We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
LdtMt2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
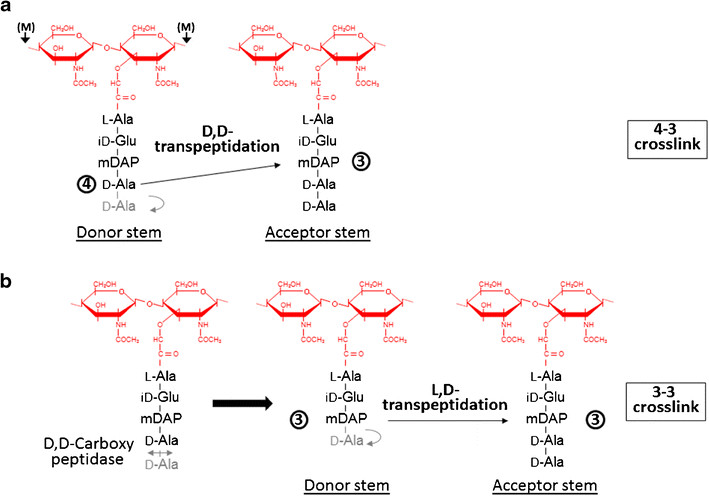
A short linker (residues 251–253) joins the two domains. A small <scene name='81/817533/Sub-domain/2'>C-terminal subdomain</scene> (CTSD; residues 379–407) extends the ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. In this subdomain, Trp394 and two Trp residues of the C-terminal helix a3 (398 and 401) make a <scene name='81/817533/Zipper/1'>zipper-like</scene> interaction with the IgD N-terminal domain that fixes the relative orientation of the two domains. | A short linker (residues 251–253) joins the two domains. A small <scene name='81/817533/Sub-domain/2'>C-terminal subdomain</scene> (CTSD; residues 379–407) extends the ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. In this subdomain, Trp394 and two Trp residues of the C-terminal helix a3 (398 and 401) make a <scene name='81/817533/Zipper/1'>zipper-like</scene> interaction with the IgD N-terminal domain that fixes the relative orientation of the two domains. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Figure model.jpg]] | ||
== Active site == | == Active site == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
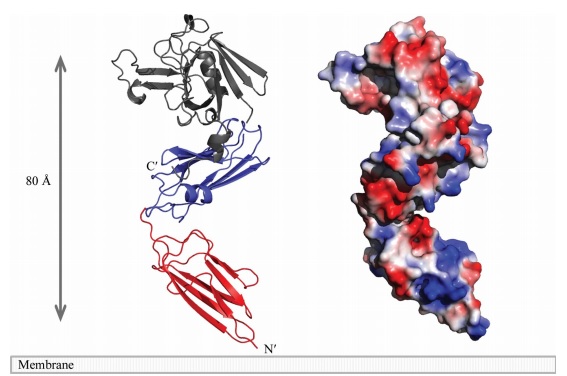
The <scene name='81/817533/Activesite/1'>catalytic site</scene> of LdtMt2 is located at the entrance of a narrow tunnel connecting two cavities and there is a lid covering the active site formed by a pair of antiparallel B-strands and their connecting loop. | The <scene name='81/817533/Activesite/1'>catalytic site</scene> of LdtMt2 is located at the entrance of a narrow tunnel connecting two cavities and there is a lid covering the active site formed by a pair of antiparallel B-strands and their connecting loop. | ||
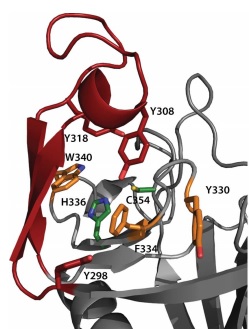
The large hydrophobic residues of the <scene name='81/817533/Lid/1'>lid</scene> (Tyr298, Tyr308 and Tyr318) and the residues surrounding the entrance to the active site (Tyr330, Phe334 and Trp340) contribute to the closure and to the exclusion of solvent, which may support efficient catalysis. | The large hydrophobic residues of the <scene name='81/817533/Lid/1'>lid</scene> (Tyr298, Tyr308 and Tyr318) and the residues surrounding the entrance to the active site (Tyr330, Phe334 and Trp340) contribute to the closure and to the exclusion of solvent, which may support efficient catalysis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Figure active site.jpg]] | ||
In LdtMt2, the (<scene name='81/817533/Conserved_residues/1'>catalytic residues</scene>), '''His336''' and '''Cys354''', reside under a flap formed by a long insert (residues 299–323) that is not part of the canonical ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. This insert, strand beta 15 and strand beta 16 fold over the beta sheet formed by strands beta 17, beta 18, and beta 19 (residues 324–357). The closed flap creates two large cavities connected by a narrow tunnel. These cavities are open to solvent: one at the end of the molecule, and the other at the interface between the CD and IgD. | In LdtMt2, the (<scene name='81/817533/Conserved_residues/1'>catalytic residues</scene>), '''His336''' and '''Cys354''', reside under a flap formed by a long insert (residues 299–323) that is not part of the canonical ErfK/YbiS/YhnG fold. This insert, strand beta 15 and strand beta 16 fold over the beta sheet formed by strands beta 17, beta 18, and beta 19 (residues 324–357). The closed flap creates two large cavities connected by a narrow tunnel. These cavities are open to solvent: one at the end of the molecule, and the other at the interface between the CD and IgD. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
