We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Cholera toxin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
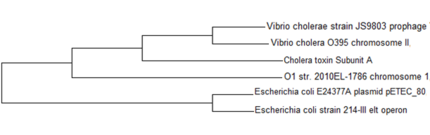
6. Vibrio cholera O1 str. 2010EL-1786 chromosome 1, complete | 6. Vibrio cholera O1 str. 2010EL-1786 chromosome 1, complete | ||
[[Image:TREE - MAXIMUM LIKEHOOD.PNG|left|430px|thumb|Phylogenetic Tree of MSA of CTX, Statistic Method:Maximum Likelihood, made by MEGA 5.05]] | [[Image:TREE - MAXIMUM LIKEHOOD.PNG|left|430px|thumb|Phylogenetic Tree of MSA of CTX, Statistic Method:Maximum Likelihood, made by MEGA 5.05]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of Cholera toxin == | ||
| + | [[Cholera toxin 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
Revision as of 09:42, 12 May 2019
| |||||||||||
Contents |
External Links
PDB ID: 1XTC [1]
MMDB ID: 52036 [2]
PubMed[3]
3D Structures of Cholera toxin
Updated on 12-May-2019
See also Toxins
Reference
- ↑ Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. p. 375. ISBN 0838585299.
- ↑ Faruque SM; Nair GB (editors). (2008). Vibrio cholerae: Genomics and Molecular Biology. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-33-2.
- ↑ Jennifer McDowall, Cholera Toxin, EMBL-EMI, Interpro
- ↑ Jennifer McDowall, Cholera Toxin, EMBL-EMI, Interpro
- ↑ Davis B, Waldor M (2003). "Filamentous phages linked to virulence of Vibrio cholerae". Curr Opin Microbiol 6 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(02)00005-X. PMID 12615217.
- ↑ Luppi P.H.. "The Discovery of Cholera-Toxin as a Powerful Neuroanatomical Tool". Retrieved 2011-03-23.
- ↑ Luppi P.H., Fort P., Jouvet M. Iontophoretic application of unconjugated cholera toxin B subunit (CTb) combined with immunohistochemistry of neurochemical substances: a method for transmitter identification of retrogradely labeled neurons. Brain Res. 534 (1-2) pages : 209-224 (1990)