This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Hyaluronidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
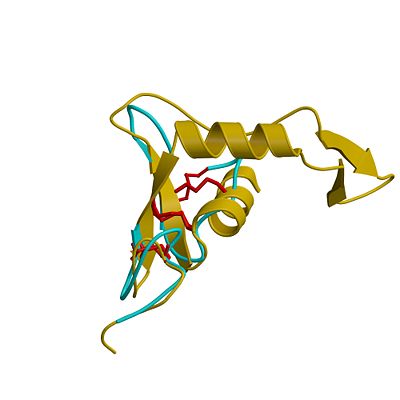
[[Image:hya_xdt_100906.jpeg|left|thumb|'''Superposition of the EGF-like domain of hyaluronidase-1 (yellow) and the heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (light blue)'''. The three disulphide bonds of the EGF domains (highlighted red) exhibit the same pattern in the primary structure and are located in similar positions in the 3D structure. |400px]] | [[Image:hya_xdt_100906.jpeg|left|thumb|'''Superposition of the EGF-like domain of hyaluronidase-1 (yellow) and the heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (light blue)'''. The three disulphide bonds of the EGF domains (highlighted red) exhibit the same pattern in the primary structure and are located in similar positions in the 3D structure. |400px]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
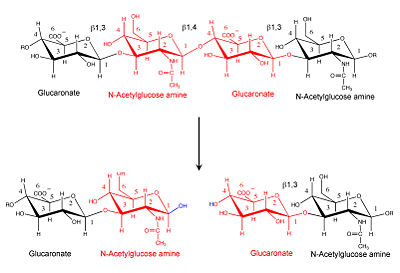
| - | [[Image:Hyal reaction.jpg|thumb|left|'''Hyaluronidase cleaves the β1,4-glycosidic bond of the glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan''' | | + | [[Image:Hyal reaction.jpg|thumb|left|'''Hyaluronidase cleaves the β1,4-glycosidic bond of the glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan''' |400px]] |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 19 May 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of hyaluronidase
Updated on 19-May-2019
Reference
- ↑ Chao KL, Muthukumar L, Herzberg O. Structure of human hyaluronidase-1, a hyaluronan hydrolyzing enzyme involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 12;46(23):6911-20. Epub 2007 May 16. PMID:17503783 doi:10.1021/bi700382g
- ↑ Ponnuraj K, Jedrzejas MJ. Mechanism of hyaluronan binding and degradation: structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae hyaluronate lyase in complex with hyaluronic acid disaccharide at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 2000 Jun 16;299(4):885-95. PMID:10843845 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3817
Created with the participation of Osnat Herzberg, Eran Hodis, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky.