn-258. These interactions keep acetyl-CoA in the correct position of the active site for the transfer of the acetyl-group.
Mechanism
Of the five classes of HAT enzymes, the catalytic mechanisms for two of those enzymes, HAT1 and Rtt109, remains unclear. A structural overlay of HAT1 and Gcn5, a better-understood HAT enzyme, found a conserved glutamate residue in the active site of both molecules. Previous studies found that a mutation at the active site glutamate residue greatly alters the catalytic ability of HAT1, proving it to be structurally important. [1] Using this information and structural information from the crystallized structure of the HAT1/HAT2 complex regarding the proximity of potentially catalytic residues, the most plausible mechanism for histone acetylation involves the following relevant residues and cofactor: .
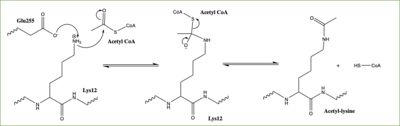
Figure 2: HAT1 Arrow-Pushing Mechanism
In this mechanism, the glutamate at residue 255 in the active site of the protein acts as a general base by deprotonating lysine 12 of histone 4 (the numbering of the modified lysine residue on histone 4 is shifted two residues in the pdb file 4psw).The deprotonated lysine then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of acetyl coenzyme Acetyl CoA (notshown in pdb file), forming a tetrahedral transition state with an oxyanion. The negative charge on the oxyanion then shift to down to reform the double bond between the oxygen and carbonyl carbon, breaking the scissle bond between the carbonyl carbon and the sulfur atom of acetyl CoA. The resulting product of this reaction is histone 4 with an acetyl-lysine at residue 12 and CoEnzyme A.
Application
References
Li, Y. et. al. Hat2p recognizes the histone H3 tail to specify the acetylation of the newly synthesized H3/H4 heterodimer by the Hat1p/Hat2p complex.(2014). Genes Dev.28:1217-1227. DOI:10.1101/gad.240531.114
[2].
- ↑ Li Y, Zhang L, Liu T, Chai C, Fang Q, Wu H, Agudelo Garcia PA, Han Z, Zong S, Yu Y, Zhang X, Parthun MR, Chai J, Xu RM, Yang M. Hat2p recognizes the histone H3 tail to specify the acetylation of the newly synthesized H3/H4 heterodimer by the Hat1p/Hat2p complex. Genes Dev. 2014 Jun 1;28(11):1217-27. doi: 10.1101/gad.240531.114. Epub 2014 May , 16. PMID:24835250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.240531.114
- ↑ Marmorstein R. Structure of histone acetyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 2001 Aug 17;311(3):433-44. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4859. PMID:11492997 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.4859
Student Contributors
- Caitlin Gaich
- Jordan Finch
- Morgan Buckley