strand beta 19 (residues 353–357) line the outer cavity. The residues of the conserved motif are readily accessible through the outer cavity, with the catalytic residues located deep within it. With the exceptions of His336 and | strand beta 19 (residues 353–357) line the outer cavity. The residues of the conserved motif are readily accessible through the outer cavity, with the catalytic residues located deep within it. With the exceptions of His336 and | ||
Ser337 (both in beta 18), the conserved motifs extend through the end of loop Lc and strand beta 19. Ser351, His352, and Gly353 are located in loop Lc, whereas Cys354 and Asn356 in strand beta 19. | Ser337 (both in beta 18), the conserved motifs extend through the end of loop Lc and strand beta 19. Ser351, His352, and Gly353 are located in loop Lc, whereas Cys354 and Asn356 in strand beta 19. | ||
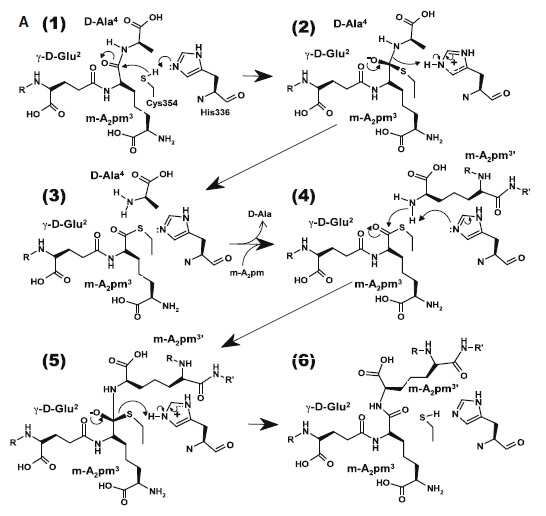
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Figure mode of action.jpg]] | ||
At one end of the tunnel <scene name='81/817533/D-chiral_center_recognition/2'>Tyr318 and the carbonyl group of Gly332</scene> recognize the D chiral center of the meso-diaminopimelic acid side chain, making H bonds to its carboxylate and amide group. At the other end, the L chiral center is surrounded by an <scene name='81/817533/Anion_hole/1'>anion hole</scene> formed by the backbone NH group of residues 352–354 at the C terminus of loop Lc. In this position, the acyl group of the m-DAP L chiral center is within reach of Cys354. '''His336''' is close and ready to accept a H+ from '''Cys354''' (<scene name='81/817533/Conserved_residues/1'>conserved residues</scene>). The cysteine thiolate formed by this H+ abstraction attacks the acyl carbon and forms a tetrahedral intermediate stabilized by the ‘‘anion hole’’ and by the just protonated His336. After the intermediate thioester formation and protonation by His336, D-Ala4 is released. Then another peptide stem can enter the catalytic site and bind to active site residues with the side-chain amide of the mDAP residue. Nucleophilic attack by this amine group forms the new peptide bond that crosslinks the two stems with release and protonation of the cysteine thiolate by His336. The last step in the transpeptidation reaction requires that donor and acceptor peptidoglycan stems both be at the catalytic site for the reaction to occur. | At one end of the tunnel <scene name='81/817533/D-chiral_center_recognition/2'>Tyr318 and the carbonyl group of Gly332</scene> recognize the D chiral center of the meso-diaminopimelic acid side chain, making H bonds to its carboxylate and amide group. At the other end, the L chiral center is surrounded by an <scene name='81/817533/Anion_hole/1'>anion hole</scene> formed by the backbone NH group of residues 352–354 at the C terminus of loop Lc. In this position, the acyl group of the m-DAP L chiral center is within reach of Cys354. '''His336''' is close and ready to accept a H+ from '''Cys354''' (<scene name='81/817533/Conserved_residues/1'>conserved residues</scene>). The cysteine thiolate formed by this H+ abstraction attacks the acyl carbon and forms a tetrahedral intermediate stabilized by the ‘‘anion hole’’ and by the just protonated His336. After the intermediate thioester formation and protonation by His336, D-Ala4 is released. Then another peptide stem can enter the catalytic site and bind to active site residues with the side-chain amide of the mDAP residue. Nucleophilic attack by this amine group forms the new peptide bond that crosslinks the two stems with release and protonation of the cysteine thiolate by His336. The last step in the transpeptidation reaction requires that donor and acceptor peptidoglycan stems both be at the catalytic site for the reaction to occur. | ||
Revision as of 00:41, 17 June 2019
Overview
| |||||||||||