We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
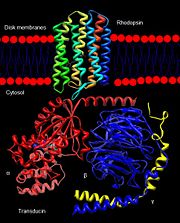
Rhodopsin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
__NOEDITSECTION__ | __NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of rhodopsin== | ||
| + | [[Rhodopsin 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of rhodopsin== | ==3D structures of rhodopsin== | ||
| Line 81: | Line 85: | ||
*Rhodopsin (Rn) | *Rhodopsin (Rn) | ||
| - | **[[3aym]], [[3ayn]], [[2z73]], [[2ziy]], [[4ww3]] – Rn + retinal – Flying squid<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3am6]] – AaRn-2 + cholesterol + retinal – ''Acetabularia acetabulum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5awz]], [[5ax0]], [[5ax1]] – AaRn-1 + retinal<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4tl3]] – AaRn-1 (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[5te5]], [[5te3]] – bRn - bovine<br /> | **[[5te5]], [[5te3]] – bRn - bovine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ofj]] – bRn – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1vqx]], [[1nzs]] – bRn C terminal – NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1edx]] - bRn N terminal – NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1eds]], [[1edv]], [[1edw]] – bRn intradiskal loop – NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1fdf]] – bRn helix 7 - NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[2x72]] – bRn + retinal + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide <br /> | **[[2x72]] – bRn + retinal + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide <br /> | ||
**[[3qc9]] – bRn + Mg + ADP<br /> | **[[3qc9]] – bRn + Mg + ADP<br /> | ||
| Line 97: | Line 102: | ||
**[[4bey]] - bRn (mutant) + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide <br /> | **[[4bey]] - bRn (mutant) + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide <br /> | ||
**[[5en0]] - bRN (mutant) + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide + retinal<br /> | **[[5en0]] - bRN (mutant) + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide + retinal<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1vqx]], [[1nzs]] – bRn C terminal – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1edx]] - bRn N terminal – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1eds]], [[1edv]], [[1edw]] – bRn intradiskal loop – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1fdf]] – bRn helix 7 - NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[4pxf]] – bRn + arrestin peptide<br /> | **[[4pxf]] – bRn + arrestin peptide<br /> | ||
**[[5wkt]] – bRn + transducin peptide<br /> | **[[5wkt]] – bRn + transducin peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6fuf]] – bRn + G0 + retinal <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6oy9]] – bRn (mutant) + transducin + GI + retinal – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6qno]], [[6oya]] – bRn (mutant) + transducin + antibody + GI + retinal – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3aym]], [[3ayn]], [[2z73]], [[2ziy]], [[4ww3]] – Rn + retinal – Flying squid<br /> | ||
**[[1xio]] – AnRn - ''Anabaena''<br /> | **[[1xio]] – AnRn - ''Anabaena''<br /> | ||
**[[2m3g]] – AnRn – NMR<br /> | **[[2m3g]] – AnRn – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[4tl3]] - AnRn (mutant) + retinal<br /> | **[[4tl3]] - AnRn (mutant) + retinal<br /> | ||
**[[4hyj]] - Rn + retinal + lipid – ''Exiguobacterium Sibiricum''<br /> | **[[4hyj]] - Rn + retinal + lipid – ''Exiguobacterium Sibiricum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[3am6]] – AaRn-2 + cholesterol + retinal – ''Acetabularia acetabulum''<br /> |
| + | **[[5awz]], [[5ax0]], [[5ax1]] – AaRn-1 + retinal<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4tl3]] – AaRn-1 (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6sqg]] - Rn + retinal + lipid – lake phycodnavirus<br /> | ||
*Sensory rhodopsin II | *Sensory rhodopsin II | ||
| Line 120: | Line 128: | ||
**[[4xtl]], [[4xtn]], [[4xto]], [[3x3b]], [[3x3c]], [[5jrf]] – DeRn – ''Dokdonia eikastra''<br /> | **[[4xtl]], [[4xtn]], [[4xto]], [[3x3b]], [[3x3c]], [[5jrf]] – DeRn – ''Dokdonia eikastra''<br /> | ||
**[[5jrf]] – DeRn + detergent + I<br /> | **[[5jrf]] – DeRn + detergent + I<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6rew]], [[6rex]], [[6rez]], [[6rf0]], [[6rf1]], [[6rf4]], [[6rf5]], [[6rf6]], [[6rf7]] – DeRn + detergent + Na + retinal<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6rf3]], [[6rf9]], [[6rfa]], [[6rfb]], [[6rfc]] – DeRn (mutant) + detergent + Na + retinal<br /> | ||
*Chloride pump rhodopsin | *Chloride pump rhodopsin | ||
| - | **[[5g28]], [[5g2a]], [[5b2n]], [[5fjg]], [[5g54]] – NmRn + retinal – ''Nonlabens marinus''<br /> | + | **[[5g28]], [[5g2a]], [[5b2n]], [[5fjg]], [[5g54]], [[5ztk]], [[5ztl]], [[6ab9]], [[6aba]] – NmRn + retinal – ''Nonlabens marinus''<br /> |
**[[5g2c]], [[5g2d]] - NmRn (mutant) + retinal<br /> | **[[5g2c]], [[5g2d]] - NmRn (mutant) + retinal<br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:12, 16 December 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of rhodopsin
Updated on 16-December-2019
References
- ↑ Hornak V, Ahuja S, Eilers M, Goncalves JA, Sheves M, Reeves PJ, Smith SO. Light activation of rhodopsin: insights from molecular dynamics simulations guided by solid-state NMR distance restraints. J Mol Biol. 2010 Feb 26;396(3):510-27. Epub 2009 Dec 11. PMID:20004206 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.003
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Sakmar TP. Structure of rhodopsin and the superfamily of seven-helical receptors: the same and not the same. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;14(2):189-95. PMID:11891118
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Kristiansen K. Molecular mechanisms of ligand binding, signaling, and regulation within the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors: molecular modeling and mutagenesis approaches to receptor structure and function. Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jul;103(1):21-80. PMID:15251227 doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.05.002
- ↑ Millar RP, Newton CL. The year in G protein-coupled receptor research. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):261-74. Epub 2009 Dec 17. PMID:20019124 doi:10.1210/me.2009-0473
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Meng EC, Bourne HR. Receptor activation: what does the rhodopsin structure tell us? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):587-93. PMID:11698103
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Shieh T, Han M, Sakmar TP, Smith SO. The steric trigger in rhodopsin activation. J Mol Biol. 1997 Jun 13;269(3):373-84. PMID:9199406 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1035
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 Okada T, Ernst OP, Palczewski K, Hofmann KP. Activation of rhodopsin: new insights from structural and biochemical studies. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001 May;26(5):318-24. PMID:11343925
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Okada T, Sugihara M, Bondar AN, Elstner M, Entel P, Buss V. The retinal conformation and its environment in rhodopsin in light of a new 2.2 A crystal structure. J Mol Biol. 2004 Sep 10;342(2):571-83. PMID:15327956 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.044
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Janz JM, Farrens DL. Assessing structural elements that influence Schiff base stability: mutants E113Q and D190N destabilize rhodopsin through different mechanisms. Vision Res. 2003 Dec;43(28):2991-3002. PMID:14611935
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kisselev OG. Focus on molecules: rhodopsin. Exp Eye Res. 2005 Oct;81(4):366-7. PMID:16051215 doi:10.1016/j.exer.2005.06.018
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Verhoeven MA, Bovee-Geurts PH, de Groot HJ, Lugtenburg J, DeGrip WJ. Methyl substituents at the 11 or 12 position of retinal profoundly and differentially affect photochemistry and signalling activity of rhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 2006 Oct 13;363(1):98-113. Epub 2006 Jul 28. PMID:16962138 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.039
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Morris MB, Dastmalchi S, Church WB. Rhodopsin: structure, signal transduction and oligomerisation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):721-4. Epub 2008 Aug 3. PMID:18692154 doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2008.04.025
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 Nelson, D., and Cox, M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. 2008. 5th edition. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York, New York, USA. pp. 462-465.
- ↑ Hurley JB, Spencer M, Niemi GA. Rhodopsin phosphorylation and its role in photoreceptor function. Vision Res. 1998 May;38(10):1341-52. PMID:9667002
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Park JH, Scheerer P, Hofmann KP, Choe HW, Ernst OP. Crystal structure of the ligand-free G-protein-coupled receptor opsin. Nature. 2008 Jul 10;454(7201):183-7. Epub 2008 Jun 18. PMID:18563085 doi:10.1038/nature07063
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Surya A, Knox BE. Enhancement of opsin activity by all-trans-retinal. Exp Eye Res. 1998 May;66(5):599-603. PMID:9628807 doi:10.1006/exer.1997.0453
See Also
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Wayne Decatur, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman, Cinting Lim