We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Madeleine Wilson/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Inhibitors== | ==Inhibitors== | ||
| - | [[Image:Sinefugin. | + | [[Image:Sinefugin.png|200px|left|thumb|Sinefungin]] |
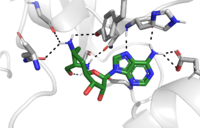
Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor. It is a structural analog of S-adenosylmethionine that is more stable due to the ability to create two additional hydrogen bonds to its amine group in the active site. It has been used experimentally to inhibit the SET 7/9 protein on peritoneal fibrosis in mice and in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. <ref name="Schluck">PMID: 8995524</ref> Tamura et al. (2018) found that sinefungin suppressed the cell accumulation and thickening in methylglyoxal peritoneal fibrosis. <ref name="Tamura">PMID: 29723250</ref> | Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor. It is a structural analog of S-adenosylmethionine that is more stable due to the ability to create two additional hydrogen bonds to its amine group in the active site. It has been used experimentally to inhibit the SET 7/9 protein on peritoneal fibrosis in mice and in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. <ref name="Schluck">PMID: 8995524</ref> Tamura et al. (2018) found that sinefungin suppressed the cell accumulation and thickening in methylglyoxal peritoneal fibrosis. <ref name="Tamura">PMID: 29723250</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:06, 16 April 2019
Histone Lysine Methyltransferase: Gene Activator
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ DesJarlais R, Tummino PJ. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1584-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210. Epub , 2016 Jan 26. PMID:26745824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2013.04.007
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dong X, Weng Z. The correlation between histone modifications and gene expression. Epigenomics. 2013 Apr;5(2):113-6. doi: 10.2217/epi.13.13. PMID:23566087 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/epi.13.13
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson JR, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn GM, Gamblin SJ. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature. 2003 Feb 6;421(6923):652-6. Epub 2003 Jan 22. PMID:12540855 doi:10.1038/nature01378
- ↑ Del Rizzo PA, Trievel RC. Substrate and product specificities of SET domain methyltransferases. Epigenetics. 2011 Sep 1;6(9):1059-67. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.9.16069. Epub 2011 Sep, 1. PMID:21847010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/epi.6.9.16069
- ↑ Schluckebier G, Kozak M, Bleimling N, Weinhold E, Saenger W. Differential binding of S-adenosylmethionine S-adenosylhomocysteine and Sinefungin to the adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase M.TaqI. J Mol Biol. 1997 Jan 10;265(1):56-67. PMID:8995524 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1996.0711
- ↑ Tamura R, Doi S, Nakashima A, Sasaki K, Maeda K, Ueno T, Masaki T. Inhibition of the H3K4 methyltransferase SET7/9 ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis. PLoS One. 2018 May 3;13(5):e0196844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196844., eCollection 2018. PMID:29723250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196844
Student Contributors
Lauryn Padgett, Alexandra Pentala, Madeleine Wilson