User:Alice Kei Endo/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
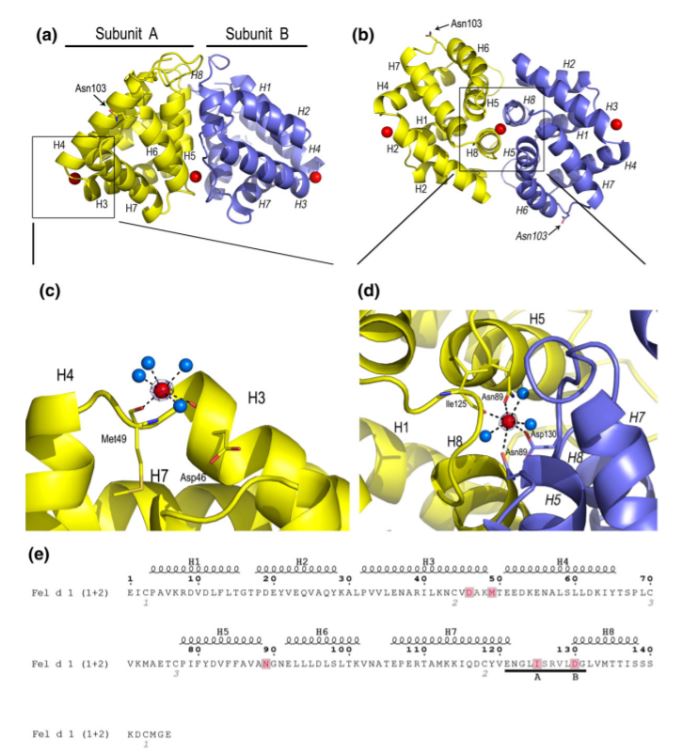
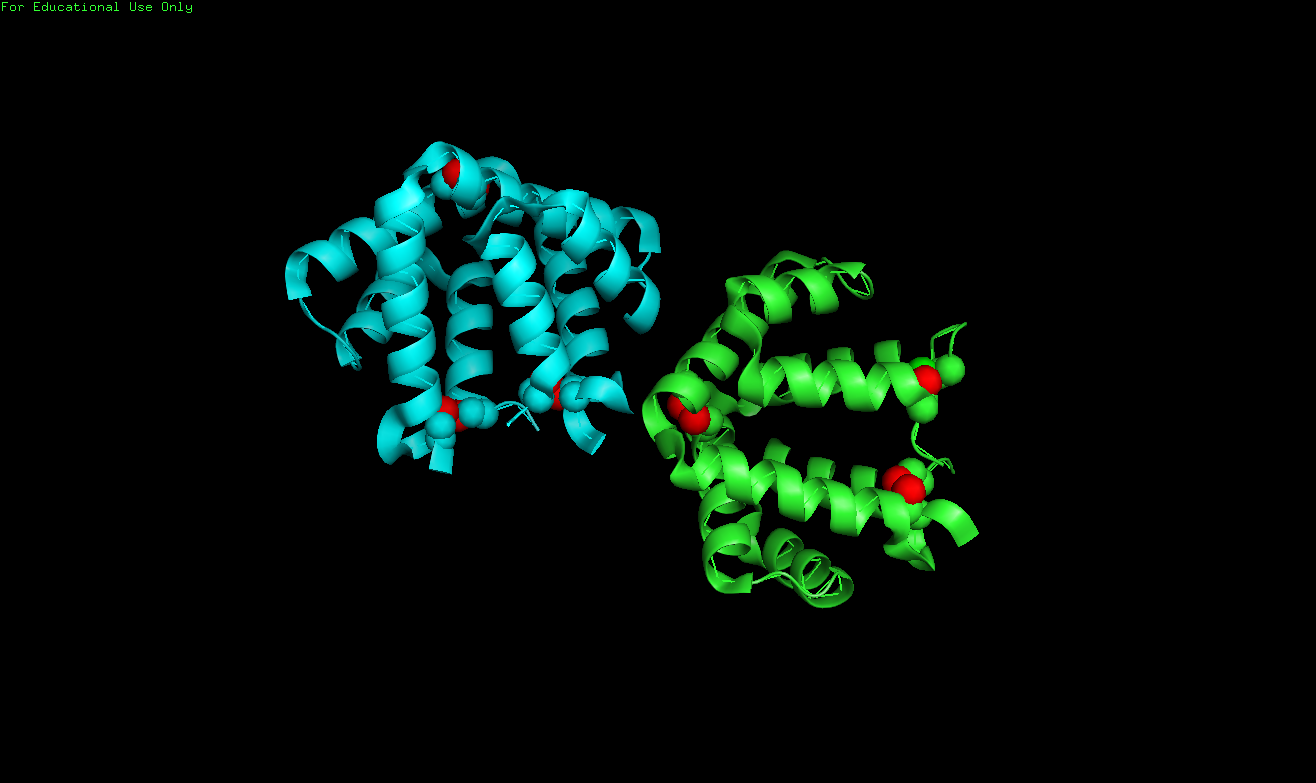
Fel d 1 has been reported as a 35 kDa tetrameric glycoprotein formed by two heterodimers. Each heterodimer consists of one 70 residue peptide and one 85, 90, or 92 residue peptide (i.e. chains 1 and 2, respectively) encoded by separate genes. These chains are linked within each heterodimer through three disulfide bonds, formed between cysteine residues Cys3 and Cys73, Cys44 and Cys48, and Cys70 and Cys7, in chains 1 and 2, respectively. | Fel d 1 has been reported as a 35 kDa tetrameric glycoprotein formed by two heterodimers. Each heterodimer consists of one 70 residue peptide and one 85, 90, or 92 residue peptide (i.e. chains 1 and 2, respectively) encoded by separate genes. These chains are linked within each heterodimer through three disulfide bonds, formed between cysteine residues Cys3 and Cys73, Cys44 and Cys48, and Cys70 and Cys7, in chains 1 and 2, respectively. | ||
Each subunit of the Fel d 1 consists of <scene name='81/817989/Subunity_a_colorido/1'>eight helices</scene> named H1–H4 (corresponding to chain 1) and H5–H8 (corresponding to chain 2). | Each subunit of the Fel d 1 consists of <scene name='81/817989/Subunity_a_colorido/1'>eight helices</scene> named H1–H4 (corresponding to chain 1) and H5–H8 (corresponding to chain 2). | ||
| + | Na imagem abaixo, pode-se notar as 3 ligações dissulfeto em vermelho. | ||
| + | [[Image:Pontes_alfa.png]] | ||
== Crystal structure == | == Crystal structure == | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 16 June 2019
Contents |
Fel d 1
|
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
