The L,D-transpeptidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of peptidoglycan crosslinking in Mycobaterium tuberculosis.
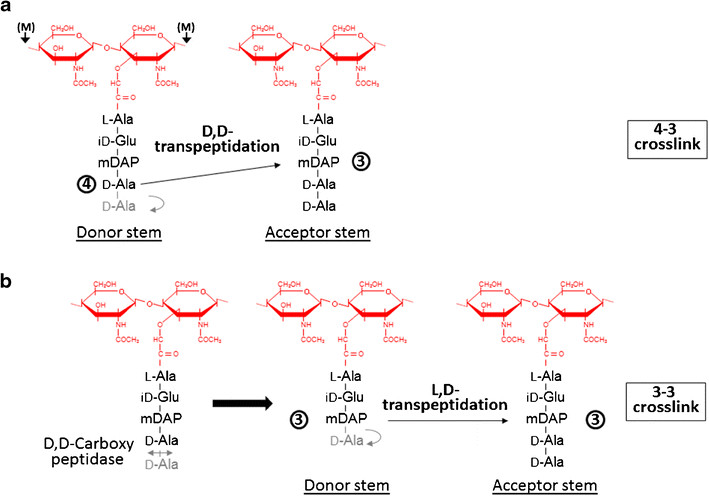
Formation of the most common type of crosslink in peptidoglycan, the (D,D) 4->3 linkage, is catalyzed by the [D,d-transpeptidase]. These enzymes generate 4 -> 3 transpeptidase linkages between the fourth amino acid (D-alanine) of one chain and the third amino acid (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of an adjacent chain. A second type of crosslink, the (L,D) 3->3 linkage is catalysed by L,D-transpeptidases such as Mtb L,D-transpeptidase LdtMt2 of Mycobaterium tuberculosis. These enzymes transfer the peptide bond between the third residue (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of a tetrapeptide donor stem to the side-chain amide group of the third residue (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of an adjacent acceptor stem. In both types of transpeptidases, the catalysis proceeds by a two-step mechanism: acylation of the enzyme by the penultimate peptide of the donor stem with the release of the stem C-terminal residue, followed by deacylation of this acyl-enzyme intermediate by an acceptor stem.
Function
The final step of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria involves the formation of crosslinking. The D,D transpeptidase catalyzes the formation of crosslinking. B-lactams antibiotics such as penicillin inhibit this D,D transpeptidases. But it was found that Mycobacterium tuberculosis was resistant to these antibiotics. This happens because mycobacteria rely mostly on L,D transpeptidase for biosynthesis and maintenance of their peptidoglycan layer. Loss of L,D transpeptidase in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ldt_Mt2 result in altered cell size, growth and virulence as well as increased susceptibility to B-lactams antibiotics. The degree of crosslinking of Mycobaterium tuberculosis is a high of 80% with 3->3 linkages comprising 70% of total linkages.
During the stationary phase of growth in bacteria, formation of new 4->3 linkages is impaired because the mature peptidoglycan layer has few pentapeptide stems, so the synthesis of crosslinking is significantly reduced. In contrast, L,D transpeptidases could still crosslink the available tetrapeptide donors. Expression of the LdtMt is upregulated in the transcriptome of laboratory models of persisting bacteria. So the L,D transpeptidase activity could be a chemotherapeutic target.
Structure
The LdtMt2 precursor consists of 408 amino acid residues that form the transmembrane domain (Met1-Ala34) and the chain of the enzyme (Cys35-Ala408), which can be divided into three domains: two non-catalytic Ig-like , (residues Ala55-Ser147 and Pro148- Gly250, respectively) and the (residues Asp251-Ala408) with transpeptidase activity. Domain A e Domain B display a variant to the immunoglobulin fold built up by a sandwich of two antiparallel sheets. And the catalytic domain consists of a Beta-sandwich with two mixed beta sheets ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold.
A short linker (residues 251–253) joins the two domains. A small C-terminal subdomain (CTSD; residues 379–407) extends the ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. In this subdomain, Trp394 and two Trp residues of the C-terminal helix a3 (398 and 401) make a zipper-like interaction with the IgD N-terminal domain that fixes
the relative orientation of the two domains.
