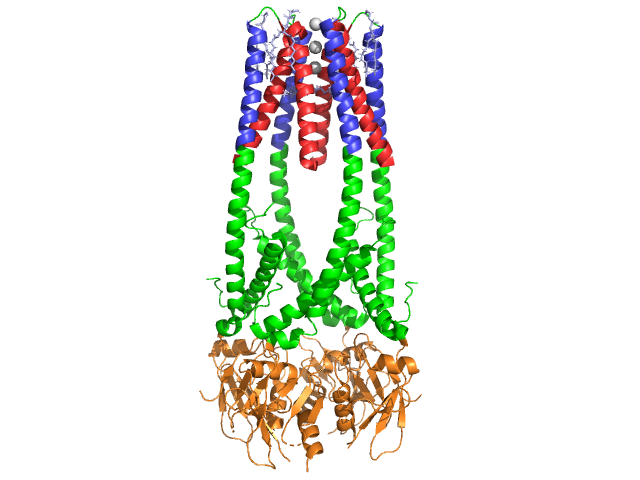
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Lipase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
== '''Clinical Significance''' == | == '''Clinical Significance''' == | ||
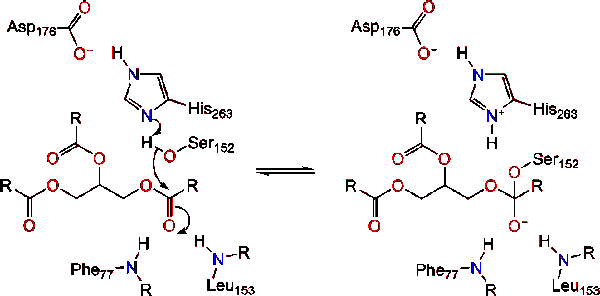
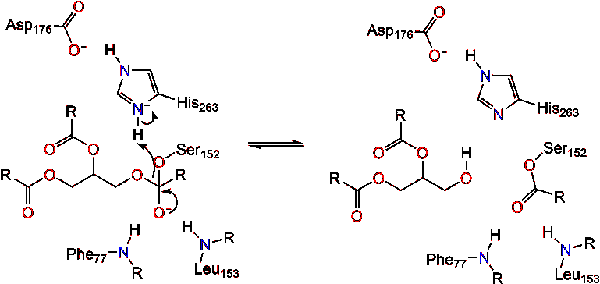
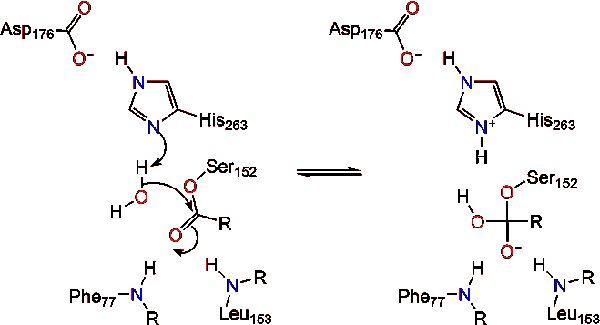
Pancreatic lipase is secreted into the duodenum through the duct system of the pancreas. In a healthy individual, it is at very low concentration in serum. Under extreme disruption of pancreatic function, such as pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer, the pancreas may begin to digest itself and release pancreatic enzymes including pancreatic lipase into serum. Measurement of serum concentration of pancreatic lipase can therefore aid in diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.<ref>"Pancreatic lipase". Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. 7 Nov 2011 [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_lipase]</ref>. Due to lipase's activity in the digestion and absorption of fat, there has been a growing market for lipase inhibitors for weight loss pharmaceuticals. The most popular is Orlistat (or Xenical®) which is a natural product from ''Streptomyces toxytricini'' and is the hydrogenation product of lipostation- an irreversible lipase inhibitor. This inhibitor also acts by binding Ser152, producing an ester which hydrolyzes so slow that it is practically irreversible <ref>Kordik, C., Reitz, A. "Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity: Therapeutic Strategies" Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1999 (42).</ref>. | Pancreatic lipase is secreted into the duodenum through the duct system of the pancreas. In a healthy individual, it is at very low concentration in serum. Under extreme disruption of pancreatic function, such as pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer, the pancreas may begin to digest itself and release pancreatic enzymes including pancreatic lipase into serum. Measurement of serum concentration of pancreatic lipase can therefore aid in diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.<ref>"Pancreatic lipase". Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. 7 Nov 2011 [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_lipase]</ref>. Due to lipase's activity in the digestion and absorption of fat, there has been a growing market for lipase inhibitors for weight loss pharmaceuticals. The most popular is Orlistat (or Xenical®) which is a natural product from ''Streptomyces toxytricini'' and is the hydrogenation product of lipostation- an irreversible lipase inhibitor. This inhibitor also acts by binding Ser152, producing an ester which hydrolyzes so slow that it is practically irreversible <ref>Kordik, C., Reitz, A. "Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity: Therapeutic Strategies" Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1999 (42).</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of Lipase == | ||
