User:Tereza Čalounová/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
m |
m |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
=== Cardiolipin === | === Cardiolipin === | ||
| - | Cardiolipin is a trivial name used for 1,3-bis(sn-3’-phosphatidyl)-sn-glycerol. <ref name="cit12">http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm</ref> It is a phospholipid mostly found in the inner membrane of mitochondria where is essential for stability of enzymes which are part of the energy metabolism. Cardiolipin is also involved in different stages of the mitochondrial apoptotic process and in mitochondrial membrane dynamics. <ref name="cit13"> | + | Cardiolipin is a trivial name used for 1,3-bis(sn-3’-phosphatidyl)-sn-glycerol. <ref name="cit12">http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm</ref> It is a phospholipid mostly found in the inner membrane of mitochondria where is essential for stability of enzymes which are part of the energy metabolism. Cardiolipin is also involved in different stages of the mitochondrial apoptotic process and in mitochondrial membrane dynamics. <ref name="cit13">CHRISTIE, William. Cardiolipin (Diphosphatidylglycerol). In: Www.lipidhome.co.uk [online]. Hutton: The LipidWeb, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm</ref> |
==== Structure ==== | ==== Structure ==== | ||
| - | [[Image:CardiolipinStructure.png|thumb|Chemical structure of cardiolipin where R1-R4 are alkyl groups, typically 18-carbon fatty acid side chains. <ref name="cit14">https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cardiolipin_structure.svg?uselang=cs</ref>]] | + | [[Image:CardiolipinStructure.png|thumb|Chemical structure of cardiolipin where R1-R4 are alkyl groups, typically 18-carbon fatty acid side chains. <ref name="cit14">Cardiolipin structure. In: Commons.wikimedia.org [online]. San Francisco: Wikimedia, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cardiolipin_structure.svg?uselang=cs</ref>]] |
Cardiolipin’s structure differs from other phospholipids since it is a dimer, it results in a highly specific conical structure. Cardiolipin consists of two phosphatidic acids, three glycerol backbones and four fatty acyl groups, so it can potentially carry two negative charges.<ref name="cit12" /> <ref name="cit13" /> | Cardiolipin’s structure differs from other phospholipids since it is a dimer, it results in a highly specific conical structure. Cardiolipin consists of two phosphatidic acids, three glycerol backbones and four fatty acyl groups, so it can potentially carry two negative charges.<ref name="cit12" /> <ref name="cit13" /> | ||
The composition of fatty acids depends on an organism. With a few exceptions like testis or central nervous system, linoleic acid creates 80 % of fatty acids in animal tissues. Testis contain mainly palmitic acid in contrast to central nervous system which contains a wide range of different fatty acids like palmitic, stearic, oleic and many others.<ref name="cit12" /> | The composition of fatty acids depends on an organism. With a few exceptions like testis or central nervous system, linoleic acid creates 80 % of fatty acids in animal tissues. Testis contain mainly palmitic acid in contrast to central nervous system which contains a wide range of different fatty acids like palmitic, stearic, oleic and many others.<ref name="cit12" /> | ||
==== Synthesis ==== | ==== Synthesis ==== | ||
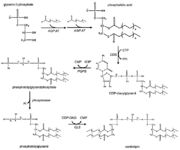
| - | [[Image:CardiolipinSynthesis.jpg|thumb|Cardiolipin synthesis. <ref name="cit16">https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Eukaryotic_pathway.jpg</ref>]] | + | [[Image:CardiolipinSynthesis.jpg|thumb|Cardiolipin synthesis. <ref name="cit16"> Rochellehx. File:Eukaryotic pathway.jpg. In: Wikimedia Commons [online]. 23. 4. 2009 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Eukaryotic_pathway.jpg</ref>]] |
The first step in the cardiolipin synthesis is a conversion of cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol to phosphatidylglycerol phosphate by the enzyme phosphatidylglycerol phosphate (PGP) synthase. Followed by dephosphorylation by PGP phosphatase to phosphatidylglycerol. Lastly phosphatidylglycerol is converted to cardiolipin in condensation reaction catalyzed by cardiolipin synthase. <ref name="cit15">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4342993/</ref> | The first step in the cardiolipin synthesis is a conversion of cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol to phosphatidylglycerol phosphate by the enzyme phosphatidylglycerol phosphate (PGP) synthase. Followed by dephosphorylation by PGP phosphatase to phosphatidylglycerol. Lastly phosphatidylglycerol is converted to cardiolipin in condensation reaction catalyzed by cardiolipin synthase. <ref name="cit15">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4342993/</ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:50, 27 April 2019
This is our page where we will share informations about protein Tafazzin as a part of a school project with my classmates. This page is under a construction so please be aware of it. Zde přidám úvod
Tafazzin
| Theoretical Model: The protein structure described on this page was determined theoretically, and hence should be interpreted with caution. |
Tafazzin is a protein located in mitochondrial inner membranes. It is involved in altering cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is key in maintaining mitochondrial shape, energy production, and protein transport within cells. The full-length tafazzin protein contains 292 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 33459 daltons. Mutations in gene associated with this protein can cause Barth Syndrome. Barth syndrome (BTHS),is a genetic disorder diagnosed almost exclusively in males. BTHS is rare, it is estimated to affect 1 in 300,000 to 400,000 individuals worldwide. Males with BTHS have weak heart and skeletal muscles which can lead to heart failure. Another of the symptoms is neutropenia which can lead to infections. [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Barth syndrome. In: Ghr.nlm.nih.gov [online]. Rockville Pike: U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/barth-syndrome#
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Q16635 (TAZ_HUMAN). In: Https://www.uniprot.org/ [online]. Cambridge, Geneva, Washington: UniProt, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16635?fbclid=IwAR3v10lUTRZfb0NFOYKC4wjaherdU9PIVJ8T63jkC9RfNu_5OQ2IpoDR0iY
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 CHRISTIE, William. Cardiolipin (Diphosphatidylglycerol). In: Www.lipidhome.co.uk [online]. Hutton: The LipidWeb, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm
- ↑ Cardiolipin structure. In: Commons.wikimedia.org [online]. San Francisco: Wikimedia, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cardiolipin_structure.svg?uselang=cs
- ↑ Rochellehx. File:Eukaryotic pathway.jpg. In: Wikimedia Commons [online]. 23. 4. 2009 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Eukaryotic_pathway.jpg
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4342993/
- ↑ https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/TAZ#location
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16635
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4412953/
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/barth-syndrome#
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092544391830334X?via%3Dihub
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/pd.2599
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/tafazzin
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK247162/
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/Q16635
- ↑ http://pfam.xfam.org/protein/Q16635
- ↑ https://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF01553#tabview=tab4
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC107040/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4412953/