Retinoblastoma protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==pRb/EF binding in the cell cycle== | ==pRb/EF binding in the cell cycle== | ||
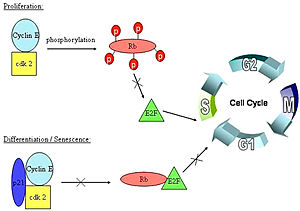
[[Image:Cell_cycle.jpg|300px|left|thumb|pRb/E2F binding in the cell cycle]] | [[Image:Cell_cycle.jpg|300px|left|thumb|pRb/E2F binding in the cell cycle]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
A cell must go through the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_cycle cell cycle] in order to grow, and replicate, and before it can replicate it has to pass through the many phases of the cell cycle. The cell cycle consists of the Go phase, also known as the resting phase in which the cell exits from the | A cell must go through the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_cycle cell cycle] in order to grow, and replicate, and before it can replicate it has to pass through the many phases of the cell cycle. The cell cycle consists of the Go phase, also known as the resting phase in which the cell exits from the | ||
cell cycle, and can remain dormant forever. Then comes the Gap-1 phase in which cell growth takes place. | cell cycle, and can remain dormant forever. Then comes the Gap-1 phase in which cell growth takes place. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
==Specific Binding sites of pRb/E2F complex== | ==Specific Binding sites of pRb/E2F complex== | ||
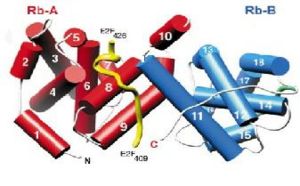
| - | [[Image:New fig 25.jpg| | + | [[Image:New fig 25.jpg|left|300px|thumb|A representation of the alpha-helices on the A and B domains that interact with E2F]] |
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
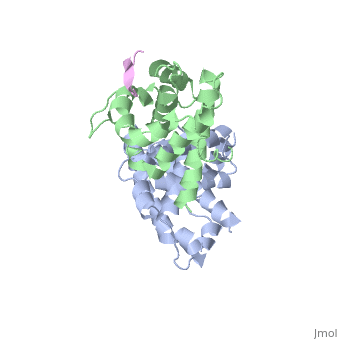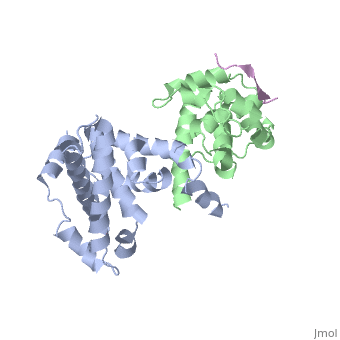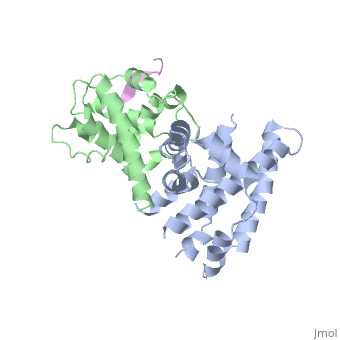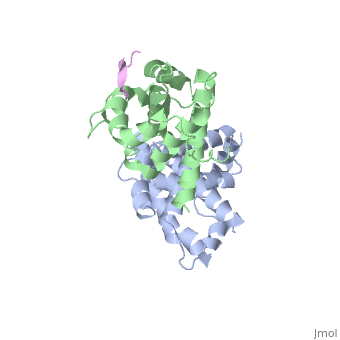
When pRB and E2F form a complex, pRB is activated, and therefore inhibits cell growth. E2F is a family of transcription factors E2F-1, E2F-2, E2F-3, E2F-4, and E2F-5. Specifically, E2F-1, E2F-2, E2F-3,and E2F-4 bind to retinoblastoma during the G0,Gap-1, and S stages of the cell cycle. This complex is held together by many weak interactions, such as hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and a salt bridge. The retinoblastoma protein’s active site is composed of two domains. <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Prb_with_e2f/1'>Domains A and B</scene>, which form the pRB pocket domain that E2F can bind to, the C-terminal residues on pRb are also necessary for E2F to bind with a higher affinity. Specifically, E2F binds to the α4, α5, α6, α8, and α9 helices of the A domain, and only bind to the α11 helix of the B domain '''(see figure to the right)'''. This structure was obtained through a diffraction image from a diffractometer <ref name=Xiao>PMID: 12598654</ref>. They also found that of the entire E2F complex only the two end regions are needed to bind pRb, the marked box region and the transactivation domain which is composed of residues 243-437.<ref name=Seville>http://hosted2.roswellpark.org/o4s/audio/references/Black5_090706.pdf</ref> | When pRB and E2F form a complex, pRB is activated, and therefore inhibits cell growth. E2F is a family of transcription factors E2F-1, E2F-2, E2F-3, E2F-4, and E2F-5. Specifically, E2F-1, E2F-2, E2F-3,and E2F-4 bind to retinoblastoma during the G0,Gap-1, and S stages of the cell cycle. This complex is held together by many weak interactions, such as hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and a salt bridge. The retinoblastoma protein’s active site is composed of two domains. <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Prb_with_e2f/1'>Domains A and B</scene>, which form the pRB pocket domain that E2F can bind to, the C-terminal residues on pRb are also necessary for E2F to bind with a higher affinity. Specifically, E2F binds to the α4, α5, α6, α8, and α9 helices of the A domain, and only bind to the α11 helix of the B domain '''(see figure to the right)'''. This structure was obtained through a diffraction image from a diffractometer <ref name=Xiao>PMID: 12598654</ref>. They also found that of the entire E2F complex only the two end regions are needed to bind pRb, the marked box region and the transactivation domain which is composed of residues 243-437.<ref name=Seville>http://hosted2.roswellpark.org/o4s/audio/references/Black5_090706.pdf</ref> | ||
[[Image:6813Fig4.jpg|left|thumb|E2F transcription factor]] | [[Image:6813Fig4.jpg|left|thumb|E2F transcription factor]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
There are 18 residues of the E2F protein that are involved in the pRb/E2F complex '''(left figure)''', residues 409-426. Within this E2F region, there are 5 essential amino acids that if altered, would cause the complex to fall apart. These amino acids are the following: <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Hydrophobic_pocket_tyr_41/2'>Tyr 411</scene> binds to pRB via a hydrophobic pocket created by phenolic ring with isoluecine amino acids on the A domain of pRb, and a hydrogen bond created by the hydroxyl group on the phenol ring. '''Leu(424)''' and '''Phe(425)''' both form many hydrophobic interactions. <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Glu_419/1'>Glu-419</scene> (in light green) hydrogen bonds to Thr(645) of pRB, and <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Asp_423/1'>Asp-423</scene> (in light purple) forms a salt bridge with Arg(467) on pRB <ref name=Seville>http://hosted2.roswellpark.org/o4s/audio/references/Black5_090706.pdf</ref>. Any point mutations of any of these amino acids will block binding of pRb, leading to deactivation of pRb’s cell inhibiting function, and will allow E2F to promote the cell cycle to move on to the S-phase. | There are 18 residues of the E2F protein that are involved in the pRb/E2F complex '''(left figure)''', residues 409-426. Within this E2F region, there are 5 essential amino acids that if altered, would cause the complex to fall apart. These amino acids are the following: <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Hydrophobic_pocket_tyr_41/2'>Tyr 411</scene> binds to pRB via a hydrophobic pocket created by phenolic ring with isoluecine amino acids on the A domain of pRb, and a hydrogen bond created by the hydroxyl group on the phenol ring. '''Leu(424)''' and '''Phe(425)''' both form many hydrophobic interactions. <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Glu_419/1'>Glu-419</scene> (in light green) hydrogen bonds to Thr(645) of pRB, and <scene name='Retinoblastoma/E2F_complex/Asp_423/1'>Asp-423</scene> (in light purple) forms a salt bridge with Arg(467) on pRB <ref name=Seville>http://hosted2.roswellpark.org/o4s/audio/references/Black5_090706.pdf</ref>. Any point mutations of any of these amino acids will block binding of pRb, leading to deactivation of pRb’s cell inhibiting function, and will allow E2F to promote the cell cycle to move on to the S-phase. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 39: | ||
==Viral oncoproteins== | ==Viral oncoproteins== | ||
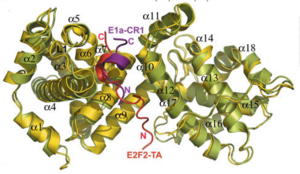
[[Image:E1a.png|thumb|300px|E1A oncoprotein disturbing pRb/E2F complex]] | [[Image:E1a.png|thumb|300px|E1A oncoprotein disturbing pRb/E2F complex]] | ||
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
pRb can interact with viral oncoproteins. These viral oncoproteins contain a strictly conserved LXCXE motif that allows them to bind to the retinoblastoma A and B pocket domain or at any other sites of the pRb protein such as the c-terminal. Binding of a viral protein out competes binding of E2F, therefore causing E2F to detach from pRb.. Examples of these viral genes are E7 oncoprotein of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_papillomavirus Human papillomavirus (HPV)], the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenoviridae adenovirus E1A] which encodes potential oncoproteins that alter cell control, and the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SV40 SV40 antigen] which is a DNA virus that can cause tumors.<ref name=Liu>PMID:17974914</ref>. The figure to the right shows binding of E1A adenovirus to pRb, and displacement of E2F. E1A binds deep within the A and B pocket domains, mainly it binds to alpha-4,5,6,8, and 11 helices of the pocket domain<ref name=Liu>PMID:17974914</ref> Biding of viral oncoproteins disrupts the pRb/E2F complex, allowing E2F to activate the cell cycle. | pRb can interact with viral oncoproteins. These viral oncoproteins contain a strictly conserved LXCXE motif that allows them to bind to the retinoblastoma A and B pocket domain or at any other sites of the pRb protein such as the c-terminal. Binding of a viral protein out competes binding of E2F, therefore causing E2F to detach from pRb.. Examples of these viral genes are E7 oncoprotein of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_papillomavirus Human papillomavirus (HPV)], the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenoviridae adenovirus E1A] which encodes potential oncoproteins that alter cell control, and the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SV40 SV40 antigen] which is a DNA virus that can cause tumors.<ref name=Liu>PMID:17974914</ref>. The figure to the right shows binding of E1A adenovirus to pRb, and displacement of E2F. E1A binds deep within the A and B pocket domains, mainly it binds to alpha-4,5,6,8, and 11 helices of the pocket domain<ref name=Liu>PMID:17974914</ref> Biding of viral oncoproteins disrupts the pRb/E2F complex, allowing E2F to activate the cell cycle. | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 25 August 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of retinoblastoma protein
Updated on 25-August-2019
References
- ↑ http://genesdev.cshlp.org/content/9/23/2873.full.pdf
- ↑ Xiao B, Spencer J, Clements A, Ali-Khan N, Mittnacht S, Broceno C, Burghammer M, Perrakis A, Marmorstein R, Gamblin SJ. Crystal structure of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein bound to E2F and the molecular basis of its regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 4;100(5):2363-8. Epub 2003 Feb 21. PMID:12598654 doi:10.1073/pnas.0436813100
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 http://hosted2.roswellpark.org/o4s/audio/references/Black5_090706.pdf
- ↑ Nevins JR. The Rb/E2F pathway and cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Apr;10(7):699-703. PMID:11257102
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Liu X, Marmorstein R. Structure of the retinoblastoma protein bound to adenovirus E1A reveals the molecular basis for viral oncoprotein inactivation of a tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2711-6. PMID:17974914 doi:21/21/2711
- ↑ http://www.jbmb.or.kr/jbmb/jbmb_files/%5B36-2%5D0303211840_223-229.pdf
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Yvonne Alva, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky