This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Cyclin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Cyclin''' (CYC) activates CYC-dependent kinase (CDK) thus acting in the control of the cell cycle. The CYC name derives from the fact that different CYCs are expressed during different phases of the cell cycle. Among the CYCs | + | '''Cyclin''' (CYC) activates CYC-dependent kinase (CDK) thus acting in the control of the cell cycle. The CYC name derives from the fact that different CYCs are expressed during different phases of the cell cycle. Among the CYCs:<br /> |
| + | * '''CYCA''' is active in the S phase<br /> | ||
| + | * '''CYCB1''' is essential for the control of the cell cycle at the G2/M (mitosis) transition.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''CYCC''' is active in the G0/G1 phase transition<ref>PMID:12910258</ref>.br /> | ||
| + | * '''CYCD''' regulates the transition from G1 to S.<ref>PMID:15130482</ref><br /> | ||
| + | * '''CYCE''' and its CDK partner are key regulators of DNA synthesis and of mitosis.<ref>PMID:11907280</ref><br /> | ||
| + | * '''CYCK''' and its CDK12 partner regulate the expression of DNA-damage response genes and thus protect cells from genomic instability.<ref>PMID:22012619</ref><br /> | ||
| + | * '''CYCT''' and its CDK9 partner regulate gene expression.<ref>PMID:15276198</ref><br /> | ||
| + | * '''Viral CYC''' could be involved in oncogenic events associated with the cyclin-encoding viruses.<ref>PMID:10815028</ref><br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Intrinsically Disordered Protein]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overexpression of CYCD1 and its catalytic partner CDK4 is seen in human cancer<ref>PMID:25486477</ref>. Overexpression of CYCH and its catalytic partner CDK7 is seen in breast cancer<ref>PMID:27301701</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
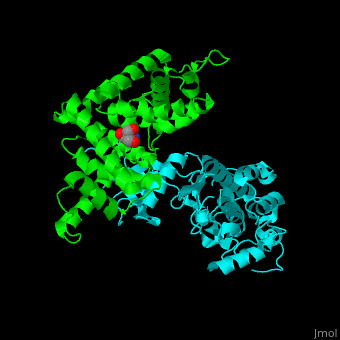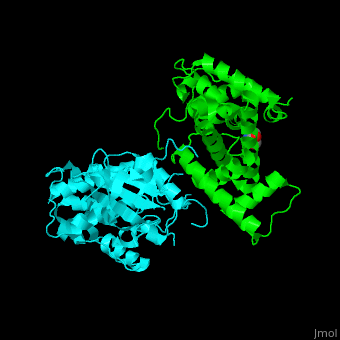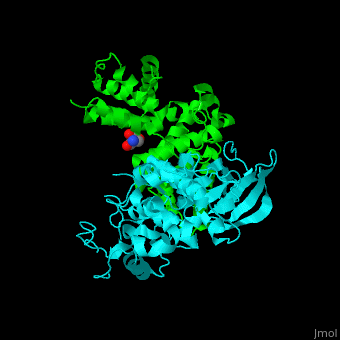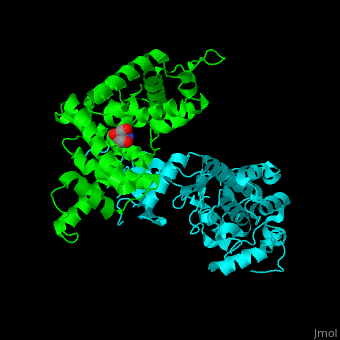
All cyclins have an all-α helix fold and share an identical ca. 100 residue domain called 'cyclin box' which binds CDK. <scene name='44/442748/Cv/3'>Two 5 α-helix cyclin boxes are shown</scene>.<ref>PMID:09433129</ref> | All cyclins have an all-α helix fold and share an identical ca. 100 residue domain called 'cyclin box' which binds CDK. <scene name='44/442748/Cv/3'>Two 5 α-helix cyclin boxes are shown</scene>.<ref>PMID:09433129</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of Cyclin == | ||
| + | [[Cyclin 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 39: | ||
**[[1jst]], [[3tnw]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P<br /> | **[[1jst]], [[3tnw]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P<br /> | ||
**[[1h24]], [[1h25]], [[1h26]], [[1h27]], [[1h28]], [[1gy3]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P+peptide<br /> | **[[1h24]], [[1h25]], [[1h26]], [[1h27]], [[1h28]], [[1gy3]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P+peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4bck]], [[4bcm]], [[4bcn]], [[4bco]], [[4bcp]], [[4bcq]], [[4cfn]], [[4cfw]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[4bck]], [[4bcm]], [[4bcn]], [[4bco]], [[4bcp]], [[4bcq]], [[4cfn]], [[4cfw]], [[6gva]], [[6guf]], [[6gue]], [[6guc]], [[6gub]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P + inhibitor<br /> |
| + | **[[6ath]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 T160P + cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[4fx3]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 + inhibitor<br /> | **[[4fx3]] - hCYCA2 +CDK2 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[4eoi]], [[4eoj]], [[4eok]], [[4eol]], [[4eom]], [[4eon]], [[4eoo]], [[4eop]], [[4eoq]], [[4eor]], [[4eos]] - hCYCA2 C-terminal +CDK2 T160P + inhibitor<br /> | **[[4eoi]], [[4eoj]], [[4eok]], [[4eol]], [[4eom]], [[4eon]], [[4eoo]], [[4eop]], [[4eoq]], [[4eor]], [[4eos]] - hCYCA2 C-terminal +CDK2 T160P + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| Line 38: | Line 56: | ||
**[[1e9h]] – hCYCA3 +CDK2 T160P+inhibitor<br /> | **[[1e9h]] – hCYCA3 +CDK2 T160P+inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | *CYCB1 | + | *CYCB1 or G2/mitotic-specific CYCB1 |
**[[2b9r]] – hCYCB1 (mutant)<br /> | **[[2b9r]] – hCYCB1 (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[2jgz]] - hCYCB1 + CDK2<br /> | **[[2jgz]] - hCYCB1 + CDK2<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6gu4]], [[6gu3]], [[6gu2]] – hCYCB1 + hCDK1 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[5hq0]], [[4yc3]], [[4y72]] – hCYCB1 + hCDK1 + CDK regulatory subunit 2<br /> | **[[5hq0]], [[4yc3]], [[4y72]] – hCYCB1 + hCDK1 + CDK regulatory subunit 2<br /> | ||
**[[5lqf]] – hCYCB1 + hCDK1 + CDK regulatory subunit 2 + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5lqf]] – hCYCB1 + hCDK1 + CDK regulatory subunit 2 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 90: | ||
**[[4cxa]] - hCYCK + CDK12 T160P + AMPPNP<br /> | **[[4cxa]] - hCYCK + CDK12 T160P + AMPPNP<br /> | ||
**[[5efq]], [[4nst]] - hCYCK + CDK13 T160P + ADP<br /> | **[[5efq]], [[4nst]] - hCYCK + CDK13 T160P + ADP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4un0]], [[5acb]], [[6b3e]] - hCYCK +CDK12 T160P + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[4un0]], [[5acb]], [[6b3e]], [[6ckx]] - hCYCK +CDK12 T160P + inhibitor<br /> |
*CYCT | *CYCT | ||
| Line 79: | Line 98: | ||
**[[4imy]], [[4or5]], [[4ogr]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9 TPO160 +AMP + AF4/MRF2 family member 4<br /> | **[[4imy]], [[4or5]], [[4ogr]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9 TPO160 +AMP + AF4/MRF2 family member 4<br /> | ||
**[[5l1z]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9 TPO160 +AMP + AF4/MRF2 family member 4 + RNA<br /> | **[[5l1z]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9 TPO160 +AMP + AF4/MRF2 family member 4 + RNA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cyt]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9 TPO160 +AMP + AF4/MRF2 family member 4 + TAT + RNA<br /> | ||
**[[3lq5]], [[3tn8]], [[3tnh]], [[3tni]], [[4bcf]], [[4bcg]], [[4bch]], [[4bci]], [[4bcj]] – hCYCT1 (mutant)+CDK9<br /> | **[[3lq5]], [[3tn8]], [[3tnh]], [[3tni]], [[4bcf]], [[4bcg]], [[4bch]], [[4bci]], [[4bcj]] – hCYCT1 (mutant)+CDK9<br /> | ||
**[[3blr]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9+inhibitor<br /> | **[[3blr]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9+inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6gzh]] - hCYCT1 TPO160 +CDK9+inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[3my1]], [[4ec8]], [[4ec9]] - hCYCT1 (mutant)+CDK9 TPO160 +inhibitor<br /> | **[[3my1]], [[4ec8]], [[4ec9]] - hCYCT1 (mutant)+CDK9 TPO160 +inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[3mi9]], [[3mia]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9+protein TAT<br /> | **[[3mi9]], [[3mia]] - hCYCT1 +CDK9+protein TAT<br /> | ||
Revision as of 10:19, 21 May 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Cyclin
Updated on 21-May-2019
References
- ↑ Galderisi U, Jori FP, Giordano A. Cell cycle regulation and neural differentiation. Oncogene. 2003 Aug 11;22(33):5208-19. PMID:12910258 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206558
- ↑ Sage J. Cyclin C makes an entry into the cell cycle. Dev Cell. 2004 May;6(5):607-8. PMID:15130482
- ↑ Jackman M, Kubota Y, den Elzen N, Hagting A, Pines J. Cyclin A- and cyclin E-Cdk complexes shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Mar;13(3):1030-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-07-0361. PMID:11907280 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.01-07-0361
- ↑ Blazek D, Kohoutek J, Bartholomeeusen K, Johansen E, Hulinkova P, Luo Z, Cimermancic P, Ule J, Peterlin BM. The Cyclin K/Cdk12 complex maintains genomic stability via regulation of expression of DNA damage response genes. Genes Dev. 2011 Oct 15;25(20):2158-72. doi: 10.1101/gad.16962311. PMID:22012619 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.16962311
- ↑ Garriga J, Grana X. Cellular control of gene expression by T-type cyclin/CDK9 complexes. Gene. 2004 Aug 4;337:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.05.007. PMID:15276198 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.05.007
- ↑ Mittnacht S, Boshoff C. Viral cyclins. Rev Med Virol. 2000 May-Jun;10(3):175-84. PMID:10815028
- ↑ Jirawatnotai S, Sharma S, Michowski W, Suktitipat B, Geng Y, Quackenbush J, Elias JE, Gygi SP, Wang YE, Sicinski P. The cyclin D1-CDK4 oncogenic interactome enables identification of potential novel oncogenes and clinical prognosis. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2889-900. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.946850. PMID:25486477 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/15384101.2014.946850
- ↑ Patel H, Abduljabbar R, Lai CF, Periyasamy M, Harrod A, Gemma C, Steel JH, Patel N, Busonero C, Jerjees D, Remenyi J, Smith S, Gomm JJ, Magnani L, Gyorffy B, Jones LJ, Fuller-Pace F, Shousha S, Buluwela L, Rakha EA, Ellis IO, Coombes RC, Ali S. Expression of CDK7, Cyclin H, and MAT1 Is Elevated in Breast Cancer and Is Prognostic in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 1;22(23):5929-5938. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1104., Epub 2016 Jun 14. PMID:27301701 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1104
- ↑ Noble ME, Endicott JA, Brown NR, Johnson LN. The cyclin box fold: protein recognition in cell-cycle and transcription control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997 Dec;22(12):482-7. PMID:9433129