We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1568
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_BHall_Chem351_F19}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_BHall_Chem351_F19}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | == | + | ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== |
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='6ojt' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> |
This is a default text for your page ''''''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | This is a default text for your page ''''''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
== Function(s) and Biological Relevance == | == Function(s) and Biological Relevance == | ||
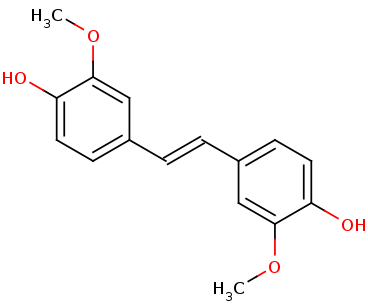
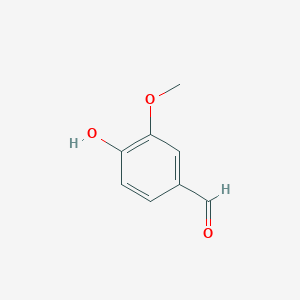
| - | Lignostilbene-α,ß-dioxygenase A (LsdA) from the bacterium ''Sphingomonas paucimobilis'' TMY1009 is a nonheme iron oxygenase that catalyzes the cleavage via oxygenolytic fission of lignostilbene, a compound arising in lignin transformation, to two vanillin molecules (see images below). Lignin is a common component of biomass from industry that scientists are interested in finding ways to break down to simpler and useful materials such as biofuels and commodity chemicals. Though natural occurring lignostilbenoids are rare, they are a very comm on byproduct of industry due to condensation reactions. Other lignin-based stilbenes are thought to be produces from bacterial catabolic processing of diaryl propane and phenylcoumarane | + | Lignostilbene-α,ß-dioxygenase A (LsdA) from the bacterium ''Sphingomonas paucimobilis'' TMY1009 is a nonheme iron oxygenase that catalyzes the cleavage via oxygenolytic fission of lignostilbene, a compound arising in lignin transformation, to two vanillin molecules (see images below). Lignin is a common component of biomass from industry that scientists are interested in finding ways to break down to simpler and useful materials such as biofuels and commodity chemicals. Though natural occurring lignostilbenoids are rare, they are a very comm on byproduct of industry due to condensation reactions. Other lignin-based stilbenes are thought to be produces from bacterial catabolic processing of diaryl propane and phenylcoumarane. |
'''Lignostilbene'''[[Image:lignostilbene.png]]'''Vanillin'''[[Image:Vanillin.png]] | '''Lignostilbene'''[[Image:lignostilbene.png]]'''Vanillin'''[[Image:Vanillin.png]] | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 29 November 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Aug 26 through Dec 12, 2019 for use in the course CHEM 351 Biochemistry taught by Bonnie_Hall at the Grand View University, Des Moines, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1556 through Sandbox Reserved 1575. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644