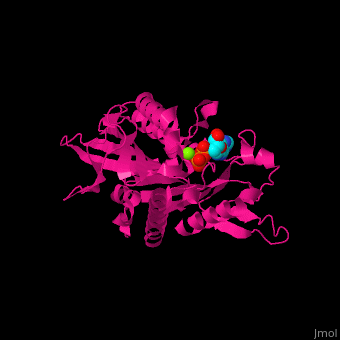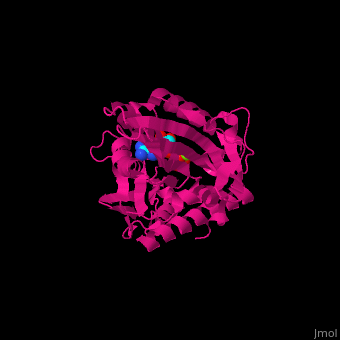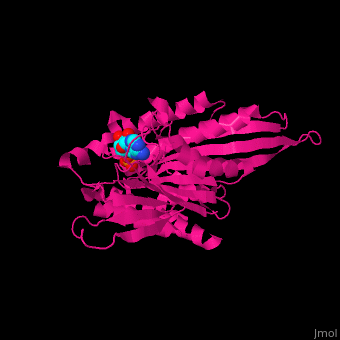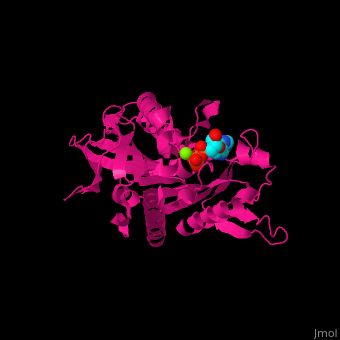We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Kinesin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <scene name='41/410296/Cv/ | + | <scene name='41/410296/Cv/10'>Active site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. Residue <scene name='41/410296/Cv/11'>Arg216 is the key residue in KIF for the chemical cycling of ATPase and for the mechanical cycling</scene>. Arg216 pivots to enable <scene name='41/410296/Cv/12'>Mg-ADP</scene> release or the phosphate release. <scene name='41/410296/Cv/13'>Arg216 forms a latch</scene> in the KIF 'closed-state' before the Mg-ADP release. Binding of β-tubulin to KIF releases the latch, enabling the KIF conformation change and detaching KIF from the microtubule and enabling the next movement cycle<ref>PMID:18806800</ref>. |
| - | <scene name='41/410296/Cv/ | + | <scene name='41/410296/Cv/14'>Mg coordination site</scene>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of Kinesin == | == 3D Structures of Kinesin == | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 3 July 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Kinesin
Updated on 03-July-2019
References
- ↑ Hirokawa N, Noda Y, Tanaka Y, Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;10(10):682-96. doi: 10.1038/nrm2774. PMID:19773780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm2774
- ↑ Ebbing B, Mann K, Starosta A, Jaud J, Schols L, Schule R, Woehlke G. Effect of spastic paraplegia mutations in KIF5A kinesin on transport activity. Hum Mol Genet. 2008 May 1;17(9):1245-52. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn014. Epub 2008 Jan, 18. PMID:18203753 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn014
- ↑ Hirokawa N, Takemura R. Biochemical and molecular characterization of diseases linked to motor proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Oct;28(10):558-65. PMID:14559185 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2003.08.006
- ↑ Grosch M, Gruner B, Spranger S, Stutz AM, Rausch T, Korbel JO, Seelow D, Nurnberg P, Sticht H, Lausch E, Zabel B, Winterpacht A, Tagariello A. Identification of a Ninein (NIN) mutation in a family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia with joint laxity (leptodactylic type)-like phenotype. Matrix Biol. 2013 Oct-Nov;32(7-8):387-92. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.05.001. Epub, 2013 May 9. PMID:23665482 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2013.05.001
- ↑ Nitta R, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. Structural model for strain-dependent microtubule activation of Mg-ADP release from kinesin. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Oct;15(10):1067-75. Epub 2008 Sep 21. PMID:18806800 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1487
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky