We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Triose Phosphate Isomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
One specific example of sequence homology is that of loop 6 and loop 7 residues, whose structural contributions are discussed above. In a sequence alignment of 133 TIM sequences, two highly conserved motifs are noticed. First, 114 sequences in loop 6 contain the PXW sequence family (where X is I,L or V in 112 sequences or otherwise a T or K). Secondly, loop 7 contains a highly conserved YGGS motif; however, this motif is only found when the N-terminal hinge contains tryptophan. | One specific example of sequence homology is that of loop 6 and loop 7 residues, whose structural contributions are discussed above. In a sequence alignment of 133 TIM sequences, two highly conserved motifs are noticed. First, 114 sequences in loop 6 contain the PXW sequence family (where X is I,L or V in 112 sequences or otherwise a T or K). Secondly, loop 7 contains a highly conserved YGGS motif; however, this motif is only found when the N-terminal hinge contains tryptophan. | ||
| + | == 3D Structures of triose phosphate isomerase== | ||
| + | [[Triose phosphate isomerase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of triose phosphate isomerase== | == 3D Structures of triose phosphate isomerase== | ||
| Line 109: | Line 112: | ||
*TIM | *TIM | ||
| + | **[[1wyi]], [[1hti]], [[2jk2]], [[4br1]], [[4poc]], [[6d43]] – hTIM - human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2vom]], [[4pod]], [[4unk]], [[4unl]], [[4zvj]], [[6c2g]], [[6nlh]] – hTIM (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1r2r]], [[1r2s]], [[1r2t]] – rTIM – rabbit<br /> | ||
**[[8tim]], [[1tim]], [[1tpb]], [[1tpc]], [[1tpw]] – cTIM – chicken<br /> | **[[8tim]], [[1tim]], [[1tpb]], [[1tpc]], [[1tpw]] – cTIM – chicken<br /> | ||
**[[1spq]], [[1sq7]], [[1ssd]], [[1ssg]], [[1su5]], [[1sw0]], [[1sw3]], [[1sw7]], [[1tpu]], [[1tpv]], [[4p61]] - cTIM (mutant) <br /> | **[[1spq]], [[1sq7]], [[1ssd]], [[1ssg]], [[1su5]], [[1sw0]], [[1sw3]], [[1sw7]], [[1tpu]], [[1tpv]], [[4p61]] - cTIM (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4ohq]], [[4obt]] – AtTIM – ''Arabidopsis thaliana''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nxq]], [[6nxr]], [[6nxs]], [[6nxw]], [[6nxx]], [[6nxy]] – AtTIM (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cg9]] – TIM – maize<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ypi]], [[3ypi]] - yTIM - yeast<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1i45]], [[4ff7]] – yTIM (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[1tmh]] – EcTIM/cTIM – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | **[[1tmh]] – EcTIM/cTIM – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
**[[1tre]], [[4k6a]], [[4iot]] - EcTIM<br /> | **[[1tre]], [[4k6a]], [[4iot]] - EcTIM<br /> | ||
**[[1amk]] – LmTIM – ''Leishmania mexicana''<br /> | **[[1amk]] – LmTIM – ''Leishmania mexicana''<br /> | ||
**[[1qds]] - LmTIM (mutant) <br /> | **[[1qds]] - LmTIM (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1dkw]], [[1ml1]], [[1mss]], [[1tpd]], [[1tpe]], [[1tpf]], [[1trd]], [[2v5l]], [[3tim]] - TbTIM – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> |
| - | + | **[[2j27]], [[1kv5]], [[2j24]], [[2v0t]], [[2v2c]], [[2v2d]], [[2v2h]], [[2y6z]], [[2y70]], [[5i3f]], [[5i3g]], [[5i3h]], [[5i3j]], [[5i3i]], [[5i3k]] - TbTIM (mutant) <br /> | |
| - | **[[2j27]], [[1kv5]], [[2j24]], [[2v0t]], [[2v2c]], [[2v2d]], [[2v2h]], [[2y6z]], [[2y70]], [[5i3f]], [[5i3g]], [[5i3h]], [[5i3j]], [[5i3i]], [[5i3k]] - TbTIM (mutant) | + | |
| - | + | ||
**[[1ci1]], [[1tcd]] - TcTIM – ''Trypanosoma cruzi''<br /> | **[[1ci1]], [[1tcd]] - TcTIM – ''Trypanosoma cruzi''<br /> | ||
**[[4hhp]], [[4jeq]] – TcTIM (mutant)<br /> | **[[4hhp]], [[4jeq]] – TcTIM (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[3q37]] – TcTIM/TbTIM<br /> | **[[3q37]] – TcTIM/TbTIM<br /> | ||
**[[1mo0]] – TIM – ''Caenorhabditis elegans''<br /> | **[[1mo0]] – TIM – ''Caenorhabditis elegans''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1i45]], [[4ff7]] – yTIM (mutant) – yeast<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ypi]], [[3ypi]] - yTIM<br /> | ||
**[[1m6j]] – TIM – ''Entamoeba histolytica''<br /> | **[[1m6j]] – TIM – ''Entamoeba histolytica''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1r2r]], [[1r2s]], [[1r2t]] – rTIM – rabbit<br /> | ||
**[[1ydv]] – PfTIM – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | **[[1ydv]] – PfTIM – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | ||
**[[1vga]], [[2vfd]], [[2vff]], [[3psv]], [[3psw]], [[3pwa]], [[3py2]], [[5gzp]], [[5gv4]], [[5brb]], [[5bnk]], [[5bmw]], [[5bmx]], [[4zz9]], [[4z0j]], [[4z0s]], [[4yxg]], [[4ywi]] – PfTIM (mutant) <br /> | **[[1vga]], [[2vfd]], [[2vff]], [[3psv]], [[3psw]], [[3pwa]], [[3py2]], [[5gzp]], [[5gv4]], [[5brb]], [[5bnk]], [[5bmw]], [[5bmx]], [[4zz9]], [[4z0j]], [[4z0s]], [[4yxg]], [[4ywi]] – PfTIM (mutant) <br /> | ||
| Line 139: | Line 145: | ||
**[[4g1k]] – TIM – ''Burkholderia thailandensis''<br /> | **[[4g1k]] – TIM – ''Burkholderia thailandensis''<br /> | ||
**[[4nvt]] – TIM – ''Brucella melitensis''<br /> | **[[4nvt]] – TIM – ''Brucella melitensis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ohq]], [[4obt]] – TIM – ''Arabidopsis thaliana''<br /> | ||
**[[5ibx]] – TIM – ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''<br /> | **[[5ibx]] – TIM – ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''<br /> | ||
**[[5csr]] – TaTIM – ''Thermoplasma acidophilum''<br /> | **[[5csr]] – TaTIM – ''Thermoplasma acidophilum''<br /> | ||
| Line 147: | Line 152: | ||
**[[4y8f]] – TIM – ''Clostridium perfringens''<br /> | **[[4y8f]] – TIM – ''Clostridium perfringens''<br /> | ||
**[[4x22]] - LiTIM – ''Leptospira interrogans''<br /> | **[[4x22]] - LiTIM – ''Leptospira interrogans''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mkn]] - TIM – ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii''<br /> | ||
*TIM binary complexes with phosphoglycolate | *TIM binary complexes with phosphoglycolate | ||
| + | **[[6oog]] - TIM + 2-phosphoglycolate – pork tapeworm<br /> | ||
**[[2ypi]] - yTIM + 2-phosphoglycolate<br /> | **[[2ypi]] - yTIM + 2-phosphoglycolate<br /> | ||
**[[1aw1]] – MmTIM + 2-phosphoglycolate – ''Moritella marina''<br /> | **[[1aw1]] – MmTIM + 2-phosphoglycolate – ''Moritella marina''<br /> | ||
| Line 157: | Line 164: | ||
**[[1lyx]], [[1lzo]] - PfTIM + 2-phosphoglycolate<br /> | **[[1lyx]], [[1lzo]] - PfTIM + 2-phosphoglycolate<br /> | ||
**[[4bi7]], [[4bi6]] - GiTIM (mutant) + 2-phosphoglycolate<br /> | **[[4bi7]], [[4bi6]] - GiTIM (mutant) + 2-phosphoglycolate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ooi]] - TIM + 2-phosphoglycolate – ''Schistosoma mansoni''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6bve]] - TIM + 2-phosphoglycolate – ''Synechocystis''<br /> | ||
*TIM binary complexes with phosphoglycerate | *TIM binary complexes with phosphoglycerate | ||
| Line 168: | Line 177: | ||
*TIM binary complexes with phosphoglycohydroxamate | *TIM binary complexes with phosphoglycohydroxamate | ||
| - | **[[2vxn]] - LmTIM (mutant) + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | ||
**[[1tph]] – cTIM + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | **[[1tph]] – cTIM + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3tao]] - MtTIM + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | ||
**[[7tim]] - yTIM + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | **[[7tim]] - yTIM + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2vxn]] - LmTIM (mutant) + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3tao]] - MtTIM + phosphoglycohydroxamate<br /> | ||
*Other TIM binary complexes | *Other TIM binary complexes | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[4owg]] – rTIM + phosphoenolpyruvate<br /> |
| + | **[[1ney]]– yTIM + dihydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1nf0]] – yTIM (mutant) + dihydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> | ||
**[[1aw2]] – MmTIM + sulfate<br /> | **[[1aw2]] – MmTIM + sulfate<br /> | ||
**[[1hg3]] – TIM + carboxyethylphosphonate – ''Pyrococcus woesei''<br /> | **[[1hg3]] – TIM + carboxyethylphosphonate – ''Pyrococcus woesei''<br /> | ||
| Line 181: | Line 192: | ||
**[[2y61]], [[2y62]] - LmTIM (mutant) + glycidol phosphate<br /> | **[[2y61]], [[2y62]] - LmTIM (mutant) + glycidol phosphate<br /> | ||
**[[2y63]] - LmTIM (mutant) + hydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> | **[[2y63]] - LmTIM (mutant) + hydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ag1]] – TbTIM + phosphate<br /> | ||
**[[1iig]] - TbTIM + 3-phosphonopropionate<br /> | **[[1iig]] - TbTIM + 3-phosphonopropionate<br /> | ||
**[[1tsi]] – TbTIM + phosphonobutanamide<br /> | **[[1tsi]] – TbTIM + phosphonobutanamide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ney]]– yTIM + dihydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1nf0]] – yTIM (mutant) + dihydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4ymz]] - LiTIM + dihydroxyacetonephosphate <br /> | **[[4ymz]] - LiTIM + dihydroxyacetonephosphate <br /> | ||
**[[5ujw]] – TIM + dihydroxyacetonephosphate – ''Francisella tularensis''<br /> | **[[5ujw]] – TIM + dihydroxyacetonephosphate – ''Francisella tularensis''<br /> | ||
| Line 191: | Line 201: | ||
**[[2oma]] – TcTIM + dithiobenzylamine<br /> | **[[2oma]] – TcTIM + dithiobenzylamine<br /> | ||
**[[4mva]] – EcTIM + acetyl phosphate<br /> | **[[4mva]] – EcTIM + acetyl phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4owg]] – rTIM + phosphoenolpyruvate<br /> | ||
*MonoTIM – stable monomeric variant of TIM | *MonoTIM – stable monomeric variant of TIM | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 8 March 2020
This page, as it appeared on June 30, 2011, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D Structures of triose phosphate isomerase
Updated on 08-March-2020
Additional Resources
- Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Triosephosphate Isomerase by Grabowski et al.
- Triose Phosphate Isomerase Structure & Mechanism by Krenk and Reese.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this proteopedia page would like to acknowledge and thank the authors of Triosephosphate Isomerase: Paula Grabowski, Jacqueline Townsend, Kara Pryke, and Regina D. Kettering. Some content from that article was incorporated into the present article.
