This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Cystathionine β-synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Full-length CBS contains a C-terminal regulatory domain of ~140 residues, including two so-called 'CBS domains' (CBS1 of 53 residues and CBS2 of 57 residues). The C-terminal domain of CBS contains an autoinhibitory region that gets displaced from the active site upon binding of the allosteric activator AdoMet. | Full-length CBS contains a C-terminal regulatory domain of ~140 residues, including two so-called 'CBS domains' (CBS1 of 53 residues and CBS2 of 57 residues). The C-terminal domain of CBS contains an autoinhibitory region that gets displaced from the active site upon binding of the allosteric activator AdoMet. | ||
The fact that truncated CBS forms dimers rather than tetramers or higher order oligomers suggests that the regulatory domain is involved in tetramer formation. | The fact that truncated CBS forms dimers rather than tetramers or higher order oligomers suggests that the regulatory domain is involved in tetramer formation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == The Reaction Catalyzed by CBS == | ||
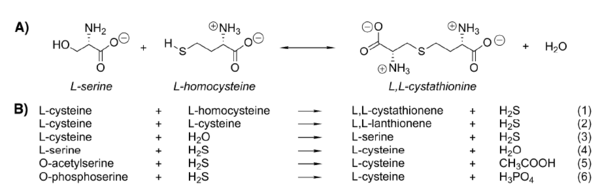
| + | Cystathionine β-synthase catalyzes β-elimination and β-replacement reactions. In a typical situation it condensates L-serine and L-homocysteine to give cystathionine but there are also other possible substrates for this enzyme leading to different products. | ||
| + | The reaction for synthesis of cystathionine starts with displacement of the internal aldimine between the enzyme active site lysine and pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (E-PLP) by the incoming L-serine. The serine external aldimine adduct (E-PLP-L-ser) forms an aminoacrylate intermediate (E-PLP-aa) that reacts with the incoming second substrate, such as L-homocysteine, to form the (L,L)-cystathionine external aldimine, which is then displaced by the active site lysine to regenerate the active enzyme (7). | ||
| + | The type of reaction mechanisms used by the CBS is known as a double displacement or ping-pong mechanism. The rate determining step in the reaction is hydrolysis of the external aldimine of cystathionine (5). | ||
[[Image:Reactions catalyzed by CBS.png|600px|left Reactions catalyzed by CBS. (A) Canonical reaction of CBS. (B) CBS reactions that generate or utilize H2S.]] | [[Image:Reactions catalyzed by CBS.png|600px|left Reactions catalyzed by CBS. (A) Canonical reaction of CBS. (B) CBS reactions that generate or utilize H2S.]] | ||
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 28 April 2019
3D Structure of Human Cystathionine β-synthase (4coo)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P. Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):3910-6. PMID:11483494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910
- ↑ Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P. Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):3910-6. PMID:11483494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910
- ↑ Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P. Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):3910-6. PMID:11483494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910
- ↑ Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P. Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):3910-6. PMID:11483494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910
- ↑ Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P. Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):3910-6. PMID:11483494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910
- ↑ Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P. Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J. 2001 Aug 1;20(15):3910-6. PMID:11483494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910