Active site
The of LdtMt2 is located at the entrance of a narrow tunnel connecting two cavities and there is a lid covering the active site formed by a pair of antiparallel B-strands and their connecting loop.
The large hydrophobic residues of the (Tyr298, Tyr308 and Tyr318) and the residues surrounding the entrance to the active site (Tyr330, Phe334 and Trp340) contribute to the closure and to the exclusion of solvent, which may support efficient catalysis.
In LdtMt2, the (), His336 and Cys354, reside under a flap formed by a long insert (residues 299–323) that is not part of the canonical ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. This insert, strand beta 15 and strand beta 16 fold over the beta sheet formed by strands beta 17, beta 18, and beta 19 (residues 324–357). The closed flap creates two large cavities connected by a narrow tunnel. These cavities are open to solvent: one at the end of the molecule, and the other at the interface between the CD and IgD.
Strand beta 16 (residues 318–323), the C-terminal end of beta 18 (residues 336 and 337), the loop Lc (residues 338–352), and the
strand beta 19 (residues 353–357) line the outer cavity. The residues of the conserved motif are readily accessible through the outer cavity, with the catalytic residues located deep within it. With the exceptions of His336 and
Ser337 (both in beta 18), the conserved motifs extend through the end of loop Lc and strand beta 19. Ser351, His352, and Gly353 are located in loop Lc, whereas Cys354 and Asn356 in strand beta 19.
At one end of the tunnel recognize the D chiral center of the meso-diaminopimelic acid side chain, making H bonds to its carboxylate and amide group. At the other end, the L chiral center is surrounded by an formed by the backbone NH group of residues 352–354 at the C terminus of loop Lc. In this position, the acyl group of the m-DAP L chiral center is within reach of Cys354. His336 is close and ready to accept a H+ from Cys354 (). The cysteine thiolate formed by this H+ abstraction attacks the acyl carbon and forms a tetrahedral intermediate stabilized by the ‘‘anion hole’’ and by the just protonated His336. After the intermediate thioester formation and protonation by His336, D-Ala4 is released. Then another peptide stem can enter the catalytic site and bind to active site residues with the side-chain amide of the mDAP residue. Nucleophilic attack by this amine group forms the new peptide bond that crosslinks the two stems with release and protonation of the cysteine thiolate by His336. The last step in the transpeptidation reaction requires that donor and acceptor peptidoglycan stems both be at the catalytic site for the reaction to occur.
References
Böth, D., Steiner, E. M., Stadler, D., Lindqvist, Y., Schnell, R., & Schneider, G. (2013). Structure of LdtMt2, an L, D-transpeptidase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Acta Crystallographica Section D: Biological Crystallography, 69(3), 432-441.[1]
Brammer, L. B., Ghosh, A., Pan, Y., Jakoncic, J., Lloyd, E. P., Townsend, C. A., ... & Bianchet, M. A. (2015). Loss of a Functionally and Structurally Distinct ld-Transpeptidase, LdtMt5, Compromises Cell Wall Integrity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The Journal of biological chemistry, 290(42), 25670-25685.[2]
Erdemli, S. B., Gupta, R., Bishai, W. R., Lamichhane, G., Amzel, L. M., & Bianchet, M. A. (2012). Targeting the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: structure and mechanism of L, D-transpeptidase 2. Structure, 20(12), 2103-2115. [3]
Li, W. J., Li, D. F., Hu, Y. L., Zhang, X. E., Bi, L. J., & Wang, D. C. (2013). Crystal structure of L, D-transpeptidase Ldt Mt2 in complex with meropenem reveals the mechanism of carbapenem against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell research, 23(5), 728 [4]
Mainardi, J. L., Fourgeaud, M., Hugonnet, J. E., Dubost, L., Brouard, J. P., Ouazzani, J., ... & Arthur, M. (2005). A novel peptidoglycan cross-linking enzyme for a β-lactam-resistant transpeptidation pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(46), 38146-38152. [5]

