We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Riboswitch
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
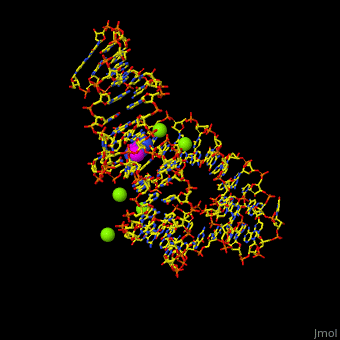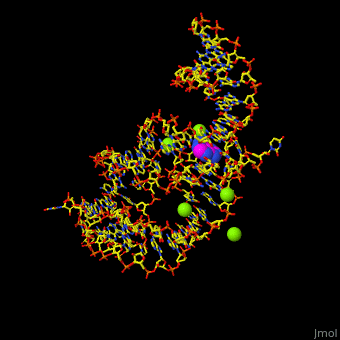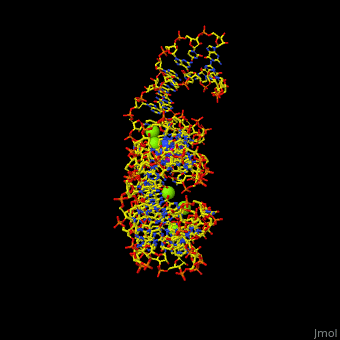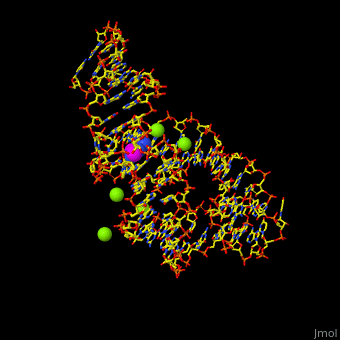
| - | Atomic-resolution structures of riboswitch binding sites show that they make numerous hydrogen bonds with their ligands, forming contacts that stabilize RNA interactions to further increase affinity. Some binding sites form pockets that entirely engulf the ligand, and in these instances an induced-fit mechanism of binding must occur. The <scene name='47/479252/Cv/ | + | Atomic-resolution structures of riboswitch binding sites show that they make numerous hydrogen bonds with their ligands, forming contacts that stabilize RNA interactions to further increase affinity. Some binding sites form pockets that entirely engulf the ligand, and in these instances an induced-fit mechanism of binding must occur. The <scene name='47/479252/Cv/4'>riboswitch-adenine complex shows the stacking interactions of the zippered-up junctional bubble which is formed by the adenine</scene><ref>PMID:15610857</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of riboswitch== | ==3D structures of riboswitch== | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 29 August 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of riboswitch
Updated on 29-August-2019
References
- ↑ Breaker, Ronald R. (28 March, 2008). Complex Riboswitches. Science, 319(5871), 1795-1797. doi:10.1126/science.1152621
- ↑ Serganov A, Yuan YR, Pikovskaya O, Polonskaia A, Malinina L, Phan AT, Hobartner C, Micura R, Breaker RR, Patel DJ. Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs. Chem Biol. 2004 Dec;11(12):1729-41. PMID:15610857 doi:S1074-5521(04)00343-6
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Joel L. Sussman