| + | [[Lipase 3D Structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 94: | ||
**[[2fx5]] – Lip – ''Pseudomonas mendocina''<br /> | **[[2fx5]] – Lip – ''Pseudomonas mendocina''<br /> | ||
**[[1yzf]] – Lip – ''Enterococcus faecalis''<br /> | **[[1yzf]] – Lip – ''Enterococcus faecalis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1dt3]], [[1dt5]], [[1dte]], [[1du4]], [[1ein]], [[1tib]], [[4dyh]], [[4ea6]], [[4flf]], [[4gbg]], [[4gwl]], [[4zgb]] - TlLip - ''Thermomyces lanuginose''<br /> | + | **[[1dt3]], [[1dt5]], [[1dte]], [[1du4]], [[1ein]], [[1tib]], [[4dyh]], [[4ea6]], [[4flf]], [[4gbg]], [[4gwl]], [[4zgb]], [[6hw1]] - TlLip - ''Thermomyces lanuginose''<br /> |
**[[5ap9]] – TlLip (mutant)<br /> | **[[5ap9]] – TlLip (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[1jfr]] – Lip – ''Streptomyces exfoliates''<br /> | **[[1jfr]] – Lip – ''Streptomyces exfoliates''<br /> | ||
**[[5mal]] – Lip – ''Streptomyces rimosus''<br /> | **[[5mal]] – Lip – ''Streptomyces rimosus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1oil]] – BcLip - ''Burkholderia cepacia''<br /> | ||
**[[2lip]] – BcLip – open state<br /> | **[[2lip]] – BcLip – open state<br /> | ||
**[[1cvl]] – Lip – ''Chromobacterium viscosum''<br /> | **[[1cvl]] – Lip – ''Chromobacterium viscosum''<br /> | ||
**[[1tic]] - Lip – ''Rhizopus oryzae''<br /> | **[[1tic]] - Lip – ''Rhizopus oryzae''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3tgl]], [[4tgl]], [[1tgl]] – RmLip – ''Rhyzomucor miehei''<br /> | + | **[[3tgl]], [[4tgl]], [[1tgl]], [[6qpp]] – RmLip – ''Rhyzomucor miehei''<br /> |
| + | **[[6qpr]] – RmLip (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[2zvd]] – PsLip - ''Pseudomonas sp.'' – open state<br /> | **[[2zvd]] – PsLip - ''Pseudomonas sp.'' – open state<br /> | ||
**[[2z8x]] - PsLip – extracellular<br /> | **[[2z8x]] - PsLip – extracellular<br /> | ||
| Line 110: | Line 113: | ||
**[[5ce5]] – GtLip (mutant)<br /> | **[[5ce5]] – GtLip (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[1ji3]], [[1ku0]], [[4fmp]], [[4x6u]] – BstLip – ''Bacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | **[[1ji3]], [[1ku0]], [[4fmp]], [[4x6u]] – BstLip – ''Bacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4x71]], [[4x7b]], [[4x85]] – BstLip (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[4x71]], [[4x7b]], [[4x85]], [[6s3g]], [[6s3j]], [[6s3v]], [[6fz1]], [[6fz7]], [[6fz8]], [[6fz9]], [[6fza]], [[6fzc]], [[6fzd]] – BstLip (mutant)<br /> |
**[[1ah7]] - Lip – ''Bacillus cereus''<br /> | **[[1ah7]] - Lip – ''Bacillus cereus''<br /> | ||
**[[2ory]] – Lip – ''Photobacterium lypoliticum''<br /> | **[[2ory]] – Lip – ''Photobacterium lypoliticum''<br /> | ||
| Line 129: | Line 132: | ||
**[[3guu]] – CaLipA – ''Candida Antarctica''<br /> | **[[3guu]] – CaLipA – ''Candida Antarctica''<br /> | ||
**[[2veo]] – CaLipA – closed state<br /> | **[[2veo]] – CaLipA – closed state<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qua]], 2qub]] – SmLipA – ''Serratia marcescens''<br /> | + | **[[2qua]], [[2qub]] – SmLipA – ''Serratia marcescens''<br /> |
| - | **[[2qxt]], 2qxu]], 1isp]], 1i6w]], [[5ct4]], [5ct5]], [[5ct6]], [[5cri]] - BsLipA – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> | + | **[[2qxt]], [[2qxu]], [[1isp]], [[1i6w]], [[5ct4]], [[5ct5]], [[5ct6]], [[5cri]] - BsLipA – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> |
| - | **[[3d2a]], 3d2b]], 3d2c]], 1t2n]], 1t4m]], [[5ct8]], [[5ct9]], [[5cta]], [[5cur]], [[3qzu]], [[3qmm]] - BsLipA (mutant) <br /> | + | **[[3d2a]], [[3d2b]], [[3d2c]], [[1t2n]], [[1t4m]], [[5ct8]], [[5ct9]], [[5cta]], [[5cur]], [[3qzu]], [[3qmm]] - BsLipA (mutant) <br /> |
**[[1r4z]] – BsLipA+Rc-IPG-phosphonate<br /> | **[[1r4z]] – BsLipA+Rc-IPG-phosphonate<br /> | ||
**[[1r50]] – BsLipA +Sc-IPG-phosphonate<br /> | **[[1r50]] – BsLipA +Sc-IPG-phosphonate<br /> | ||
| Line 141: | Line 144: | ||
**[[5gv5]] - CaLipB + phosphonate<br /> | **[[5gv5]] - CaLipB + phosphonate<br /> | ||
**[[3icw]] – CaLipB (mutant) + phosphonate<br /> | **[[3icw]] – CaLipB (mutant) + phosphonate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5x7k]] – SmLipB NBD <br /><br /> | + | **[[5x7k]] – SmLipB NBD <br /> |
| + | **[[6isp]], [[6isq]], [[6isr]] – LipB (mutant) – ''Pseudozyma antarctica''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6idy]] - AfLipB - ''Aspergillus fumigatus''<br /> | ||
*Bacterial lipase C | *Bacterial lipase C | ||
| Line 196: | Line 201: | ||
**[[1qz3]] – EaEst2(mutant) (LIPE)+hexadecanesulfonate <br /> | **[[1qz3]] – EaEst2(mutant) (LIPE)+hexadecanesulfonate <br /> | ||
| - | * | + | *Bile-salt activated lipase |
| - | **[[1aql]] – | + | **[[6h0t]] – hBAL (mutant) <br /> |
| + | **[[6h0v]], [[6h18]], [[6h19]], [[6h1a]] – hBAL (mutant) + nerve agent<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1aql]] – bBAL+taurocholate - bovine<br /> | ||
*Monoacylglycerol lipase | *Monoacylglycerol lipase | ||
| - | **[[3rm3]], [[4lhe]], [[5xks]] - BaMAGL – ''Bacillus'' <BR /> | ||
**[[3hju]], [[3jw8]] - hMAGL <BR /> | **[[3hju]], [[3jw8]] - hMAGL <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3jwe]], [[3pe6]], [[4uuq]], [[6ax1]], [[6bq0]] – hMAGL + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4uuq]] - hMAGLip + SAR <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5zun]] – hMAGL (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3rm3]], [[4lhe]], [[5xks]] - BaMAGL – ''Bacillus'' <BR /> | ||
**[[3rli]] – BaMAGL + PMSF<br /> | **[[3rli]] – BaMAGL + PMSF<br /> | ||
**[[4ke7]], [[4ke8]], [[4ke9]] – BaMAGL + ligand<br /> | **[[4ke7]], [[4ke8]], [[4ke9]] – BaMAGL + ligand<br /> | ||
**[[4ke6]], [[4kea]] – BaMAGL (mutant) + ligand<br /> | **[[4ke6]], [[4kea]] – BaMAGL (mutant) + ligand<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3jwe]], [[3pe6]], [[4uuq]], [[6ax1]], [[6bq0]] – hMAGL + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[4zwn]] – yMAGL – yeast<br /> | **[[4zwn]] – yMAGL – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[4zxf]] – yMAGLip + substrate analog<br /> | **[[4zxf]] – yMAGLip + substrate analog<br /> | ||
| Line 238: | Line 247: | ||