References
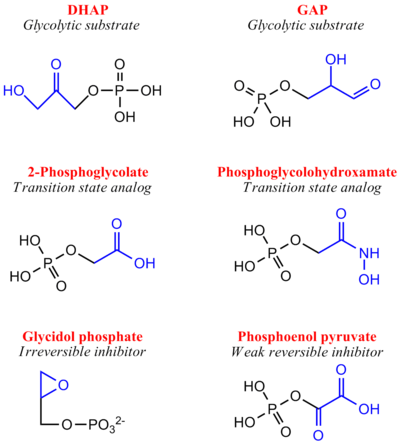
- ↑ Davenport RC, Bash PA, Seaton BA, Karplus M, Petsko GA, Ringe D. Structure of the triosephosphate isomerase-phosphoglycolohydroxamate complex: an analogue of the intermediate on the reaction pathway. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 18;30(24):5821-6. PMID:2043623
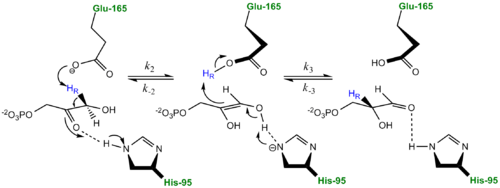
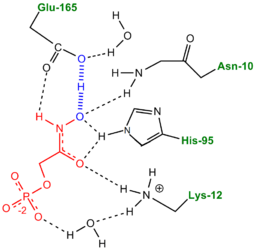
- ↑ Harris TK, Abeygunawardana C, Mildvan AS. NMR studies of the role of hydrogen bonding in the mechanism of triosephosphate isomerase. Biochemistry. 1997 Dec 2;36(48):14661-75. PMID:9398185 doi:10.1021/bi972039v
- ↑ Saadat D, Harrison DH. The crystal structure of methylglyoxal synthase from Escherichia coli. Structure. 1999 Mar 15;7(3):309-17. PMID:10368300
- ↑ Harris TK, Abeygunawardana C, Mildvan AS. NMR studies of the role of hydrogen bonding in the mechanism of triosephosphate isomerase. Biochemistry. 1997 Dec 2;36(48):14661-75. PMID:9398185 doi:10.1021/bi972039v
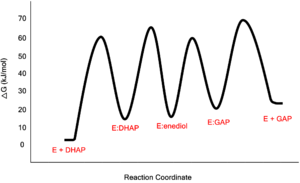
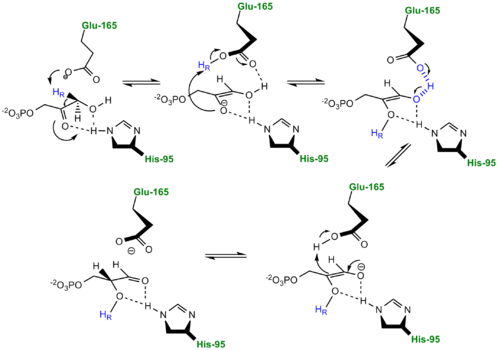
- ↑ Rozovsky S, McDermott AE. Substrate product equilibrium on a reversible enzyme, triosephosphate isomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2080-5. Epub 2007 Feb 7. PMID:17287353 doi:http://dx.doi.org/0608876104
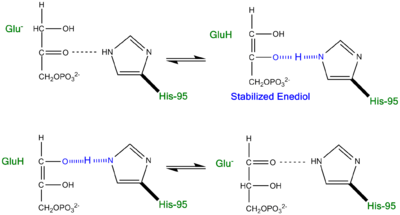
- ↑ Cleland WW, Kreevoy MM. Low-barrier hydrogen bonds and enzymic catalysis. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1887-90. PMID:8009219
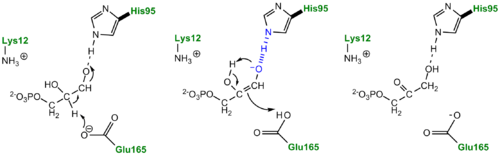
- ↑ Jogl G, Rozovsky S, McDermott AE, Tong L. Optimal alignment for enzymatic proton transfer: structure of the Michaelis complex of triosephosphate isomerase at 1.2-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jan 7;100(1):50-5. Epub 2002 Dec 30. PMID:12509510 doi:10.1073/pnas.0233793100
- ↑ O'Donoghue AC, Amyes TL, Richard JP. Hydron transfer catalyzed by triosephosphate isomerase. Products of isomerization of (R)-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in D2O. Biochemistry. 2005 Feb 22;44(7):2610-21. PMID:15709774 doi:10.1021/bi047954c
- ↑ Cleland WW, Frey PA, Gerlt JA. The low barrier hydrogen bond in enzymatic catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):25529-32. PMID:9748211
- ↑ Cleland WW, Frey PA, Gerlt JA. The low barrier hydrogen bond in enzymatic catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):25529-32. PMID:9748211
- ↑ Fonvielle M, Mariano S, Therisod M. New inhibitors of rabbit muscle triose-phosphate isomerase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2906-9. PMID:15911278 doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.03.061
- ↑ Fonvielle M, Mariano S, Therisod M. New inhibitors of rabbit muscle triose-phosphate isomerase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2906-9. PMID:15911278 doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.03.061
- ↑ Fonvielle M, Mariano S, Therisod M. New inhibitors of rabbit muscle triose-phosphate isomerase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2906-9. PMID:15911278 doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.03.061
- ↑ Kursula I, Wierenga RK. Crystal structure of triosephosphate isomerase complexed with 2-phosphoglycolate at 0.83-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 14;278(11):9544-51. Epub 2003 Jan 9. PMID:12522213 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M211389200
- ↑ Rodriguez-Almazan C, Arreola R, Rodriguez-Larrea D, Aguirre-Lopez B, de Gomez-Puyou MT, Perez-Montfort R, Costas M, Gomez-Puyou A, Torres-Larios A. Structural basis of human triosephosphate isomerase deficiency: mutation E104D is related to alterations of a conserved water network at the dimer interface. J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 22;283(34):23254-63. Epub 2008 Jun 18. PMID:18562316 doi:10.1074/jbc.M802145200
- ↑ Schnackerz KD, Gracy RW. Probing the catalytic sites of triosephosphate isomerase by 31P-NMR with reversibly and irreversibly binding substrate analogues. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 1;199(1):231-8. PMID:2065677
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv
- ↑ Joseph D, Petsko GA, Karplus M. Anatomy of a conformational change: hinged "lid" motion of the triosephosphate isomerase loop. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1425-8. PMID:2402636
- ↑ Derreumaux P, Schlick T. The loop opening/closing motion of the enzyme triosephosphate isomerase. Biophys J. 1998 Jan;74(1):72-81. PMID:9449311 doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77768-9
- ↑ Casteleijn MG, Alahuhta M, Groebel K, El-Sayed I, Augustyns K, Lambeir AM, Neubauer P, Wierenga RK. Functional role of the conserved active site proline of triosephosphate isomerase. Biochemistry. 2006 Dec 26;45(51):15483-94. Epub 2006 Dec 19. PMID:17176070 doi:10.1021/bi061683j
- ↑ Kursula I, Wierenga RK. Crystal structure of triosephosphate isomerase complexed with 2-phosphoglycolate at 0.83-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 14;278(11):9544-51. Epub 2003 Jan 9. PMID:12522213 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M211389200
- ↑ Schneider AS. Triosephosphate isomerase deficiency: historical perspectives and molecular aspects. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2000 Mar;13(1):119-40. PMID:10916682
- ↑ Ralser M, Heeren G, Breitenbach M, Lehrach H, Krobitsch S. Triose phosphate isomerase deficiency is caused by altered dimerization--not catalytic inactivity--of the mutant enzymes. PLoS ONE. 2006 Dec 20;1:e30. PMID:17183658 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000030
- ↑ Guix FX, Ill-Raga G, Bravo R, Nakaya T, de Fabritiis G, Coma M, Miscione GP, Villa-Freixa J, Suzuki T, Fernandez-Busquets X, Valverde MA, de Strooper B, Munoz FJ. Amyloid-dependent triosephosphate isomerase nitrotyrosination induces glycation and tau fibrillation. Brain. 2009 May;132(Pt 5):1335-45. Epub 2009 Feb 27. PMID:19251756 doi:10.1093/brain/awp023
- ↑ Joseph-McCarthy D, Lolis E, Komives EA, Petsko GA. Crystal structure of the K12M/G15A triosephosphate isomerase double mutant and electrostatic analysis of the active site. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 15;33(10):2815-23. PMID:8130194
- ↑ The conservation pattern shown was calculated by ConSurfDB and might obscure some conservation due to inclusion of proteins of different functions. However in the case of 2ypi, all sequences used in the multiple sequence alignment were TPI sequences. A manual run at the ConSurf Server, using 500 TPI sequences, gave a nearly identical result. Both runs gave an average pairwise distance close to 1.0. Hence, the conservation pattern shown is correct for TPI.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Gregg Snider, Eric Martz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Eran Hodis, Stephen Everse, Angel Herraez, Jane S. Richardson