Rac
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
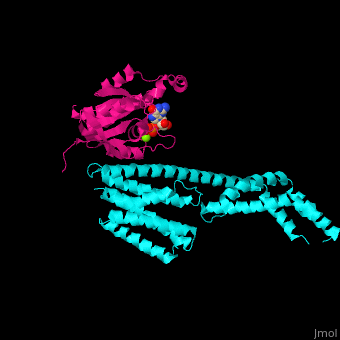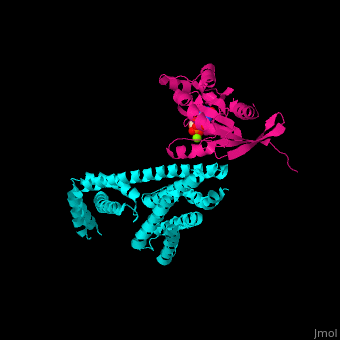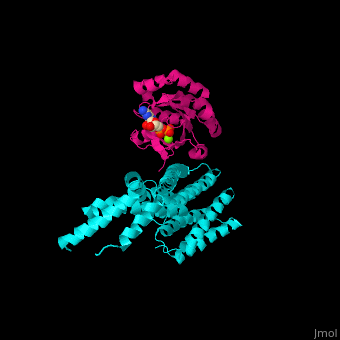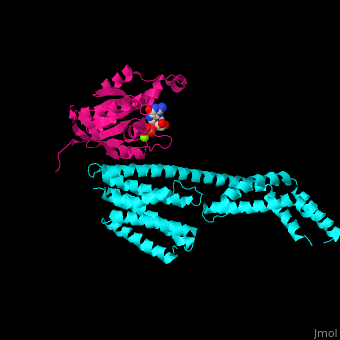
The interactions between Rac1 and YpkA are via <scene name='75/752232/Cv/8'>switch I and switch II of Rac1 and a helical portion of the protein kinase YpkA</scene><ref>PMID:16959567</ref>. <scene name='75/752232/Cv/9'>GDP binding site on Rac1</scene>. | The interactions between Rac1 and YpkA are via <scene name='75/752232/Cv/8'>switch I and switch II of Rac1 and a helical portion of the protein kinase YpkA</scene><ref>PMID:16959567</ref>. <scene name='75/752232/Cv/9'>GDP binding site on Rac1</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of Rac== | ||
| + | [[Rac 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 22: | ||
**[[3th5]], [[1ryh]], [[1mh1]] – hRac1 + GNP – human<br /> | **[[3th5]], [[1ryh]], [[1mh1]] – hRac1 + GNP – human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2p2l]], [[1ryf]] – hRac1 + GDP <br /> | + | **[[2p2l]], [[1ryf]], [[5n6o]] – hRac1 + GDP <br /> |
| + | **[[6agp]] – hRac1 (mutant) + GDP <br /> | ||
**[[4gzl]], [[3sbd]], [[3sbe]] – hRac1 (mutant) + GNP <br /> | **[[4gzl]], [[3sbd]], [[3sbe]] – hRac1 (mutant) + GNP <br /> | ||
**[[4gzm]] – hRac1 (mutant) + GSP <br /> | **[[4gzm]] – hRac1 (mutant) + GSP <br /> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 48: | ||
**[[2h7v]] – hRac1 (mutant) + YpkA + GDP <br /> | **[[2h7v]] – hRac1 (mutant) + YpkA + GDP <br /> | ||
**[[1hh4]], [[1ds6]] – hRac1 + RhoGD1 + GDP <br /> | **[[1hh4]], [[1ds6]] – hRac1 + RhoGD1 + GDP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6bc1]] – hRac1 + RhoGEF + GTP analog<br /> | ||
**[[1i4d]], [[1i4l]] – hRac1 + arfaptin + GDP <br /> | **[[1i4d]], [[1i4l]] – hRac1 + arfaptin + GDP <br /> | ||
**[[1i4t]] – hRac1 + arfaptin + GNP <br /> | **[[1i4t]] – hRac1 + arfaptin + GNP <br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:51, 8 December 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Rac
Updated on 08-December-2019
References
- ↑ Asahara S, Shibutani Y, Teruyama K, Inoue HY, Kawada Y, Etoh H, Matsuda T, Kimura-Koyanagi M, Hashimoto N, Sakahara M, Fujimoto W, Takahashi H, Ueda S, Hosooka T, Satoh T, Inoue H, Matsumoto M, Aiba A, Kasuga M, Kido Y. Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1) regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion via modulation of F-actin. Diabetologia. 2013 May;56(5):1088-97. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2849-5. Epub 2013, Feb 15. PMID:23412604 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2849-5
- ↑ Prehna G, Ivanov MI, Bliska JB, Stebbins CE. Yersinia virulence depends on mimicry of host Rho-family nucleotide dissociation inhibitors. Cell. 2006 Sep 8;126(5):869-80. PMID:16959567 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.056