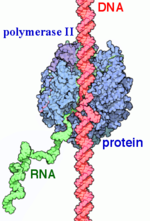
RNA Polymerase II
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1i6h' size='340' side='right' caption='RNA Polymerase II''> | + | <StructureSection load='1i6h' size='340' side='right' caption='Yeast RNA Polymerase II complex with RNA (PDB code [[1i6h]])''> |
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[ Image:Label RNA pol II (1).png|150px|right|thumb| RNAP II transcription process.]] | [[ Image:Label RNA pol II (1).png|150px|right|thumb| RNAP II transcription process.]] | ||
| - | RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) is an enzyme that transcribes protein-encoding genes, and it therefore is responsible for the synthesis of mRNA. There are three RNA polymerase enzymes found in eukaryotic nuclei but RNAP II is the most studied. RNAP II is a 550 kDa multi-protein complex that includes 12 subunits. Several transcription factors are used to bind promoters upstream of the start site and are necessary for joining RNAP II and DNA. Bound RNAP II transcribes DNA into a strand of messenger RNA. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to the template strand of DNA. The mRNA stand transports genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is used to specify the amino acid sequence for the production of proteins. | + | '''RNA polymerase II''' (RNAP II) is an enzyme that transcribes protein-encoding genes, and it therefore is responsible for the synthesis of mRNA. There are three RNA polymerase enzymes found in eukaryotic nuclei but RNAP II is the most studied. RNAP II is a 550 kDa multi-protein complex that includes 12 subunits. Several transcription factors are used to bind promoters upstream of the start site and are necessary for joining RNAP II and DNA. Bound RNAP II transcribes DNA into a strand of messenger RNA. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to the template strand of DNA. The mRNA stand transports genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is used to specify the amino acid sequence for the production of proteins. |
== Structural Components == | == Structural Components == | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 16 January 2020
| |||||||||||
References
Bushnell, D. A.; Westover, K. D.; Davis, R. E.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II-TFIIB Cocrystal at 4.5 Angstroms. Science. 2004, 303, 983-988
Cramer, P.; Bushnell, D. A.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: RNA Polymerase II at 2.8 Ångstrom Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1863-1876
Evans, D. A.; Fitch, D. M.; Smith, T. E.; Cee, V. J. Application of Complex Aldol Reactions to the Total Synthesis of Phorboxazole B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10033-10046.
Gnatt, A. L.; Cramer, P; Fu, J.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complex at 3.3 Å Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1876-1882 1i6h
He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.
Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683
Uzman, A.; Voet, D. Student companion Fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level, 4th ed., Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt; John Wiley & amp; Sons, 2012.
Xu, J.; Lahiri, I.; Wang, W.; Wier, A.; Cianfrocco, M. A.; Chong, J.; Hare, A. A.; Dervan, P. B.; DiMaio, F.; Leschziner, A. E.; Wang, D. Structural Basis for the Initiation of Eukaryotic Transcription-coupled DNA Repair. Nature. 2017. 551, 653-657 5vvr
Yan, C., Dodd, T., He, Y., Tainer, J. A., Tsutakawa, S. E., & Ivanov, I. (2019). Transcription preinitiation complex structure and dynamics provide insight into genetic diseases. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 26(6), 397-406.
Alpha-aminitin chemical structure image courtesy of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-Amanitin#/media/File:Alpha-amanitin_structure.png
Notes
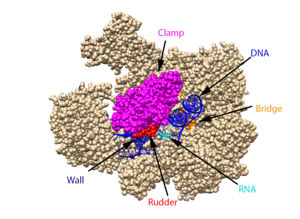
From structural components:
Structural overview: [PDB: 5VVR: with highlighted sections mentioned below]
Bridge: Depicted: [PDB: 1I6H: 810-845.a]
Wall: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 853-919.b; 933-972.b]
Clamp: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 3-345.a; 1395-1435.a; 1158-1124.b]
Rudder: Depicted: [PDB: 5VVR: 306-321.a]
Content Donators
This page was created as a final project for the Advanced Biochemistry course at Wabash College during the Fall of 2019. This page was reviewed by Dr. Wally Novak of Wabash College.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Titus Edwards, Abraham Kiesel, Wally Novak, James Daniel Andry, Michal Harel, Karsten Theis