Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
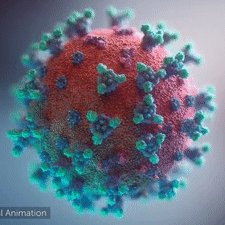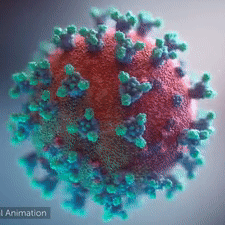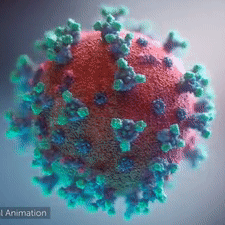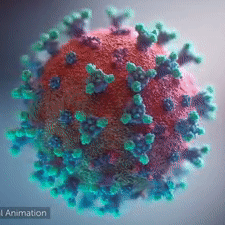
<br>An animation shows how the virus [http://youtu.be/hwVl_-lnoys '''interacts with its host'''], via these spikes, thus permitting its genome to enter the human (host) cell and begin infection (by [http://elarasystems.com Elara Systems)].</span> | <br>An animation shows how the virus [http://youtu.be/hwVl_-lnoys '''interacts with its host'''], via these spikes, thus permitting its genome to enter the human (host) cell and begin infection (by [http://elarasystems.com Elara Systems)].</span> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 24 March 2020
A novel coronavirus was found to be the cause of a respiratory illness first detected in Wuhan, China in 2019.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, Goldsmith JA, Hsieh CL, Abiona O, Graham BS, McLellan JS. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020 Feb 19. pii: science.abb2507. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2507. PMID:32075877 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2507
- ↑ Gordon, et al. A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map Reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-Repurposing: bioRxiv (online) 2020 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386
- ↑ Gautret, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open- label non-randomized clinical trial: Intl J Antimcrob Agents (in press) 2020 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
- ↑ Zhang L, Lin D, Sun X, Curth U, Drosten C, Sauerhering L, Becker S, Rox K, Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved alpha-ketoamide inhibitors. Science. 2020 Mar 20. pii: science.abb3405. doi: 10.1126/science.abb3405. PMID:32198291 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3405
- ↑ Gao, et al. Structure of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from 2019-nCoV, a major antiviral drug target: bioRxiv (online) 2020 https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.16.993386
- ↑ Jin, et al. Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors: bioRxiv (online) 2020 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.26.964882
- ↑ Kim, et al. Crystal structure of Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2: bioRxiv (online) 2020 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.02.968388
- ↑ Andersen, et al. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2: Nature Med (in press) 2020 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9]
- ↑ Yan R, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xia L, Guo Y, Zhou Q. Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science. 2020 Mar 4. pii: science.abb2762. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2762. PMID:32132184 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2762
- ↑ Dong L, Hu S, Gao J. Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Drug Discov Ther. 2020;14(1):58-60. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2020.01012. PMID:32147628 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5582/ddt.2020.01012
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Eric Martz, Jurgen Bosch, David Sehnal, Gianluca Santoni