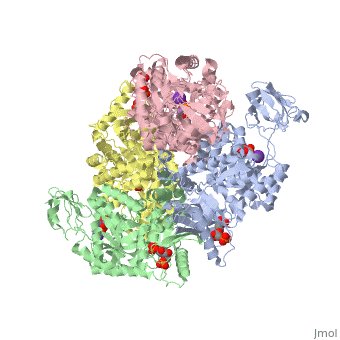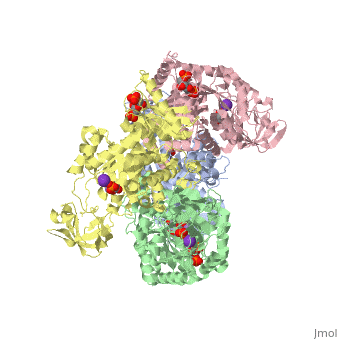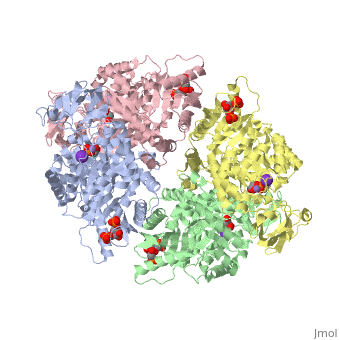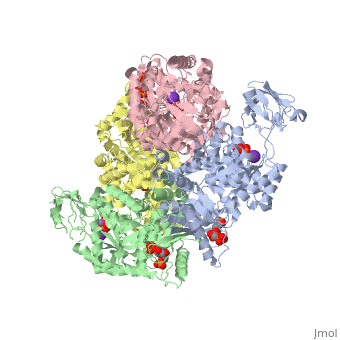
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Pyruvate Kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Red blood cells, in a state of pyruvate kinase deficiency, rapidly become deficient in ATP and can undergo hemolysis.This is transmitted as an autosomal recessive trit. The severity of hemolysis is extremely variable such as a mild case to life-threatening neonatal anaemia requiring transfusions. Over one hundred eighty different mutations have been discovered in relation to this deficiency with most being autosomal recessive, but a few strands are autosomal dominant. The deficiency causes red blood cells to deform into echinocytes on peripheral blood smears. This causes the buildup of reaction intermediates which can also increase the level of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate in the cells. This causes a rightward shift in the hemoglobin oxygen saturation curve, which means that there is a decreased oxygen affinity for the hemoglobin and earlier oxygen unloading than under normal conditions | Red blood cells, in a state of pyruvate kinase deficiency, rapidly become deficient in ATP and can undergo hemolysis.This is transmitted as an autosomal recessive trit. The severity of hemolysis is extremely variable such as a mild case to life-threatening neonatal anaemia requiring transfusions. Over one hundred eighty different mutations have been discovered in relation to this deficiency with most being autosomal recessive, but a few strands are autosomal dominant. The deficiency causes red blood cells to deform into echinocytes on peripheral blood smears. This causes the buildup of reaction intermediates which can also increase the level of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate in the cells. This causes a rightward shift in the hemoglobin oxygen saturation curve, which means that there is a decreased oxygen affinity for the hemoglobin and earlier oxygen unloading than under normal conditions | ||
<ref>PMID:17360088</ref>. | <ref>PMID:17360088</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of pyruvate kinase== | ||
| + | [[Pyruvate kinase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of pyruvate kinase== | ==3D structures of pyruvate kinase== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 53: | ||
*Pyruvate kinase | *Pyruvate kinase | ||
| - | **[[3hqn]], [[3e0w]], [[1pkl]] – LmPyK – ''Leishmania mexicana''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3khd]] – PyK – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3gg8]], [[3eoe]] – PyK – ''Toxoplasma gondii''<br /> | ||
**[[3bjf]], [[3bjt]], [[1t5a]], [[1zjh]], [[3srf]], [[3srh]] - hPyK M1/M2 - human<br /> | **[[3bjf]], [[3bjt]], [[1t5a]], [[1zjh]], [[3srf]], [[3srh]] - hPyK M1/M2 - human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4wj8]], [[4qg6]], [[4qg8]], [[4qg9]], [[4qgc]], [[3g2g]], [[4yj5]] - hPyK M1/M2 (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[4wj8]], [[4qg6]], [[4qg8]], [[4qg9]], [[4qgc]], [[3g2g]], [[4yj5]], [[6b6u]] - hPyK M1/M2 (mutant)<br /> |
**[[2vgb]] – hPyK R/L<br /> | **[[2vgb]] – hPyK R/L<br /> | ||
**[[2vgf]], [[2vgg]], [[2vgi]] - hPyK R/L (mutant) <br /> | **[[2vgf]], [[2vgg]], [[2vgi]] - hPyK R/L (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6nn5]], [[6nn7]], [[6nn8]] – hPyK PKLR (mutant)<br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1pkm]], [[1pyk]] – PyK – cat<br /> |
**[[1f3w]] – rPyK – rabbit<br /> | **[[1f3w]] – rPyK – rabbit<br /> | ||
**[[1f3x]] - rPyK (mutant) <br /> | **[[1f3x]] - rPyK (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[1pky]], [[4yng]] – EcPyK - ''Eschericia coli''<br /> | **[[1pky]], [[4yng]] – EcPyK - ''Eschericia coli''<br /> | ||
**[[1e0t]], [[1e0u]] - EcPyK (mutant) <br /> | **[[1e0t]], [[1e0u]] - EcPyK (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1pkm]], [[1pyk]] – PyK – cat<br /> | ||
**[[3t05]], [[3t0t]] – SaPyK – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | **[[3t05]], [[3t0t]] – SaPyK – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
**[[3qtg]] – PyK – ''Pyrobaculum aerophilum''<br /> | **[[3qtg]] – PyK – ''Pyrobaculum aerophilum''<br /> | ||
**[[4krz]] - TcPyK – ''Trypanosoma cruzei''<br /> | **[[4krz]] - TcPyK – ''Trypanosoma cruzei''<br /> | ||
**[[5wrp]] - MtPyK – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<br /> | **[[5wrp]] - MtPyK – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3hqn]], [[3e0w]], [[1pkl]] – LmPyK – ''Leishmania mexicana''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3khd]] – PyK – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3gg8]], [[3eoe]] – PyK – ''Toxoplasma gondii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3ma8]], [[4drs]] – PyK – ''Cryptosporidium parvum''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2e28]] - PyK (mutant) – ''Geobacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | ||
*Pyruvate kinase binary complex | *Pyruvate kinase binary complex | ||
