We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Mark Macbeth/Sandbox8
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
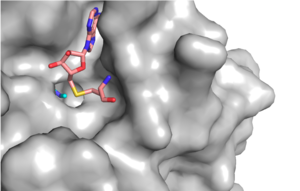
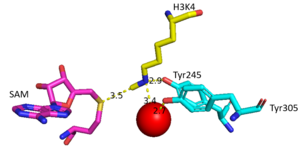
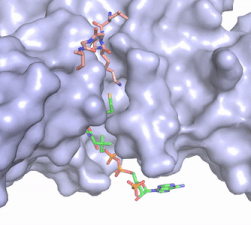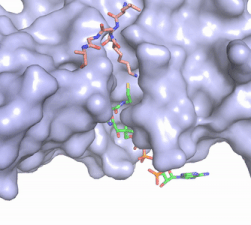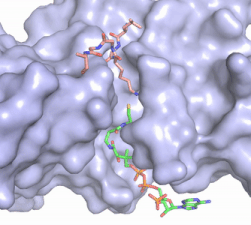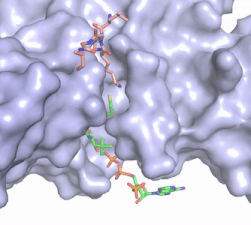
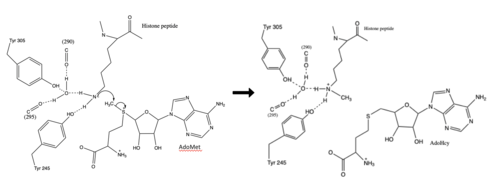
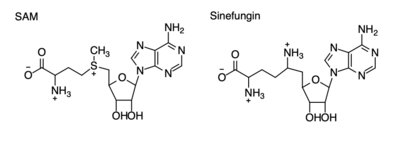
The beta hairpin stabilizes the <scene name='81/811707/Beta_hairpin_stabilizing_tyrs/1'>conformation of Tyr335 and Tyr337</scene>, while also shaping one side of the channel which the peptide binds to.<ref name="Xiao" /> The <scene name='81/811707/Peptide_binding_site/1'>peptide binding groove</scene> is composed of residues 255-268.<ref name="Xiao" /> Lysine would have trouble coming down into the active site in its charged form, but it is facilitated by the faces of the flanking tyrosines.<ref name="Xiao" /> The orientation of the lysine is such that the amine-methyl bond is aligned towards the sulfur on SAM so that it can provide the methyl. There is an important water in the active site (Figure 2) as well that acts as a stabilizer for lysine, and helps to shift the lone pair on the nitrogen towards the sulfur of SAM. <ref name="Xiao" /> | The beta hairpin stabilizes the <scene name='81/811707/Beta_hairpin_stabilizing_tyrs/1'>conformation of Tyr335 and Tyr337</scene>, while also shaping one side of the channel which the peptide binds to.<ref name="Xiao" /> The <scene name='81/811707/Peptide_binding_site/1'>peptide binding groove</scene> is composed of residues 255-268.<ref name="Xiao" /> Lysine would have trouble coming down into the active site in its charged form, but it is facilitated by the faces of the flanking tyrosines.<ref name="Xiao" /> The orientation of the lysine is such that the amine-methyl bond is aligned towards the sulfur on SAM so that it can provide the methyl. There is an important water in the active site (Figure 2) as well that acts as a stabilizer for lysine, and helps to shift the lone pair on the nitrogen towards the sulfur of SAM. <ref name="Xiao" /> | ||
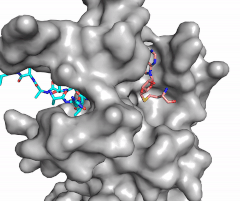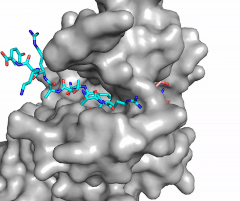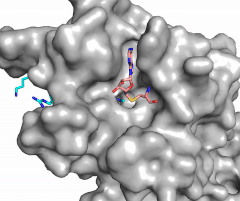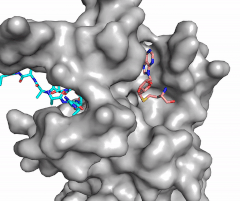
| - | [[Image:Hat1.gif|300 px|left|thumb|Figure X: The substrate ( | + | [[Image:Hat1.gif|300 px|left|thumb|Figure X: The substrate (pink sticks) and Coenzyme A (green sticks) binding channel in Hat1]] |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 22:42, 19 April 2019
H. sapiens Lysine Methyltransferase, SET 7/9
| |||||||||||
References
[3] [8] [5] [6] [7] [9] [10] [11] [1] [2] [4]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 DesJarlais R, Tummino PJ. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1584-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210. Epub , 2016 Jan 26. PMID:26745824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Marino-Ramirez L, Kann MG, Shoemaker BA, Landsman D. Histone structure and nucleosome stability. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2005 Oct;2(5):719-29. PMID:16209651 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1586/14789450.2.5.719
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson JR, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn GM, Gamblin SJ. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature. 2003 Feb 6;421(6923):652-6. Epub 2003 Jan 22. PMID:12540855 doi:10.1038/nature01378
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.15406/mojcsr.2016.03.00047
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Schubert HL, Blumenthal RM, Cheng X. Many paths to methyltransfer: a chronicle of convergence. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Jun;28(6):329-35. PMID:12826405
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Yeates TO. Structures of SET domain proteins: protein lysine methyltransferases make their mark. Cell. 2002 Oct 4;111(1):5-7. PMID:12372294
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Huang S, Shao G, Liu L. The PR domain of the Rb-binding zinc finger protein RIZ1 is a protein binding interface and is related to the SET domain functioning in chromatin-mediated gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 26;273(26):15933-9. PMID:9632640
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/C2014-0-02189-2
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Del Rizzo PA, Couture JF, Dirk LM, Strunk BS, Roiko MS, Brunzelle JS, Houtz RL, Trievel RC. SET7/9 catalytic mutants reveal the role of active site water molecules in lysine multiple methylation. J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31849-58. Epub 2010 Aug 1. PMID:20675860 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.114587
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Sun G, Reddy MA, Yuan H, Lanting L, Kato M, Natarajan R. Epigenetic histone methylation modulates fibrotic gene expression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Dec;21(12):2069-80. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010060633. Epub 2010, Oct 7. PMID:20930066 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2010060633
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Tian X, Zhang S, Liu HM, Zhang YB, Blair CA, Mercola D, Sassone-Corsi P, Zi X. Histone lysine-specific methyltransferases and demethylases in carcinogenesis: new targets for cancer therapy and prevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Jun;13(5):558-79. doi:, 10.2174/1568009611313050007. PMID:23713993 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1568009611313050007
Student Contributors
Ashley Crotteau
Parker Hiday
Lauren Allman