User:Tereza Čalounová/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
m |
m |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==== Remodeling ==== | ==== Remodeling ==== | ||
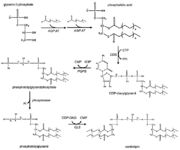
| - | The remodeling is based on unsaturation of the acyl chains of the cardiolipin. This process has two steps. Firstly, the fatty acyl group is removed by a specific cardiolipin deacylase forming monolysocardiolipin. Then | + | The remodeling is based on unsaturation of the acyl chains of the cardiolipin. This process has two steps. Firstly, the fatty acyl group is removed by a specific cardiolipin deacylase forming monolysocardiolipin. Then tafazzin recyclates monolysocardiolipin and makes the final product, unsaturated cardiolipin. <ref name="cit15" /> |
==== Function ==== | ==== Function ==== | ||
As mentioned, cardiolipin is mainly located on the mitochondrial inner membrane, but is also present on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cardiolipin is essential for some enzyme systems such as energy metabolism, membrane transport and cell division. For example, when the apoptosis, programmed cell death, or mitophagy, mitochondrial degradation, is needed, cardiolipin is externalized on the surface of mitochondria and acts like a signaling molecule. <ref name="cit12" /> | As mentioned, cardiolipin is mainly located on the mitochondrial inner membrane, but is also present on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cardiolipin is essential for some enzyme systems such as energy metabolism, membrane transport and cell division. For example, when the apoptosis, programmed cell death, or mitophagy, mitochondrial degradation, is needed, cardiolipin is externalized on the surface of mitochondria and acts like a signaling molecule. <ref name="cit12" /> | ||
| - | On top of that, cardiolipin has many other functions. It is an important cofactor for cholesterol translocation from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane. It also has a role in the regulation of gene expression. | + | On top of that, cardiolipin has many other functions. It is an important cofactor for cholesterol translocation from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane. It also has a role in the regulation of gene expression. What is more, it can act like a molecular chaperone, so it helps mitochondrial proteins with folding. <ref name="cit13" /> |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Cardiolipin and Barth Syndrome ==== | ||
| + | When having Barth syndrome, the gene coding enzyme tafazzin is mutated. This is the reason why monolysocardiolipin is accumulated and the unsaturated cardiolipin species are missing. So, in total, patients have a low level of cardiolipin, which is due to its function devastating for the human body. <ref name="cit15" /> | ||
== TAZ gene == | == TAZ gene == | ||
Revision as of 18:31, 27 April 2019
This is our page where we will share informations about protein Tafazzin as a part of a school project with my classmates. This page is under a construction so please be aware of it. Zde přidám úvod
Tafazzin
| Theoretical Model: The protein structure described on this page was determined theoretically, and hence should be interpreted with caution. |
Tafazzin is a protein located in mitochondrial inner membranes. It is involved in altering cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is key in maintaining mitochondrial shape, energy production, and protein transport within cells. The full-length tafazzin protein contains 292 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 33459 daltons. Mutations in gene associated with this protein can cause Barth Syndrome. Barth syndrome (BTHS),is a genetic disorder diagnosed almost exclusively in males. BTHS is rare, it is estimated to affect 1 in 300,000 to 400,000 individuals worldwide. Males with BTHS have weak heart and skeletal muscles which can lead to heart failure. Another of the symptoms is neutropenia which can lead to infections. [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/barth-syndrome#
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16635?fbclid=IwAR3v10lUTRZfb0NFOYKC4wjaherdU9PIVJ8T63jkC9RfNu_5OQ2IpoDR0iY
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00018-008-8030-5
- ↑ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cardiolipin_structure.svg?uselang=cs
- ↑ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Eukaryotic_pathway.jpg
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4342993/
- ↑ https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/TAZ#location
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16635
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4412953/
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/barth-syndrome#
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092544391830334X?via%3Dihub
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/pd.2599
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/tafazzin
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK247162/
- ↑ http://pfam.xfam.org/protein/Q16635