We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Léa Wick/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Complex with dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid == | == Complex with dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: TTR-DDRF1.png | thumb | left | alt=Puzzle globe| TTR in complexe with Dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (DDBF)| 200 px]] | ||
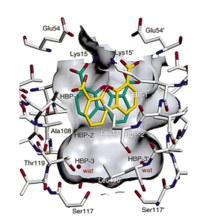
The TTR complexed with dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid has been produced from ''homo sapiens gene'' in ''Escherichia coli'' and it structure determined by X-Ray diffraction ([https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1dvu/1dvu]). | The TTR complexed with dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid has been produced from ''homo sapiens gene'' in ''Escherichia coli'' and it structure determined by X-Ray diffraction ([https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1dvu/1dvu]). | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
DDBF is bounded according two symmetric equivalent modes [2]. Indeed, DDBF wears a tricyclic ring system, with 2 hydrogen bond donors and 5 hydrogen bond acceptors, allowing to bound the dimer-dimer interface of the TTR cavity. [Pubchem,1]. Thanks to the complementarity of shape and hydrophobicity, DDBF enters nicely the outer portion of HBPs pockets [2]. Besides, the tricyclic ring system interacts with Lys15, Val17 and Ala108 from two adjacent TTR subunits [2]. Additionally, carboxylates at the position 4 and 6 of DDBF make electrostatic interactions at the entrance of HBP1 and HBP1’ with Lys15 on the ε-NH3+ groups[2]. | DDBF is bounded according two symmetric equivalent modes [2]. Indeed, DDBF wears a tricyclic ring system, with 2 hydrogen bond donors and 5 hydrogen bond acceptors, allowing to bound the dimer-dimer interface of the TTR cavity. [Pubchem,1]. Thanks to the complementarity of shape and hydrophobicity, DDBF enters nicely the outer portion of HBPs pockets [2]. Besides, the tricyclic ring system interacts with Lys15, Val17 and Ala108 from two adjacent TTR subunits [2]. Additionally, carboxylates at the position 4 and 6 of DDBF make electrostatic interactions at the entrance of HBP1 and HBP1’ with Lys15 on the ε-NH3+ groups[2]. | ||
| - | [[Image: EXAMPLE.png | thumb | left | alt=Puzzle globe| TTR in complexe with Dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (DDBF)| 300 px]] | ||
| - | 1 TTR in complexe with Dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (DDBF) | ||
TTR in complex with dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid keeps the general apo-structure, with water molecules bind to HBP3 and HBP3’ cavities of TTR [1]. There is not conformational change of Ser117 and Thr119 of TTR, contrary to other inhibitor, such as FLU. | TTR in complex with dibenzofuran-4,6-dicarboxylic acid keeps the general apo-structure, with water molecules bind to HBP3 and HBP3’ cavities of TTR [1]. There is not conformational change of Ser117 and Thr119 of TTR, contrary to other inhibitor, such as FLU. | ||
Consequently, DDBF creates a bridge between two adjacent subunits stabilized by ionic and hydrophobic interactions. | Consequently, DDBF creates a bridge between two adjacent subunits stabilized by ionic and hydrophobic interactions. | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 6 January 2020
| |||||||||||