Lysine-specific histone demethylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
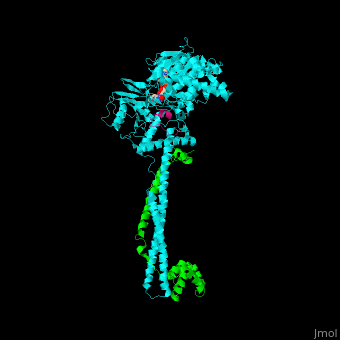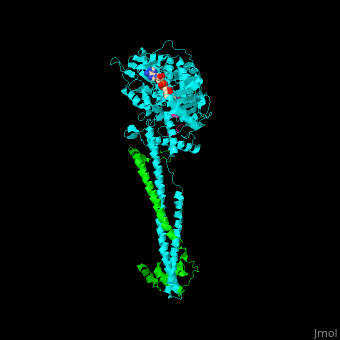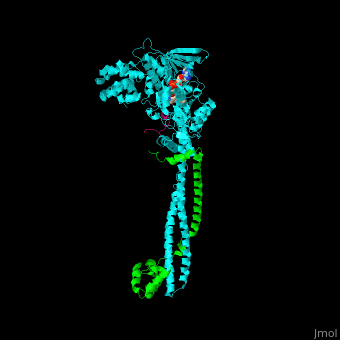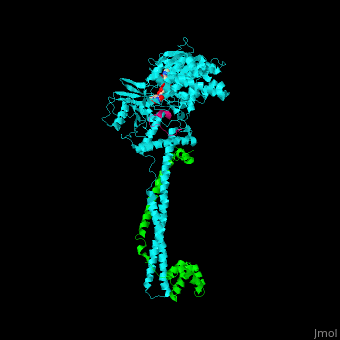
<scene name='48/485631/Cv/5'>Human FAD-containing LSD1 with CoREST and histone H3 helix</scene>. <scene name='48/485631/Cv/6'>LSD1 contains several domains</scene>: a flexible N-terminal domain, a SWIRM domain (an α-helical domain found in chromosomal proteins mediating protein-protein interactions in chromatin), a substrate and FAD-binding domain, a tower domain (a pair of 2 long anti-parallel helices supporting a 3-helix bundle) and a C-terminal domain<ref>PMID:16956976</ref>. <scene name='48/485631/Cv/7'>FAD binding site</scene>. | <scene name='48/485631/Cv/5'>Human FAD-containing LSD1 with CoREST and histone H3 helix</scene>. <scene name='48/485631/Cv/6'>LSD1 contains several domains</scene>: a flexible N-terminal domain, a SWIRM domain (an α-helical domain found in chromosomal proteins mediating protein-protein interactions in chromatin), a substrate and FAD-binding domain, a tower domain (a pair of 2 long anti-parallel helices supporting a 3-helix bundle) and a C-terminal domain<ref>PMID:16956976</ref>. <scene name='48/485631/Cv/7'>FAD binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of lysine-specific histone demethylase== | ||
| + | [[Lysine-specific histone demethylase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of lysine-specific histone demethylase== | ==3D structures of lysine-specific histone demethylase== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 23: | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | *lysine-specific histone demethylase | + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A |
**[[2com]], [[2l3d]] - hLSD1 SWIRM domain – human – NMR<br /> | **[[2com]], [[2l3d]] - hLSD1 SWIRM domain – human – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5it3]] - hLSD1 SWIRM domain<br /> | + | **[[5it3]], [[6e1f]] - hLSD1 SWIRM domain<br /> |
**[[2h94]], [[2dw4]], [[2z3y]], [[2z5u]], [[4fwe]], [[4fwj]], [[4gu1]] – hLSD1<br /> | **[[2h94]], [[2dw4]], [[2z3y]], [[2z5u]], [[4fwe]], [[4fwj]], [[4gu1]] – hLSD1<br /> | ||
**[[2hko]] – hLSD1 (mutant)<br /> | **[[2hko]] – hLSD1 (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[2ejr]], [[3abt]], [[3abu]] – hLSD1 + tranylcypromine derivative<br /> | **[[2ejr]], [[3abt]], [[3abu]] – hLSD1 + tranylcypromine derivative<br /> | ||
**[[4gut]], [[4guu]] – hLSD1 + oxidoreductase<br /> | **[[4gut]], [[4guu]] – hLSD1 + oxidoreductase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nqu]] – hLSD1 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nr5]] – hLSD1 + phenelzine sulfate<br /> | ||
*LSD1 complex with histone H3 peptide | *LSD1 complex with histone H3 peptide | ||
| Line 50: | Line 56: | ||
**[[4uxn]], [[5yjb]] - hLSD1 + CoREST + pyrrolydine inhibitor<br /> | **[[4uxn]], [[5yjb]] - hLSD1 + CoREST + pyrrolydine inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | *lysine-specific histone demethylase | + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 1B |
**[[4gu1]] – hLSD2<br /> | **[[4gu1]] – hLSD2<br /> | ||
| Line 57: | Line 63: | ||
**[[4guu]] – hLSD2 + NPAC + tranylcypromine <br /> | **[[4guu]] – hLSD2 + NPAC + tranylcypromine <br /> | ||
**[[4gu0]] – hLSD2 + histone 3.3 peptide <br /> | **[[4gu0]] – hLSD2 + histone 3.3 peptide <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6r25]], [[6r1u]] – hLSD2 + NPAC + histones 3,4,2A,2B + DNA – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
*lysine-specific histone demethylase 5B or JARID1B or KDM5B. Domains: zinc finger 1 306-360; PHD-type zinc finger 1487-1544; ARID 94-208; JmjC 26-101 + 374-772 | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 5B or JARID1B or KDM5B. Domains: zinc finger 1 306-360; PHD-type zinc finger 1487-1544; ARID 94-208; JmjC 26-101 + 374-772 | ||
| Line 73: | Line 80: | ||
**[[5fy4]] – hLSD5B JmjC domain + succinate<br /> | **[[5fy4]] – hLSD5B JmjC domain + succinate<br /> | ||
**[[5fv3]], [[5a1f]] – hLSD5B JmjC domain + oxalyl glycine<br /> | **[[5fv3]], [[5a1f]] – hLSD5B JmjC domain + oxalyl glycine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6h4z]], [[6h50]], [[6h51]], [[6h52]] – hLSD5B JmjC domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
*lysine-specific histone demethylase 2A or KDM2A | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 2A or KDM2A | ||
| Line 80: | Line 88: | ||
**[[4tn7]], [[4qxh]], [[4qxc]], [[4qxb]], [[4qx8]], [[4qx7]], [[4qwn]] – hKDM2A residues 36-364 + histone peptide <br /> | **[[4tn7]], [[4qxh]], [[4qxc]], [[4qxb]], [[4qx8]], [[4qx7]], [[4qwn]] – hKDM2A residues 36-364 + histone peptide <br /> | ||
| - | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 2B or | + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 2B or KDM2Bsee [[Jumanji domain-containing protein 3D structures]] |
| + | |||
| + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 4A or KDM4A see [[Jumanji domain-containing protein 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 4D see [[Jumanji domain-containing protein 3D structures]] | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6ete]], [[6fuk]], [[6ful]] – hKDM6A + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | *lysine-specific histone demethylase | + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase 6A |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6g8f]], [[6fuk]], [[6ful]] – hKDM6A + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | *lysine-specific histone demethylase Ref6 see [[Jumanji domain-containing protein 3D structures]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 08:22, 24 October 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of lysine-specific histone demethylase
Updated on 24-October-2019
References
- ↑ Chen Y, Jie W, Yan W, Zhou K, Xiao Y. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1 (LSD1): A potential molecular target for tumor therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2012;22(1):53-9. PMID:22339659
- ↑ Kong SY, Kim W, Lee HR, Kim HJ. The histone demethylase KDM5A is required for the repression of astrocytogenesis and regulated by the translational machinery in neural progenitor cells. FASEB J. 2018 Feb;32(2):1108-1119. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700780R. Epub 2018 Jan 3. PMID:29212818 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700780R
- ↑ Pollock JA, Larrea MD, Jasper JS, McDonnell DP, McCafferty DG. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1 inhibitors control breast cancer proliferation in ERalpha-dependent and -independent manners. ACS Chem Biol. 2012 Jul 20;7(7):1221-31. doi: 10.1021/cb300108c. Epub 2012 May, 10. PMID:22533360 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cb300108c
- ↑ van Essen D, Zhu Y, Saccani S. A feed-forward circuit controlling inducible NF-kappaB target gene activation by promoter histone demethylation. Mol Cell. 2010 Sep 10;39(5):750-60. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.010. PMID:20832726 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.010
- ↑ Li X, Liu L, Yang S, Song N, Zhou X, Gao J, Yu N, Shan L, Wang Q, Liang J, Xuan C, Wang Y, Shang Y, Shi L. Histone demethylase KDM5B is a key regulator of genome stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 13;111(19):7096-101. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1324036111. Epub 2014 Apr 28. PMID:24778210 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1324036111
- ↑ Chen Y, Yang Y, Wang F, Wan K, Yamane K, Zhang Y, Lei M. Crystal structure of human histone lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Sep 19;103(38):13956-61. Epub 2006 Sep 6. PMID:16956976
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky