We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Lisinopril-Angiotensin Converting Enzyme
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Structure of Enzyme== | == Structure of Enzyme== | ||
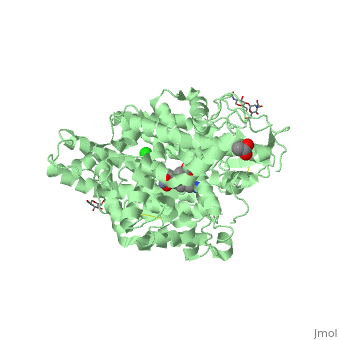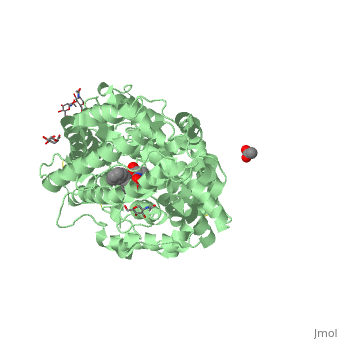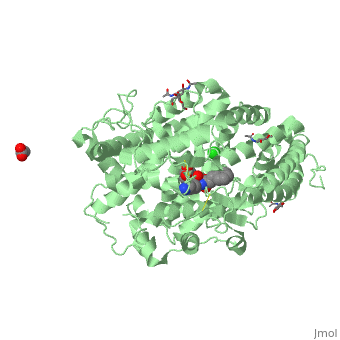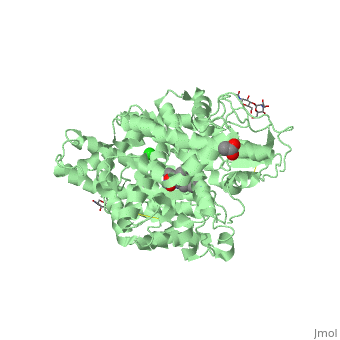
| - | This enzyme is a type 1 membrane bound protein that has 28 residue C- terminal cytosolic domains as well as 22- residue hydrophobic transmembrane domains and it has 1227 residue extracellular domain. The extracellular domain has two more isoforms of ACE, which are N- domains and C-domains. The N-domain plays a role in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation and proliferation while C-domain is mainly involved in blood pressure regulation. In each of these domains are two histidine residues which are used to binding zinc ligands with glutamine to make the geometry tetrahedral. Through mutational analyses and detailed kinetics, it is clear that both zinc sites have activity which is considered to be catalytic | + | This enzyme is a type 1 membrane bound protein that has 28 residue C- terminal cytosolic domains as well as 22- residue hydrophobic transmembrane domains and it has 1227 residue extracellular domain. The extracellular domain has two more isoforms of ACE, which are N- domains and C-domains. The N-domain plays a role in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation and proliferation while C-domain is mainly involved in blood pressure regulation. In each of these domains are two histidine residues which are used to binding zinc ligands with glutamine to make the geometry tetrahedral. Through mutational analyses and detailed kinetics, it is clear that both zinc sites have activity which is considered to be catalytic <ref>Riordan, James F. “Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and its relatives.” Genome biology vol. 4,8 (2003): 225. doi:10.1186/gb-2003-4-8-225</ref> |
== Function of Enzyme== | == Function of Enzyme== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Mechanism of Action == | == Mechanism of Action == | ||
| - | Lisinopril works by preventing the conversation of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. When there is a decrease in angiotensin II, it causes a reduction in aldosterone section and this in turn causes a decrease in sodium reabsorption within the collecting ducts as well as decrease potassium excretion. In the end by removing the negative feedback of angiotensin II, the drug can lead to an increase in serum renin activity. [ | + | Lisinopril works by preventing the conversation of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. When there is a decrease in angiotensin II, it causes a reduction in aldosterone section and this in turn causes a decrease in sodium reabsorption within the collecting ducts as well as decrease potassium excretion. In the end by removing the negative feedback of angiotensin II, the drug can lead to an increase in serum renin activity. <ref>Olvera Lopez E, Terrell JM. Lisinopril. [Updated 2019 Jan 20]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482230/ |
| + | /</ref> As explained above there are two isoforms of the enzyme ACE, C- domain and N- Domain. While both of these domains play different roles the medication inhibits both domain’s activity however, the active part of this drug is the peptides derivatives that contain the C-terminal proline. <ref>Sondes Bouabdallah, Med Thaieb Ben Dhia, and Med Rida Driss, “Study of a Conformational Equilibrium of Lisinopril by HPLC, NMR, and DFT,” International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, vol. 2014, Article ID 494719, 8 pages, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/494719.</ref> | ||
==Side Effects== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Revision as of 20:00, 3 May 2019
ACE Structure
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Riordan, James F. “Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and its relatives.” Genome biology vol. 4,8 (2003): 225. doi:10.1186/gb-2003-4-8-225
- ↑ Olvera Lopez E, Terrell JM. Lisinopril. [Updated 2019 Jan 20]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482230/ /
- ↑ Sondes Bouabdallah, Med Thaieb Ben Dhia, and Med Rida Driss, “Study of a Conformational Equilibrium of Lisinopril by HPLC, NMR, and DFT,” International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, vol. 2014, Article ID 494719, 8 pages, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/494719.