Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
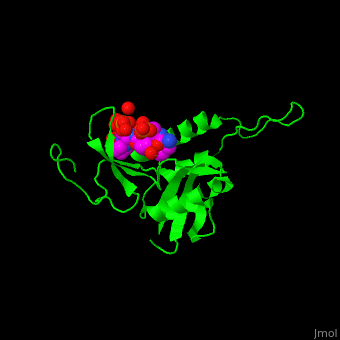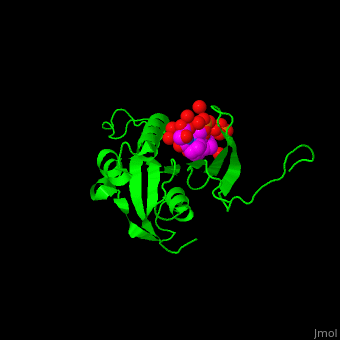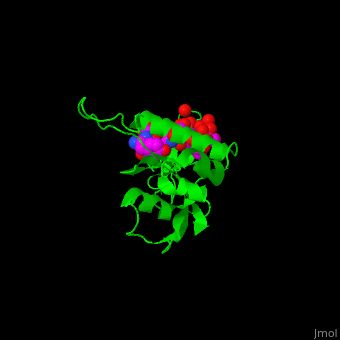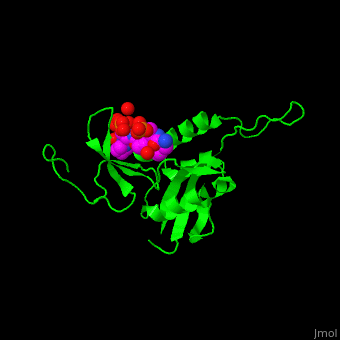
The phosphoserine containing peptide found in the heptad repeat of RNA polymerase II large subunit interacts with the WW domain of PPIase Pin1<ref>PMID:10922246</ref>. <scene name='67/677404/Cv/4'>The phosphoserine containing peptide binding site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | The phosphoserine containing peptide found in the heptad repeat of RNA polymerase II large subunit interacts with the WW domain of PPIase Pin1<ref>PMID:10922246</ref>. <scene name='67/677404/Cv/4'>The phosphoserine containing peptide binding site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase == | ||
| + | [[Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 41: | ||
**[[4s1e]], [[4s1j]] – PPIase (mutant) – ''Leishmania donovani''<BR /> | **[[4s1e]], [[4s1j]] – PPIase (mutant) – ''Leishmania donovani''<BR /> | ||
**[[2m08]] – PPIase – ''Nitrosopumilus maritimus'' - NMR<BR /> | **[[2m08]] – PPIase – ''Nitrosopumilus maritimus'' - NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6h3j]] – FjPPIase + plug + SPRA – ''Flavobacterium johnsoniae'' – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6h3j]] – FjPPIase + porv + SPRA – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
*PPIase Pin1; Domains – WW 1-39; PPIase 51-163 | *PPIase Pin1; Domains – WW 1-39; PPIase 51-163 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 64: | ||
**[[2itk]] – hPin1 (mutant) + D-peptide<BR /> | **[[2itk]] – hPin1 (mutant) + D-peptide<BR /> | ||
**[[2q5a]] – hPin1 (mutant) + L-peptide<BR /> | **[[2q5a]] – hPin1 (mutant) + L-peptide<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3ikd]], [[3ikg]], [[3kac]], [[3jyj]], [[3i6c]], [[3tc5]] – hPin1 PPIase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[4tns]] – hPin1 PPIase domain (mutant) + retinoic acid<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3kab]], [[3kad]], [[3kaf]], [[3kag]], [[3kah]], [[3kai]], [[3kce]], [[3odk]], [[2xp3]], [[2xp4]], [[2xp5]], [[2xp6]], [[2xp7]], [[2xp8]], [[2xp9]], [[2xpa]], [[2xpb]], [[3oob]], [[3ntp]], [[3tcz]], [[3tdb]], [[4qib]], [[4tyo]] – hPin1 (mutant) + inhibitor<BR /> | ||
**[[4u84]], [[4u85]], [[4u86]] – hPin1 + inhibitor<BR /> | **[[4u84]], [[4u85]], [[4u86]] – hPin1 + inhibitor<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3ikd]], [[3ikg]], [[3kac]], [[3jyj]], [[3i6c]], [[3tc5]], [[4tyo]] – hPin1 PPIase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3kab]], [[3kad]], [[3kaf]], [[3kag]], [[3kah]], [[3kai]], [[3kce]], [[3odk]], [[2xp3]], [[2xp4]], [[2xp5]], [[2xp6]], [[2xp7]], [[2xp8]], [[2xp9]], [[2xpa]], [[2xpb]], [[3oob]], [[3ntp]], [[3tcz]], [[3tdb]], [[4qib]] – hPin1 (mutant) + inhibitor<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[4tns]] – hPin1 PPIase domain (mutant) + retinoic acid<BR /> | ||
**[[3wh0]] – hPin1 (mutant) + crown ether<BR /> | **[[3wh0]] – hPin1 (mutant) + crown ether<BR /> | ||
**[[3oob]] – hPin1 (mutant) + dexamethasone phosphate<BR /> | **[[3oob]] – hPin1 (mutant) + dexamethasone phosphate<BR /> | ||
Revision as of 09:47, 14 November 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase
Updated on 14-November-2019
References
- ↑ Guito J, Gavina A, Palmeri D, Lukac DM. The cellular peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase Pin1 regulates reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus from latency. J Virol. 2014 Jan;88(1):547-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02877-13. Epub 2013 Oct 30. PMID:24173213 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02877-13
- ↑ Fischer G, Bang H, Ludwig B, Mann K, Hacker J. Mip protein of Legionella pneumophila exhibits peptidyl-prolyl-cis/trans isomerase (PPlase) activity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1375-83. PMID:1379319
- ↑ Quistgaard EM, Nordlund P, Low C. High-resolution insights into binding of unfolded polypeptides by the PPIase chaperone SlpA. FASEB J. 2012 Jun 26. PMID:22735173 doi:10.1096/fj.12-208397
- ↑ McClements L, Annett S, Yakkundi A, Robson T. The Role of Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerases in Aging and Vascular Diseases. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2015;9(2):165-79. PMID:25986561
- ↑ Westerman ST. Tasting instilled otologic drops is not a reliable test of eustachian tube function. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000 Aug;126(8):1042. PMID:10922246
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky