Introduction
Histones
Histones are basic proteins that interact with nuclear DNA to help condense this DNA into chromatin. Nucleosomes are chromatin beads made up of this nuclear DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins, or a histone octamer in order to fit into the nucleus[1]. The chromatin found inside the nucleus are catagorized into heterochromatin, which are compact and transcriptionally silent, and euchromatin, which are less compact and transcriptionally active [2]. Modifying histones is a type of epigenetics, where changes are made in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence. Four different examples of histone modifications include histone acetylation, histone deacetylation, histone methylation and histone demethylation[1] .
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)
HDACs are versatile enzymes that participate in regulating histone-DNA interactions, along with non-histone proteins, the cell cycle, cell differentiation and DNA-histone interactions. Histone acetylation is the reversal process, performed by HATs. HDACs perform ε-amino-lysine deacetylation on acetylated lysines, the amount and residue number of which are unclear, within the histone [3].
There are different classes of HDACs based on phylogenetic analysis: Class I (HDACs 1-3 and 8), Class II (HDACs 4-7, 9 and 10), Class III (Sirtuin deacetylases), and Class IV (HDAC 11)[4].
HDACs 1-11 are metalloenzymes, all with similar reaction mechanisms, due to their utilization of a zinc ion used in deacetylation[4]. One type of HDAC, Histone Deacetylase 8, is an enzyme found in Homo sapiens. HDAC8 decreases gene expression by increasing DNA-histone interactions, condensing the DNA tighter, into the transcriptionally silent heterochromatin.
Structure
The structure of HDAC8 was determined via hanging-drop crystallization using a Tyr306Phe mutation (PDB: 2v5w), which was inactive. This allowed the structure to be captured with the substrate bound. The crystallization conditions were: 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM MgCl2, 10% polyethylene glycol 4000, 2 mM tri(2-carboxyethyl)phosphin and 30 mM glycyl-glycyl-glycine at 22°C. The structure was determined at 2.0 angstroms[4].
HDAC8 exists as a dimer in the crystal structure, is 388 residues long and consists of one eight-stranded parallel surrounded by 11 [4]. HDAC8 is the only functional HDAC that is found to be a single polypeptide instead of being high molecular-weight multi-protein complexes[4].
The Ligand
The bound to the HDAC8 includes an acetyl group, one arginine, one histidine, two lysines and MCM (a Coumarin fluorescence tag, used as a fluorogenic substrate in enzyme kinetics). It was derived from the p53 tumor suppressor gene.
The substrate is held in the binding pocket via several interactions. At the rim of the active site, a conserved makes three hydrogen bonds to two adjacent backbone amides. These interactions force the substrate into a cis conformation. There are also several water molecules that interact with backbone substrate oxygens, assisting the Asp in holding to substrate in the binding pocket during deacetylation reaction. Inhibitors previously crystallized also show these interactions and cis conformation. Mutating Asp101 to an alanine was also shown to abolish enzymatic activity, indicating the importance of the Asp101[4].
The ligand is also held in place via hydrophobic between Phe152, Phe208 and the nonpolar chain of the acetylated lysine. Gly151 also hydrogen-bonds to the amide of the acetyl group, further helping the substrate stay in place[4].
Potassium Ions
There are two potassium ions within HDAC8, which increase the catalytic activity and stability of the enzyme overall. The first is closest to the active site and interacts with active site residues (side chain oxygen of Ser199/Asp176 and the backbone oxygen of Asp176/Asp178/His180/Leu200), with an octahedral geometry. The second potassium ion is about 20 Å from the catalytic center and regulates the enzymatic activity by an allosteric effect [5].
Active Site
The HDAC8 contains features of zinc and serine proteases. Substrates are deacetylated via a classic divalent metal ion mechanism. Zinc pentacoordinates with , the nucleophilic water (making it more acidic) and the carbonyl oxygen of the substrate[4].
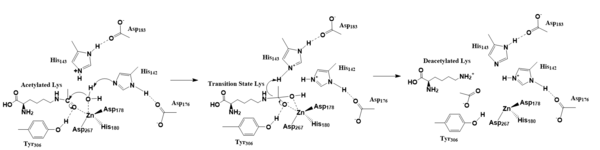
Figure 1. Deacetylation by HDAC8
The zinc ion by withdrawing electron density from the water due to the positive charge, making the water more acidic, therefore a better nucleophile. The zinc ion also coordinates to the carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl group on the lysine, polarizing the carbonyl carbon, making it more electrophilic. There are two present in the active site. His142 deprotonates the water, the first step of the deacetylation (Figure 1). His 142 (stabilized by Asp 176) is closer to the water molecule than His 143 (stabilized by Asp 183), which was also thought to deprotonate the water. However, a mutation done to His143 only reduced activity, not abolished it, showing it is important but not crucial. His143 is instead thought to orient the substrate[4].
The attack by the deprotonated water forces the carbonyl carbon into a tetrahedral transition state. [4] acts as the oxyanion hole, stabilizing this transition state via its protruding -OH group hydrogen-bonding with the negatively charged oxygen. The transition state collapses, and His 143 simultaneously gets deprotonated by the amide of the leaving acetyl group in order to weaken the scissile bond. Breaking this scissile bond results in a neutral lysine and an acetate ion, among other products (Fig. 1). Body pH is around 7 typically and the pKa of carboxylic acids is around 2; the hydrogen from the acetic acid is lost and picked up by the lysine, providing the hydrogen necessary for lysine to become basic, per its nature[4].

Figure 2. Conserved Residues Across HDAC Families
Though there are several different families of HDACs, each with their own structural intricacies, many residues are conserved throughout them. The residues that come in contact with the acetylated lysine, with the exception of Tyr306, are conserved (Figure 2), emphasizing how crucial these specific residues are in the function of an HDAC[4].
Inhibition
HDAC Inhibitors
HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) are a class of compounds that deactivate histone deacetylases. While a variety of these inhibitors are used to target different HDACs, common structural motifs among them include a zinc-binding moiety in the catalytic pocket opposite of the capping group, and a straight chain alkyl, vinyl, or aryl linker connecting the catalytic pocket and capping group, usually a hydrophobic chain of six carbons. HDAC inhibitors bind and deactivate the HDACs through the amino acid sequence of the rim surrounding the catalytic site of the different HDACs ()[6]. The capping group is generally hydrophobic and interacts with the rim amino acids of the HDAC. Binding occurs via interaction between conserved sections of HDAC active sites and the alkyl, vinyl, or aryl functional groups of the HDACi. The zinc binding moiety catalyzes hydrolysis of the acetyl-lysine bond at the bottom of the catalytic pocket, allowing for deactivation of the HDAC [7]. () [8].
Clinical Application
A variety of HDAC inhibitors are currently being tested for use as a cancer treatment. HDACs are over expressed in tumor tissue compared to healthy tissue, implying that high amounts of HDAC are reacting with and deacetylating the p53 gene of which the substrate is derived. The p53 gene is a tumor suppressor that, when deacetylated, is rendered inactive due to decreased transcriptional activity and upregulation of oncogenes. The uncontrolled growth of tumors can manifest and lead to cancer. A variety of HDAC inhibitors have been synthesized by modification of the zinc binding moiety or the capping group and tested for development as potential anticancer agents. The rim of amino acids on the catalytic site of HDACs have also been modified to allow for broader specificity of HDAC inhibitors that can bind. Current types of HDAC inhibitors include hydroxamic acids, cyclic peptides, electrophilic ketones, short chain fatty acids, benzamides, boronic acid based compounds, benzofuranone and sulfonamide. Of these, two HDAC inhibitors are currently in clinical trials as cancer drugs, known as vorinostat and romidepsin [7].


