We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Lauryn Padgett/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Inhibitor== | ==Inhibitor== | ||
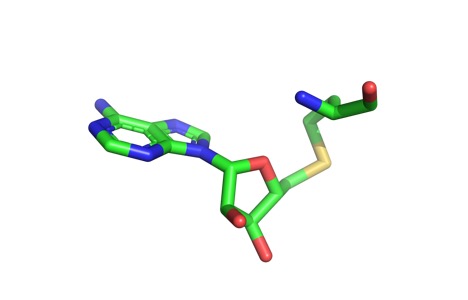
Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor that is a natural nucleoside isolated from the ''Streptomyces'' species. Also referred to as adenosyl-ornithine, it is the delta (5’ adenosyl) derivative of ornithine and a structural analog of S-adenosylmethionine. Sinefungin is more stable bound in the active site than SAM due to the ability to create two additional hydrogen bonds to its amine group that are not possible with SAM’s sulfur. | Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor that is a natural nucleoside isolated from the ''Streptomyces'' species. Also referred to as adenosyl-ornithine, it is the delta (5’ adenosyl) derivative of ornithine and a structural analog of S-adenosylmethionine. Sinefungin is more stable bound in the active site than SAM due to the ability to create two additional hydrogen bonds to its amine group that are not possible with SAM’s sulfur. | ||
| - | Sinefungin has been used experimentally to inhibit the SET 7/9 protein on peritoneal fibrosis in mice and in human peritoneal mesothelial cells | + | Sinefungin has been used experimentally to inhibit the SET 7/9 protein on peritoneal fibrosis in mice and in human peritoneal mesothelial cells <ref name=”Tamura” />. SET 7/9 is involved in peritoneal fibrosis because it mono-methylates H3K4, which activates the transcription of fibrosis related genes. The administration of Sinefungin to mice correlated with decreasing levels of methylated H3K4 (H3K4me1) protein, as well as suppressed cell accumulation and thickening in methylglyoxial peritoneal fibrosis. The decreased levels of H3K4me1 suggest that the methylation of H3K4 was inhibited by Sinefungin. |
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Schluckebier”>PMID:8995524</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Tamura”>PMID:29723250</ref> | ||
| + | |||
Schluckebier et al. (1997), Differential binding of S-andeosylmethionine S-adenosylhomocysteine and Sinefungin to adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase M. TaqI; J. Mol. Biol., 265 56 | Schluckebier et al. (1997), Differential binding of S-andeosylmethionine S-adenosylhomocysteine and Sinefungin to adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase M. TaqI; J. Mol. Biol., 265 56 | ||
Revision as of 06:07, 25 April 2019
Homo sapiens Histone Methyl Transferase SET7/9 (KMT)==
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
Schluckebier et al. (1997), Differential binding of S-andeosylmethionine S-adenosylhomocysteine and Sinefungin to adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase M. TaqI; J. Mol. Biol., 265 56