We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
LdtMt2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Expression System: Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | Expression System: Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | ||
' scene='81/817533/All/1'> | ' scene='81/817533/All/1'> | ||
| - | + | ||
The L,D-transpeptidase <scene name='81/817533/All/1'>LdtMt2</scene> is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of peptidoglycan crosslinking in ''Mycobaterium tuberculosis''. | The L,D-transpeptidase <scene name='81/817533/All/1'>LdtMt2</scene> is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of peptidoglycan crosslinking in ''Mycobaterium tuberculosis''. | ||
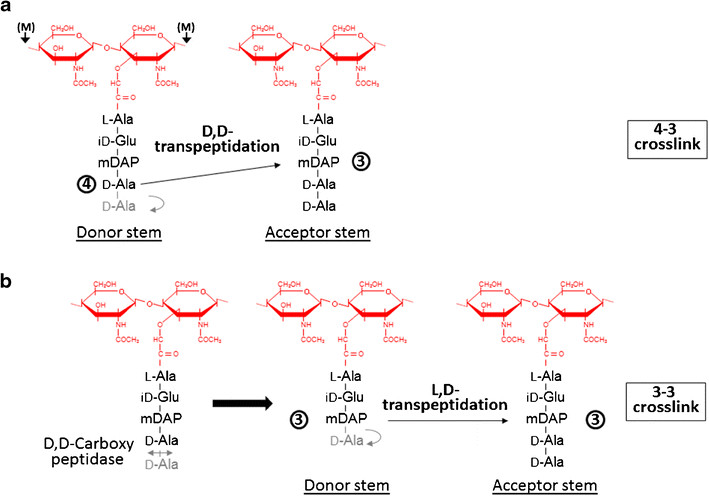
| - | Formation of the most common type of crosslink in peptidoglycan, the (D,D) 4->3 linkage, is catalyzed by the [D,d-transpeptidase]. These enzymes generate 4 -> 3 transpeptidase linkages between the fourth amino acid (D-alanine) of one chain and the third amino acid (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of an adjacent chain. A second type of crosslink, the (L,D) 3->3 linkage is catalysed by L,D-transpeptidases such as Mtb L,D-transpeptidase LdtMt2 of ''Mycobaterium tuberculosis''. These enzymes transfer the peptide bond between the third residue (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of a tetrapeptide donor stem to the side-chain amide group of the third residue (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of an adjacent acceptor stem. In both types of transpeptidases, the catalysis proceeds by a two-step mechanism: acylation of the enzyme by the penultimate peptide of the donor stem with the release of the stem C-terminal residue, followed by deacylation of this acyl-enzyme intermediate by an acceptor stem. | + | Formation of the most common type of crosslink in peptidoglycan, the (D,D) 4->3 linkage, is catalyzed by the [[D,d-transpeptidase]]. These enzymes generate 4 -> 3 transpeptidase linkages between the fourth amino acid (D-alanine) of one chain and the third amino acid (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of an adjacent chain. A second type of crosslink, the (L,D) 3->3 linkage is catalysed by L,D-transpeptidases such as Mtb L,D-transpeptidase LdtMt2 of ''Mycobaterium tuberculosis''. These enzymes transfer the peptide bond between the third residue (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of a tetrapeptide donor stem to the side-chain amide group of the third residue (meso-diaminopimelic acid) of an adjacent acceptor stem. In both types of transpeptidases, the catalysis proceeds by a two-step mechanism: acylation of the enzyme by the penultimate peptide of the donor stem with the release of the stem C-terminal residue, followed by deacylation of this acyl-enzyme intermediate by an acceptor stem. |
[[Image:Figure transpeptidases.png]] | [[Image:Figure transpeptidases.png]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | The LdtMt2 precursor consists of 408 amino acid residues that form the transmembrane domain (Met1-Ala34) and the chain of the enzyme (Cys35-Ala408), which can be divided into three domains: two non-catalytic Ig-like <scene name='81/817533/Domaina/1'>Domain A</scene>, <scene name='81/817533/Domainb/1'>Domain B</scene> (residues Ala55-Ser147 and Pro148- Gly250, respectively) and the <scene name='81/817533/Domaincd/1'>catalytic domain</scene> (residues Asp251-Ala408) with transpeptidase activity. Domain A e Domain B | + | The LdtMt2 precursor consists of 408 amino acid residues that form the transmembrane domain (Met1-Ala34) and the chain of the enzyme (Cys35-Ala408), which can be divided into <scene name='81/817533/Second/3'>three domains</scene>: two non-catalytic Ig-like <scene name='81/817533/Domaina/1'>Domain A</scene>, <scene name='81/817533/Domainb/1'>Domain B</scene> (residues Ala55-Ser147 and Pro148- Gly250, respectively) and the <scene name='81/817533/Domaincd/1'>catalytic domain</scene> (residues Asp251-Ala408) with transpeptidase activity. Domain A e Domain B displays a variant to the immunoglobulin fold built up by a sandwich of two antiparallel sheets. And the catalytic domain consists of a beta-sandwich with two mixed beta sheets ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. |
| - | A short linker (residues 251–253) joins the two domains. A small C-terminal subdomain (CTSD; residues 379–407) extends the ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. In this subdomain, Trp394 and two Trp residues of the C-terminal helix a3 (398 and 401) make a zipper-like interaction with the IgD N-terminal domain that fixes | + | A short linker (residues 251–253) joins the two domains. A small <scene name='81/817533/Sub-domain/2'>C-terminal subdomain</scene> (CTSD; residues 379–407) extends the ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. In this subdomain, Trp394 and two Trp residues of the C-terminal helix a3 (398 and 401) make a zipper-like interaction with the IgD N-terminal domain that fixes the relative orientation of the two domains. |
| - | the relative orientation of the two domains. | + | |
== Active site == | == Active site == | ||
Revision as of 00:16, 17 June 2019
Overview
| |||||||||||