**[[4ouk]] - LrE/L (mutant) + inhibitor <br /> | **[[4ouk]] - LrE/L (mutant) + inhibitor <br /> | ||
**[[4bzz]], [[4bzw]] - LpE/L <br /> | **[[4bzz]], [[4bzw]] - LpE/L <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6gup]] - | + | **[[6gup]] - AfE/L <br /> |
**[[1lgy]] – Lip2 – ''Rhizopus niveus''<br /> | **[[1lgy]] – Lip2 – ''Rhizopus niveus''<br /> | ||
**[[1gz7]] - CrLip2 <br /> | **[[1gz7]] - CrLip2 <br /> | ||
Revision as of 09:54, 22 October 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Lipase
Updated on 22-October-2019
References
- ↑ [1] 1HPL PDB SUM
- ↑ [2] A cross-linked complex between horse pancreatic lipase and colipase
- ↑ [3] History of Lipids
- ↑ [4] 1HPL PDB
- ↑ http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1HPL
- ↑ http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=1HPL
- ↑ http://www.springerlink.com/content/g5h1613440115701/fulltext.pdf
- ↑ Fundamentals of Biochemistry...
- ↑ Thomas, A. etc. "Role of the Lid Hydrophobicity Pattern in Pancreatic Lipase Activity", The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2005 September 22; 270 (48): 40074-40083.
- ↑ "Colipase". Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. 5 July 2011 [5]
- ↑ "Colipase Residues..."
- ↑ Fundamentals of Biochemistry...
- ↑ Crandall,W., Lowe, M. "Colipase Residues Glu64 and Arg65 Are Essential for Normal Lipase-mediated Fat Digestion in the Presence of Bile Salt Micelles" Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, (276) 12505-12512
- ↑ van Tilbeurgh H, etc."Structure of the pancreatic lipase-procolipase complex", 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):159-62. PMID:1522902.[6]
- ↑ http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1ETH
- ↑ http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v362/n6423/abs/362814a0.html
- ↑ Sussman JL, Harel M, Frolow F, Oefner C, Goldman A, Toker L, Silman I. Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):872-9. PMID:1678899
- ↑ Ollis DL, Cheah E, Cygler M, Dijkstra B, Frolow F, Franken SM, Harel M, Remington SJ, Silman I, Schrag J, et al.. The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng. 1992 Apr;5(3):197-211. PMID:1409539
- ↑ Bourne Y, Martinez C, Kerfelec B, Lombardo D, Chapus C, Cambillau C. Horse pancreatic lipase. The crystal structure refined at 2.3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 20;238(5):709-32. PMID:8182745 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1331
- ↑ [7] 1LPB PDB SUM
- ↑ "Pancreatic lipase". Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. 7 Nov 2011 [8]
- ↑ Kordik, C., Reitz, A. "Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity: Therapeutic Strategies" Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1999 (42).
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Quinn R. Murray, Natalie Ziegler, Stephanie Schell, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Katelyn Clark, Eric Martz, Leben Tadesse, Joel L. Sussman, Eran Hodis