This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
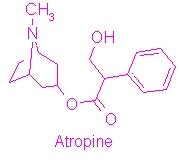
Atropine
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
The proper dose of atropine is approximately 0.1 mg/ml in adults and 0.05 mg/ml in children when taken orally or given intravenously <ref>Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm </ref>. Atropine can be given orally, intravenously, rectally, or topically, and in veterinary medicine, it can be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously. | The proper dose of atropine is approximately 0.1 mg/ml in adults and 0.05 mg/ml in children when taken orally or given intravenously <ref>Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm </ref>. Atropine can be given orally, intravenously, rectally, or topically, and in veterinary medicine, it can be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously. | ||
| - | == '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase | + | == '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase A2''' == |
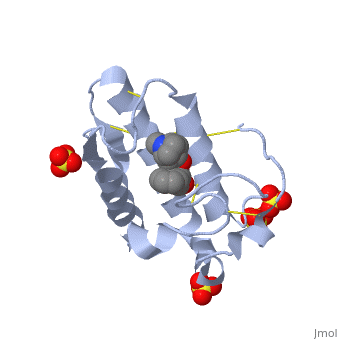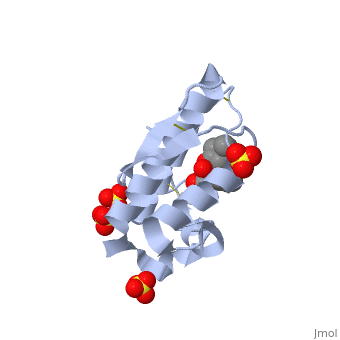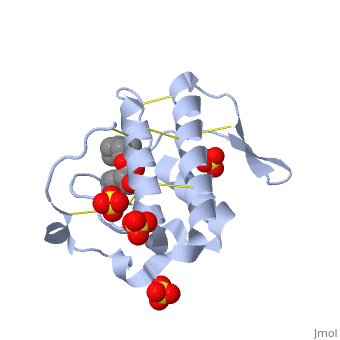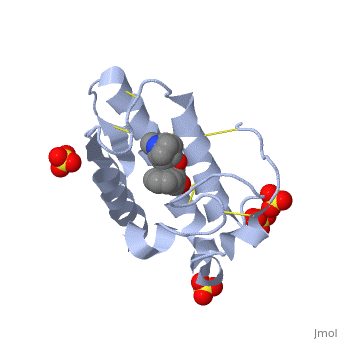
<scene name='42/420811/Cv/1'>Atropine in complex with phospholipase A2</scene> ([[1th6]]). | <scene name='42/420811/Cv/1'>Atropine in complex with phospholipase A2</scene> ([[1th6]]). | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
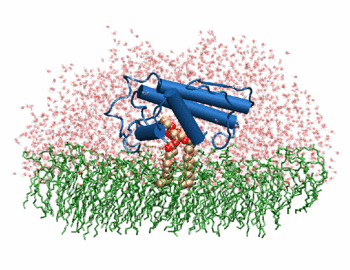
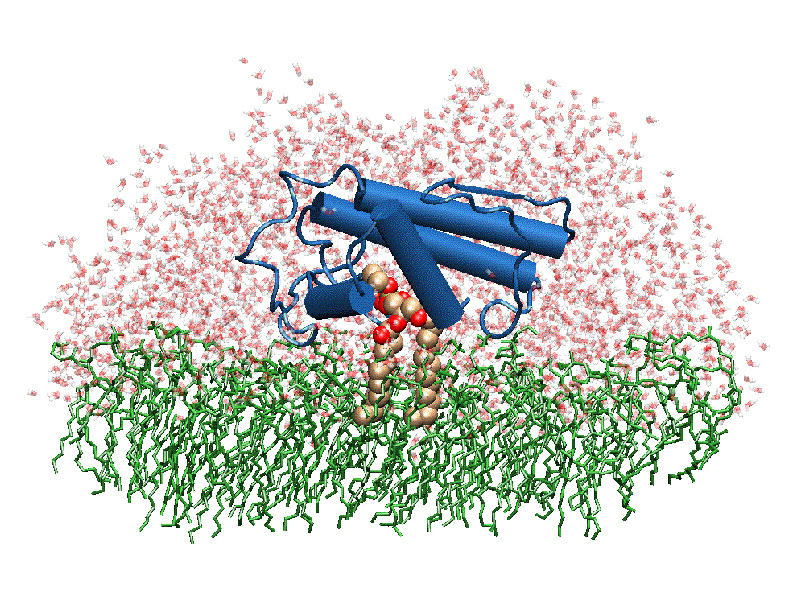
The image to the above shows the membrane-bound phospholipase A2 in blue <ref> pla2. http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/smd_imd/pla2/pla2.gif </ref>. | The image to the above shows the membrane-bound phospholipase A2 in blue <ref> pla2. http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/smd_imd/pla2/pla2.gif </ref>. | ||
| - | ==== '''Atropine in the Active Site of Phospholipase | + | ==== '''Atropine in the Active Site of Phospholipase A2''' ==== |
Atropine is an inhibitor of phospholipase 2A, and can be seen in complex with this enzyme on the left. The <scene name='Sandbox_53/Atropine_structure/1'>structure of atropine</scene> can be seen more clearly in gray using the ball-and stick representation of the drug and protein. It can also be seen in green in this <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_composition/1'>space-filling model</scene>, where protein appears in brown, ligands appear in green, and solvents appear in blue. Finally, the | Atropine is an inhibitor of phospholipase 2A, and can be seen in complex with this enzyme on the left. The <scene name='Sandbox_53/Atropine_structure/1'>structure of atropine</scene> can be seen more clearly in gray using the ball-and stick representation of the drug and protein. It can also be seen in green in this <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_composition/1'>space-filling model</scene>, where protein appears in brown, ligands appear in green, and solvents appear in blue. Finally, the | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Atropine. Encyclopedia Brittanica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/42015/atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Gnagey, Ann L; Seidenberg, Margret; Ellis, John; Site-directed mutagenesis reveals two epitopes involved in the subtype selectivity of the allosteric interactions of gallamine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Molecular Pharmocology, 56:1245-1253, 1999
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Parker, Julie C; Sarkar, Deboshree; Quick, Michael W; Lester, Robin A. Interactions of Atropine with heterologously expressed and native alpha3 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology. 138:5. p801-810. 2009.
- ↑ Image from: http://www.neurevolution.net/category/history/page/2/
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine Diphenoxylate. http://www.everydayhealth.com/drugs/atropine-diphenoxylate
- ↑ Riviere, Jim E. Papich, Mark G. Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 9th Edition. John Wiley and Sons, 2009.
- ↑ ATROPINE- ORAL. http://www.medicinenet.com/atropine-oral/article.htm
- ↑ ATROPINE- ORAL. http://www.medicinenet.com/atropine-oral/article.htm
- ↑ Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm
- ↑ Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb). Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ pla2.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Lindsey Hayes, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, OCA