User:Tereza Čalounová/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
m |
m |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
*hemopoiesis | *hemopoiesis | ||
*inner mitochondrial membrane organization | *inner mitochondrial membrane organization | ||
| - | *mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport | + | *mitochondrial [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_triphosphate ATP] synthesis coupled electron transport |
*mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly | *mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly | ||
*muscle contraction | *muscle contraction | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
=== Cardiolipin === | === Cardiolipin === | ||
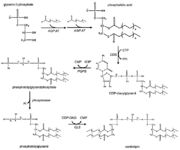
| - | Cardiolipin is a trivial name used for 1,3-bis(sn-3’-phosphatidyl)-sn-glycerol. <ref name="cit12">CHRISTIE, William. Cardiolipin (Diphosphatidylglycerol). In: Www.lipidhome.co.uk [online]. Hutton: The LipidWeb, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm</ref> It is a phospholipid mostly found in the inner membrane of mitochondria where is essential for stability of enzymes which are part of the energy metabolism. Cardiolipin is also involved in different stages of the mitochondrial apoptotic process and in mitochondrial membrane dynamics. <ref name="cit13">Houtkooper, R. H., & Vaz, F. M. (2008). Cardiolipin, the heart of mitochondrial metabolism. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 65(16), 2493–2506. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8030-5</ref> | + | Cardiolipin is a trivial name used for 1,3-bis(sn-3’-phosphatidyl)-sn-glycerol. <ref name="cit12">CHRISTIE, William. Cardiolipin (Diphosphatidylglycerol). In: Www.lipidhome.co.uk [online]. Hutton: The LipidWeb, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm</ref> It is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipid phospholipid] mostly found in the inner membrane of mitochondria where is essential for stability of enzymes which are part of the energy metabolism. Cardiolipin is also involved in different stages of the mitochondrial [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptotic] process and in mitochondrial membrane dynamics. <ref name="cit13">Houtkooper, R. H., & Vaz, F. M. (2008). Cardiolipin, the heart of mitochondrial metabolism. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 65(16), 2493–2506. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8030-5</ref> |
==== Structure ==== | ==== Structure ==== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
==== Function ==== | ==== Function ==== | ||
| - | As mentioned, cardiolipin is mainly located on the mitochondrial inner membrane, but is also present on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cardiolipin is essential for some enzyme systems such as energy metabolism, membrane transport and cell division. For example, when the apoptosis, programmed cell death, or mitophagy, mitochondrial degradation, is needed, cardiolipin is externalized on the surface of mitochondria and acts like a signaling molecule. <ref name="cit12" /> | + | As mentioned, cardiolipin is mainly located on the mitochondrial inner membrane, but is also present on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cardiolipin is essential for some enzyme systems such as energy metabolism, membrane transport and cell division. For example, when the apoptosis, programmed cell death, or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitophagy mitophagy], mitochondrial degradation, is needed, cardiolipin is externalized on the surface of mitochondria and acts like a signaling molecule. <ref name="cit12" /> |
On top of that, cardiolipin has many other functions. It is an important cofactor for cholesterol translocation from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane. It also has a role in the regulation of gene expression. What is more, it can act like a molecular chaperone, so it helps mitochondrial proteins with folding. <ref name="cit13" /> | On top of that, cardiolipin has many other functions. It is an important cofactor for cholesterol translocation from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane. It also has a role in the regulation of gene expression. What is more, it can act like a molecular chaperone, so it helps mitochondrial proteins with folding. <ref name="cit13" /> | ||
Revision as of 22:20, 27 April 2019
This is our page where we will share informations about protein Tafazzin as a part of a school project with my classmates. This page is under a construction so please be aware of it. Zde přidám úvod
Tafazzin
| Theoretical Model: The protein structure described on this page was determined theoretically, and hence should be interpreted with caution. |
Tafazzin is a protein located in mitochondrial inner membranes. It is involved in altering cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is key in maintaining mitochondrial shape, energy production, and protein transport within cells. The full-length tafazzin protein contains 292 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 33459 daltons. Mutations in gene associated with this protein can cause Barth Syndrome. Barth syndrome (BTHS) is a genetic disorder diagnosed almost exclusively in males. BTHS is rare, it is estimated to affect 1 in 300,000 to 400,000 individuals worldwide. Males with BTHS have weak heart and skeletal muscles which can lead to heart failure. Another of the symptoms is neutropenia which can lead to infections. [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Barth syndrome. In: Ghr.nlm.nih.gov [online]. Rockville Pike: U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/barth-syndrome#
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Q16635 (TAZ_HUMAN). In: Https://www.uniprot.org/ [online]. Cambridge, Geneva, Washington: UniProt, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16635?fbclid=IwAR3v10lUTRZfb0NFOYKC4wjaherdU9PIVJ8T63jkC9RfNu_5OQ2IpoDR0iY
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 CHRISTIE, William. Cardiolipin (Diphosphatidylglycerol). In: Www.lipidhome.co.uk [online]. Hutton: The LipidWeb, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/lipids/complex/dpg/index.htm
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Houtkooper, R. H., & Vaz, F. M. (2008). Cardiolipin, the heart of mitochondrial metabolism. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 65(16), 2493–2506. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8030-5
- ↑ Cardiolipin structure. In: Commons.wikimedia.org [online]. San Francisco: Wikimedia, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cardiolipin_structure.svg?uselang=cs
- ↑ Rochellehx. File:Eukaryotic pathway.jpg. In: Wikimedia Commons [online]. 23. 4. 2009 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Eukaryotic_pathway.jpg
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Raja V, Greenberg ML. The functions of cardiolipin in cellular metabolism-potential modifiers of the Barth syndrome phenotype. Chem Phys Lipids. 2014 Apr;179:49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.12.009., Epub 2014 Jan 17. PMID:24445246 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.12.009
- ↑ TAZ gene. In: Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov [online]. Rockville Pike: U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2014 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/TAZ#
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Hijikata A, Yura K, Ohara O, Go M. Structural and functional analyses of Barth syndrome-causing mutations and alternative splicing in the tafazzin acyltransferase domain. Meta Gene. 2015 Apr 22;4:92-106. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2015.04.001. eCollection, 2015 Jun. PMID:25941633 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mgene.2015.04.001
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Barth syndrome cells display widespread remodeling of mitochondrial complexes without affecting metabolic flux distribution. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease [online]. 2018, 1864(11), 3650-3658 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092544391830334X?via%3Dihub
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Barth syndrome: an X‐linked cause of fetal cardiomyopathy and stillbirth. Prenatal Diagnosis [online]. 2010, 30(10), 970-976 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/pd.2599
- ↑ Tafazzin. In: Www.sciencedirect.com [online]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/tafazzin
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Ferreira C, Thompson R, Vernon H. Barth Syndrome PMID:25299040
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Q16635 (TAZ_HUMAN) Homo sapiens (Human). In: Swissmodel.expasy.org/ [online]. Lausanne, Basel: swissmodel, 2019 [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot/Q16635
- ↑ Family: Acyltransferase (PF01553). In: Pfam.xfam.org [online]. Heidelberg: EMBL [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF01553#tabview=tab0
- ↑ Protein: TAZ_HUMAN (Q16635). In: Pfam.xfam.org [online]. Heidelberg: EMBL [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: http://pfam.xfam.org/protein/Q16635
- ↑ Family: Acyltransferase (PF01553). In: Pfam.xfam.org [online]. Heidelberg: EMBL [cit. 2019-04-27]. Available at: https://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF01553#tabview=tab4
- ↑ Heath RJ, Rock CO. A conserved histidine is essential for glycerolipid acyltransferase catalysis. J Bacteriol. 1998 Mar;180(6):1425-30. PMID:9515909