| - | **[[3qv9]] – TcPyK + Ponceau S <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qv6]] – LmPyK + acid blue 80<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3e0v]] – LmPyK + sulfate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3hqq]] - LmPyK + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qv8]] – LmPyK + benzothiazole<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3pp7]] – LmPyK + suramin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3is4]], [[3ktx]] – LmPyK + pyrenetetrasulfonic acid<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3t07]] – SaPyK + bis-indole alkaloid<br /> | ||
**[[4b2d]] - hPyK M1/M2 + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | **[[4b2d]] - hPyK M1/M2 + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | **[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4fxj]] - hPyK M1/M2 + phenylalanine<br /> | **[[4fxj]] - hPyK M1/M2 + phenylalanine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6gg3]] - hPyK M2 + alanine<br /> | ||
**[[6gg4]] - hPyK M2 + phenylalanine<br /> | **[[6gg4]] - hPyK M2 + phenylalanine<br /> | ||
**[[6gg5]] - hPyK M2 + tryptophan<br /> | **[[6gg5]] - hPyK M2 + tryptophan<br /> | ||
**[[6gg6]] - hPyK M2 + serine<br /> | **[[6gg6]] - hPyK M2 + serine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nub]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + serine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nu1]] - hPyK M2 + cysteine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nu5]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + cysteine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ech]], [[6eck]] - PyK PKLR + fructose bisphosphate - rat<br /> | ||
**[[5x1v]], [[5x1w]] - hPyK M2 + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5x1v]], [[5x1w]] - hPyK M2 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br />**[[3qv9]] – TcPyK + Ponceau S <br /> |
| + | **[[3qv6]] – LmPyK + acid blue 80<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3e0v]] – LmPyK + sulfate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3hqq]] - LmPyK + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3qv8]] – LmPyK + benzothiazole<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3pp7]] – LmPyK + suramin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3is4]], [[3ktx]] – LmPyK + pyrenetetrasulfonic acid<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3t07]] – SaPyK + bis-indole alkaloid<br /> | ||
**[[4hyw]] – TbPyK + fructose bisphosphate – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | **[[4hyw]] – TbPyK + fructose bisphosphate – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | ||
**[[5ws8]] - MtPyK + oxalate<br /> | **[[5ws8]] - MtPyK + oxalate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6p0y]] - CpPyK + ADP<br /> | ||
*Pyruvate kinase higher complex | *Pyruvate kinase higher complex | ||
| - | **[[3hqo]] – LmPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3hqp]] - LmPyK + ATP + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qv7]] – LmPyK + acid blue 25 + Ponceau S<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3srk]] – LmPyK + saccharine + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3n25]] – rPyK M1/M2 + proline + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2g50]] - rPyK M1/M2 + alanine + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1pkn]] - rPyK + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1aqf]] – rPyK + Mg + phospholactate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1a49]], [[1a5u]] - rPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | ||
**[[3me3]] – hPyK M1/M2 + aniline derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | **[[3me3]] – hPyK M1/M2 + aniline derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4g1n]] - hPyK M1/M2 + pyridazine derivative + oxalate<br /> | **[[4g1n]] - hPyK M1/M2 + pyridazine derivative + oxalate<br /> | ||
| Line 110: | Line 111: | ||
**[[4fxf]] - hPyK M1/M2 + oxalate + ATP + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | **[[4fxf]] - hPyK M1/M2 + oxalate + ATP + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4ima]], [[4ip7]] - hPyK L (mutant) + citrate + adenosine + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | **[[4ima]], [[4ip7]] - hPyK L (mutant) + citrate + adenosine + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3n25]] – rPyK M1/M2 + proline + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2g50]] - rPyK M1/M2 + alanine + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1pkn]] - rPyK + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1aqf]] – rPyK + Mg + phospholactate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1a49]], [[1a5u]] - rPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | ||
**[[1a3w]] – yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid + fructose bisphosphate – yeast<br /> | **[[1a3w]] – yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid + fructose bisphosphate – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[1a3x]] - yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid<br /> | **[[1a3x]] - yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid<br /> | ||
| Line 121: | Line 127: | ||
**[[5wsa]] – MtPyK + oxalate + glucose-6-phosphate <br /> | **[[5wsa]] – MtPyK + oxalate + glucose-6-phosphate <br /> | ||
**[[5wsb]], [[5wsc]] – MtPyK + oxalate + glucose-6-phosphate + AMP<br /> | **[[5wsb]], [[5wsc]] – MtPyK + oxalate + glucose-6-phosphate + AMP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ito]] – MtPyK + oxalate + ribose-5-phosphate + AMP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3hqo]] – LmPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3hqp]] - LmPyK + ATP + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3qv7]] – LmPyK + acid blue 25 + Ponceau S<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3srk]] – LmPyK + saccharine + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6qxl]] – PyK + malonate + glucose-6-phosphate + Mg – ''Pseudomonas aerugnosa''<br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 08:19, 8 December 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of pyruvate kinase
Updated on 08-December-2019
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008, 501-503.
- ↑ authors, The scop. "Structural Classification of Proteins". 2009. 2/26 2010. <http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html>.
- ↑ authors, The scop. "Structural Classification of Proteins". 2009. 2/26 2010. <http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html>.
- ↑ Robergs, Robert. "Exercise-Induced Metabolic Acidosis: Where do the Protons come from?". 2009. 2/27 2010. <http://www.sportsci.org/jour/0102/rar.htm>.
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008, 501-503.
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008, 501-503.
- ↑ Dann LG, Britton HG. Kinetics and mechanism of action of muscle pyruvate kinase. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):39-54. PMID:629752
- ↑ Mattevi A, Bolognesi M, Valentini G. The allosteric regulation of pyruvate kinase. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jun 24;389(1):15-9. PMID:8682196
- ↑ Jurica MS, Mesecar A, Heath PJ, Shi W, Nowak T, Stoddard BL. The allosteric regulation of pyruvate kinase by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Structure. 1998 Feb 15;6(2):195-210. PMID:9519410
- ↑ Oria-Hernandez J, Cabrera N, Perez-Montfort R, Ramirez-Silva L. Pyruvate kinase revisited: the activating effect of K+. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 11;280(45):37924-9. Epub 2005 Sep 7. PMID:16147999 doi:10.1074/jbc.M508490200
- ↑ Dann LG, Britton HG. Kinetics and mechanism of action of muscle pyruvate kinase. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):39-54. PMID:629752
- ↑ Oria-Hernandez J, Cabrera N, Perez-Montfort R, Ramirez-Silva L. Pyruvate kinase revisited: the activating effect of K+. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 11;280(45):37924-9. Epub 2005 Sep 7. PMID:16147999 doi:10.1074/jbc.M508490200
- ↑ Zanella A, Fermo E, Bianchi P, Chiarelli LR, Valentini G. Pyruvate kinase deficiency: the genotype-phenotype association. Blood Rev. 2007 Jul;21(4):217-31. Epub 2007 Mar 13. PMID:17360088 doi:10.1016/j.blre.2007.01.001
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Keegan Gelvoria, David Canner, Ann Taylor, Andrew Alexander