Introduction
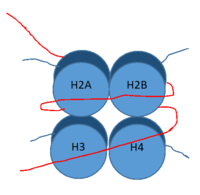
Figure 1: DNA (red) wrapped around histone proteins with histone tails (blue)
, human lysine-specific demethylase 1, is an enzyme that affects the ability of DNA to associate with histone proteins. Histone proteins are positively charged proteins that act as spools for negatively charged DNA to wrap around for storage in the nucleus (Figure 1). When DNA is tightly condensed it forms into nucleosomes which consist of 8 histone core proteins (2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3, 2 H4) with DNA tightly coiled around them. This tightly coiled DNA is known as heterochromatin, which is inaccessible to transcription factors and RNA polymerase. This can be reversed by modifications to histone protein structure that cause the DNA to relax and form euchromatin, which allows for RNA polymerase and other transcription factors to properly execute transcription. One key histone modification is the demethylation of lysine residues. Before 2004, it was believed that methylation of histone tails was stable and irreversible. In 2004, it was discovered that histone tails can also be demethylated by demethylase enzymes such as LSD-1 [1]. LSD-1 specifically demethylates mono- or di-methylated lysine substrates at Lys4 or Lys9 in the tail of histone H3. Demethylation of these lysine residues is commonly associated with transcriptional activation, but it also has the ability to silence genes depending on the residue being demethylated, the cofactors present, and the environment in which the demethylation occurs. LSD-1 is among the most well-known demethylases and has been studied since its instrumental discovery in 2004 [1].
Structure
Tower Domain
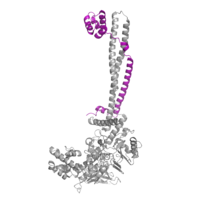
Figure 2: CoRest complex (purple) bound to LSD1 (PDB: 2h94) at the Tower domain.
The is a 100 residue protrusion off of the main protein body of LSD-1, comprised of 2 right-handed 𝛂-helices. The longer helix, T𝛂A, is an LSD-1 specific element that has not been found in any other oxidase proteins [2]. The shorter helix, T𝛂B, is positioned near the active site of the oxidase domain. T𝛂B connects directly to helix 𝛂D of the oxidase domain through a highly conserved connector loop. The exact function of the tower domain is not known, but it is proposed to regulate the size of the active site chamber through this . The T𝛂B-𝛂D interaction is responsible for the proper positioning of , a side chain of 𝛂D that is located in the catalytic chamber, for proper recognition and binding of the substrate lysine through hydrophobic interactions. In addition, the T𝛂B-𝛂D interaction positions 𝛂D in the correct manner to provide hydrogen bonding to . Tyr761 is positioned in the catalytic chamber next to the FAD cofactor and aids in the binding of the lysine substrate [2]. Therefore, the base of the tower domain forms a direct connection to the oxidase domain and plays a crucial role in the shape and catalytic activity of the active site. In fact, removing the tower domain via a mutation resulted in a drastic decrease in catalytic efficiency [2]. The tower domain has also been found to interact with other proteins and complexes, such as CoREST (Figure 2), as a molecular lever to allosterically regulate the catalytic activity of the active site [3]. Overall, the exact function of the tower domain has not yet been fully determined, but it is known to be vital to the catalytic activity of LSD-1.
SWIRM Domain
The is seen in numerous enzymes that participate in histone binding and chromatin modification. The SWIRM domain of LSD-1 is 94 residues long and is comprised of an alpha-helix bundle [2]. The longest helix, 𝛂C, separates the two other helix-turn-helix motifs, [2]. The SWIRM domain is associated with the oxidase domain via hydrophobic van der Waals interactions between : 𝛂A, 𝛂B, and 𝛂E motifs in the SWIRM domain and 𝛂A, 𝛂B, 𝛂M, motifs in the oxidase domain. The residues that create this hydrophobic interface (which spans nearly 1680 Ų) are practically invariant across histone-modifying proteins [2]. The creates a cleft or tunnel that is also present in other chromatin modifying enzymes. This is responsible for binding to DNA in the other enzymes through the presence of positively charged residues in the cleft [2]. The SWIRM domain in LSD-1 is unique because the cleft that is formed by the hydrophobic SWIRM-oxidase interactions lacks the positively charged residues common in other enzymes [2]. For this reason, it is proposed that the SWIRM cleft is used for binding of a histone tail (on the same histone as the substrate lysine) in order to hold the histone in place. Multiple experiments showed that mutations in hydrophobic residues that form the SWIRM-oxidase interface greatly reduced the catalytic activity of LSD-1 [2]. This, and the proximity to the active site in the oxidase domain, exhibit the importance of the SWIRM cleft in the mechanism of LSD-1.
