Invertase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
INV is used in the food industry to produce fructose which is sweeter and does not crystallize easily. | INV is used in the food industry to produce fructose which is sweeter and does not crystallize easily. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
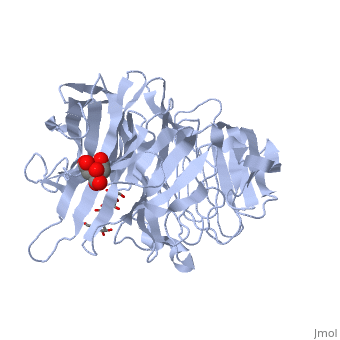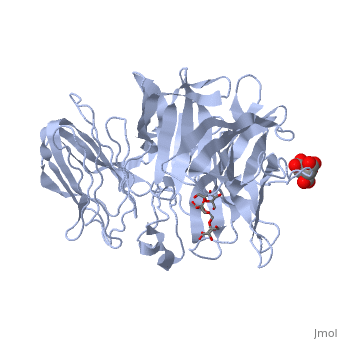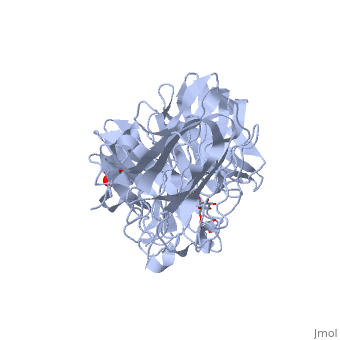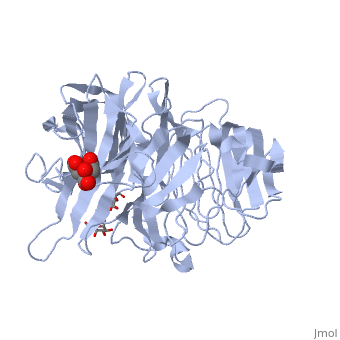
| - | The <scene name='67/676994/Cv/ | + | The <scene name='67/676994/Cv/7'>active site pocket</scene> of INV contains the catalytic residues Asp and Glu<ref>PMID:16411890</ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:04, 29 May 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of invertase
Updated on 29-May-2019
References
- ↑ Neumann NP, Lampen JO. Purification and properties of yeast invertase. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):468-75. PMID:4963242
- ↑ Proels RK, Huckelhoven R. Cell-wall invertases, key enzymes in the modulation of plant metabolism during defence responses. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Oct;15(8):858-64. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12139. Epub 2014 May, 13. PMID:24646208 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12139
- ↑ Roitsch T, Balibrea ME, Hofmann M, Proels R, Sinha AK. Extracellular invertase: key metabolic enzyme and PR protein. J Exp Bot. 2003 Jan;54(382):513-24. PMID:12508062
- ↑ Alberto F, Jordi E, Henrissat B, Czjzek M. Crystal structure of inactivated Thermotoga maritima invertase in complex with the trisaccharide substrate raffinose. Biochem J. 2006 May 1;395(3):457-62. PMID:16411890 doi:http://dx.doi.org/BJ20051936