Fel d 1 has been reported as a 35 kDa tetrameric glycoprotein formed by two heterodimers. Each heterodimer consists of one 70 residue peptide and one 85, 90, or 92 residue peptide (i.e. chains 1 and 2, respectively) encoded by separate genes. These chains are linked within each heterodimer through three disulfide bonds, formed between cysteine residues Cys3 and Cys73, Cys44 and Cys48, and Cys70 and Cys7, in chains 1 and 2, respectively.
Each subunit of the Fel d 1 consists of named H1–H4 (corresponding to chain 1) and H5–H8 (corresponding to chain 2).
Na imagem abaixo, pode-se notar as 3 ligações dissulfeto em vermelho.
Crystal structure
The crystal structure of Fel d 1 tetramer, at 1.6 Å resolution, displays a globular all helical fold that composed of having four Ca ions, 270 water molecules, a and a . As said before each subunit of the Fel d 1 consists of eight helices named H1–H4 (corresponding to chain 1) and H5–H8 (corresponding to chain 2).
A total of four Ca ions are present in the crystal structure of the Fel d 1. One Ca2+ (site 1) is bound within the dimerization interface, resulting in profound local conformational changes. The binding of the Ca2+ in this region of the Fel d 1 interface most probably stabilizes the tetrameric form, since the presence of such a positively charged ion allows for the packing of acidic residues ( Asp130 in subunits A and B) in the Fel d 1 tetramer interface. However, at the same time it also results in profound local conformational changes that affect the size and form of the different cavities.
Two additional Ca2+-binding sites are also present on both sides of the tetramer, localized at exactly the same position as suggested for Ca2+ binding sites in uteroglobin, one on each of the heterodimeric subunits A and B. A last Ca2+ site has been shown, however the position of this ion is most probably due to the packing of the molecules in the asymmetric unit.
The crystal structure of Fel d 1 also suggests a potential portal for two waterfilled cavities of different size, one in each monomer.
</StructureSection>