Oxidase Domain
The houses the catalytic site of LSD-1. The domain has two distinct regions: one non-covalently binds the FAD cofactor and the other acts in both the binding and recognition of the substrate lysine on a histone tail(H3)[2]. The active site cavity is placed within the substrate-binding subunit of the oxidase domain and is unique due to its great size. In relation to other FAD-dependent oxidases, LSD-1 has a very large active site cavity that is 15 Å deep and 25 Å at its widest opening [2]. In comparison, polyamine oxidase, another FAD-dependent oxidase, has a catalytic chamber roughly 30 Å long but only a few angstroms wide [4]. The relatively large size of the LSD-1 active site cavity suggests that other residues, in addition to the substrate lysine, enter into the active site during catalysis. These additional residues could participate in substrate recognition and may contribute to the enzyme’s specificity for H3K4 and H3K9.
Active Site and FAD Cofactor
Within the active site cavity, there are four invaginations, or , each with differing chemical properties. The catalytic pocket or invagination within the active site (residues Val317, Gly330, Ala331, Met332, Val333, Phe538, Leu659, Asn660, Lys661, Trp695, Ser749, Ser760 and Tyr761) catalyzes the interaction between the FAD cofactor and the substrate lysine [2]. This pocket binds and positions the substrate lysine so that it is exposed to the . During catalysis, the FAD cofactor is reduced and becomes an anion. Therefore, a positively charged residue is present in most FAD-dependent oxidases to assist in stabilizing the anionic form of FAD. In LSD-1, is present in the catalytic pocket of the active site to stabilize the negatively charged FAD [2]. The other three are not as well understood but predictions can be made about their functions within the active site of LSD-1. Because the active site is able to accept additional residues on the substrate histone other than the lysine, the remaining three pockets are most plausibly responsible for the recognition of chemical modifications on the histone itself [2]. The first pocket (Pocket 1) that assists in recognizing chemical modifications on the substrate histone is composed of residues Val334, Thr335, Asn340, Met342, Tyr571, Thr810, Val811 and His812 [2]. The second pocket in the active site for side-chain recognition (Pocket 2) is composed of Phe558, Glu559, Phe560, Asn806, Tyr807 and Pro808 [2]. Pocket 3 within the active site is composed of Asn540, Leu547, Trp552, Asp553, Gln554, Asp555, Asp556, Ser762, Tyr763, Val764 and Tyr773 [2]. Each of the three pockets, in addition to the catalytic pocket, are able to recognize distinct modifications on the substrate and contribute to the specificity of LSD-1.
Mechanism of Action
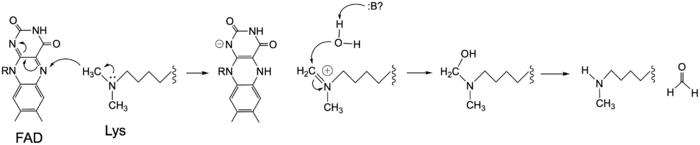
Figure 3: Hydride transfer mechanism of LSD-1 active site via FAD cofactor.
The mechanism of lysine demethylation is highly dependent on the presence of the . The FAD cofactor, positioned closely to the substrate lysine in the active site, acts as an oxidizing agent and initiates catalysis (Figure 3). A two-electron transfer occurs between the substrate lysine and FAD in the form of a hydride; the lysine is oxidized and the FAD is reduced [2]. The FAD cofactor forms an anion and is stabilized by the positively charged positioned in the catalytic pocket of the active site [2]. The oxidized lysine forms an aminium cation that is hydrolyzed into the carbinolamine intermediate [2]. The carbinolamine intermediate readily decomposes into formaldehyde and the demethylated lysine substrate [2].
Inhibition by Tri-Methylated Lysine
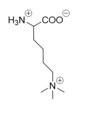
Figure 4: Tri-methylated lysine.
The proposed LSD-1 mechanism is supported by the fact that tri-methylated lysine substrates (Figure 4) competitively inhibit the enzyme. A substrate lysine that is tri-methylated binds to the active site but does not undergo catalysis; the inhibition is not steric (the active site is large enough to accommodate tri-methylated lysines), but is rather chemical in nature. Tri-methylated lysines do not have a free lone pair to form an aminium cation as is necessitated by the proposed mechanism, resulting in chemical inhibition of LSD-1 [2]. Thus, the mechanism of LSD-1 contributes to its specificity for mono- or di-methylated lysine substrates (Figure 4).
Medical Implications
The possible physiological implications that LSD-1 may have on medical conditions is being researched. LSD-1 has proposed roles in both diabetes and in cancer development.
1. Diabetes
Gluconeogenesis is a process in the body that results in the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate forms (such as lactic acid). Glucose 6-phosphatase (G6Pase) and Fructose-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) are critical enzymes in the gluconeogenesis pathway. LSD-1, although it can have both activating and inhibiting effects depending on external conditions, is proposed to have inhibiting effects on the transcription of both G6Pase and FBP1 [5]. Under healthy conditions, LSD-1 inhibits the transcription of these enzymes in order to regulate the blood glucose levels in the body. It was found that decreased amounts of LSD-1 can induce hyperglycemia that contributes to the onset of both types of diabetes [5].
2. Cancer
Research has found that LSD-1 is over-expressed in many tumorous cancers. The proposed mechanism behind the carcinogenic role of LSD-1 focuses on the known tumor-suppressor gene, p53. The p53 protein acts as a transcription factor that activates the expression of many anti-proliferative proteins. LSD-1 has been found to remove a methyl group from the di-methylated Lys370 on p53 [6]. Similar to the proposed role of LSD-1 in diabetes, its demethylation of p53 is inhibitory and prevents its binding to DNA [6]. This inactivation of p53 is thought to prevent anti-proliferative operations in the cell and contribute to the development of multiple types of cancers.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P, Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA, Shi Y. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell. 2004 Dec 29;119(7):941-53. PMID:15620353 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.012
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 2.21 Stavropoulos P, Blobel G, Hoelz A. Crystal structure and mechanism of human lysine-specific demethylase-1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Jul;13(7):626-32. Epub 2006 Jun 25. PMID:16799558 doi:10.1038/nsmb1113
- ↑ Yang M, Gocke CB, Luo X, Borek D, Tomchick DR, Machius M, Otwinowski Z, Yu H. Structural basis for CoREST-dependent demethylation of nucleosomes by the human LSD1 histone demethylase. Mol Cell. 2006 Aug 4;23(3):377-87. PMID:16885027 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.07.012
- ↑ Binda C, Angelini R, Federico R, Ascenzi P, Mattevi A. Structural bases for inhibitor binding and catalysis in polyamine oxidase. Biochemistry. 2001 Mar 6;40(9):2766-76. PMID:11258887
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Pan D, Mao C, Wang YX. Suppression of gluconeogenic gene expression by LSD1-mediated histone demethylation. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 5;8(6):e66294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066294. Print 2013. PMID:23755305 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066294
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Jin L, Hanigan CL, Wu Y, Wang W, Park BH, Woster PM, Casero RA. Loss of LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) suppresses growth and alters gene expression of human colon cancer cells in a p53- and DNMT1(DNA methyltransferase 1)-independent manner. Biochem J. 2013 Jan 15;449(2):459-68. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121360. PMID:23072722 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20121360




