We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Ona Ambrozaite/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
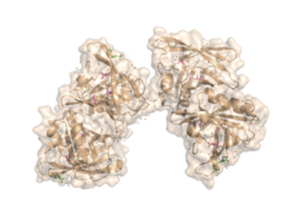
The fully functional trichosurin consists of two monomers joining to form a dimer of identical eight-stranded, anti-parallel β-barrels. The study of lipocalin dimerization modes has shown six variations in orientation, with trichosurin adding a seventh one to the list. Overall, there are four main chains (A, B, C, and D), in the dimer, with each chain a length of 166 amino acids. There is also a signal sequence at the N-terminus of the chain that is cleaved before a fully functional molecule is formed. Currently, there are two crystal structures of trichosurin that can be found at RCSB, one determined at pH 8.2 and another at a lower pH of 4.6. | The fully functional trichosurin consists of two monomers joining to form a dimer of identical eight-stranded, anti-parallel β-barrels. The study of lipocalin dimerization modes has shown six variations in orientation, with trichosurin adding a seventh one to the list. Overall, there are four main chains (A, B, C, and D), in the dimer, with each chain a length of 166 amino acids. There is also a signal sequence at the N-terminus of the chain that is cleaved before a fully functional molecule is formed. Currently, there are two crystal structures of trichosurin that can be found at RCSB, one determined at pH 8.2 and another at a lower pH of 4.6. | ||
| - | With regards to the binding cavity, there are the three asparagine residues, Asn49, Asn97 and Asn127, which lie in the pocket and offer hydrogen-bonding sites for a potential ligand, especially Asn49. | + | With regards to the binding cavity, there are the three asparagine residues, Asn49, Asn97 and Asn127, which lie in the pocket and offer hydrogen-bonding sites for a potential ligand, especially Asn49. The shape and charge distribution within the pocket suggest that small hydrophobic molecules can be accommodated within, with such sites providing the necessary hydrogen bonding opportunities. |
The SCOP website classifies trichosurin as a fatty acid retinoid binding protein, just like the nematode fatty acid retinoid binding protein from ''Necator americanus'' species. Trichosurin belongs to the calycin beta-barrel core domain superfamily, as indicated by the search results on the CATH website, which emphasizes the presence of the β-barrels throughout the structure. | The SCOP website classifies trichosurin as a fatty acid retinoid binding protein, just like the nematode fatty acid retinoid binding protein from ''Necator americanus'' species. Trichosurin belongs to the calycin beta-barrel core domain superfamily, as indicated by the search results on the CATH website, which emphasizes the presence of the β-barrels throughout the structure. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<Structure load='2RA6' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal Structure of the Possum Milk Whey Lipocalin Trichosurin at pH 4.6 with Bound 4-ethylphenol' scene='Hydrogen Bond Interactions with Ligands' /> | <Structure load='2RA6' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal Structure of the Possum Milk Whey Lipocalin Trichosurin at pH 4.6 with Bound 4-ethylphenol' scene='Hydrogen Bond Interactions with Ligands' /> | ||
| - | The binding site is found in the centre of the β-barrel and can be occupied by water and isopropanol molecules from the corresponding crystallization medium. | + | As expected for an extracellular protein, trichosurin displays a large amount of hydrophilic surface area, with the more hydrophobic areas between the helix, the outside of the barrel, and the dimer interface where ligands such as 2-naphthol can bind. The binding site is found in the centre of the β-barrel and can be occupied by water and isopropanol molecules from the corresponding crystallization medium. In fact, researchers were able to crystallize trichosurin with 2-naphthol and 4-ethylphenol, the presence of which provides clues to the function of trichosurin. |
| - | Overall, trichosurin follows the general lipocalin superfamily fold pattern by having a β-barrel, several extended loop regions between β strands that close the ends of the barrel, a helix near the C-terminus which is common to all lipocalins, and a major conserved feature of the lipocalin fold, a disulfide bond, formed by two cysteines (Cys73 and Cys166 ) in each chain that ties the C-terminus to the corresponding β-strand. | ||
| - | + | Overall, trichosurin follows the general lipocalin superfamily fold pattern by having a β-barrel, several extended loop regions between β strands that close the ends of the barrel, a helix near the C-terminus which is common to all lipocalins, and a major conserved feature of the lipocalin fold, a disulfide bond, formed by two cysteines (Cys73 and Cys166 ) in each chain that ties the C-terminus to the corresponding β-strand. | |
| - | + | The binding preference for small phenolic compounds such as 2-naphthol and 4-ethylphenol with high Kd values signifies that very similar compounds can have higher affinities and act as natural ligands for trichosurin as well. | |
== Evolutionarily Related Proteins == | == Evolutionarily Related Proteins == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
Trichosurin, an important marsupial milk protein, is highly conserved across metatherians. The opossum, a metatherian, shares a common ancestor with humans around 130 million years ago, is of particular importance to study the differences between the development of metatherians and other mammals. In opossums, lactation is divided into three stages that each have a very unique milk composition, and trichosurin is one of three predominant lipocalins found in the milk of T. vulpecula. | Trichosurin, an important marsupial milk protein, is highly conserved across metatherians. The opossum, a metatherian, shares a common ancestor with humans around 130 million years ago, is of particular importance to study the differences between the development of metatherians and other mammals. In opossums, lactation is divided into three stages that each have a very unique milk composition, and trichosurin is one of three predominant lipocalins found in the milk of T. vulpecula. | ||
| + | It is known that phenolic compounds are found in plants and used to deter herbivores, including possums, who then have to metabolize these compounds. It has also been shown that female possums concentrate phenolic compounds in their milk, which could act as a priming source for the young's liver to produce detoxifying enzymes that they can then use to survive while eating toxic plant sources. | ||
== Available Structures == | == Available Structures == | ||
Revision as of 23:36, 6 March 2020
Trichosurin
| |||||||||||