We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
WD repeat-containing protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
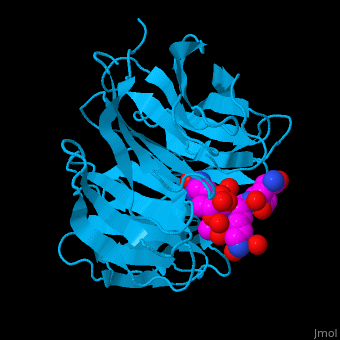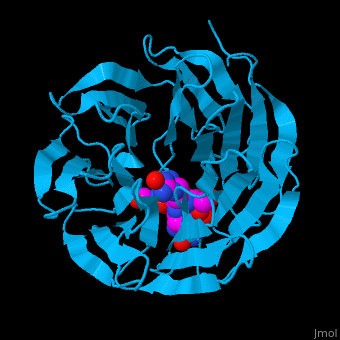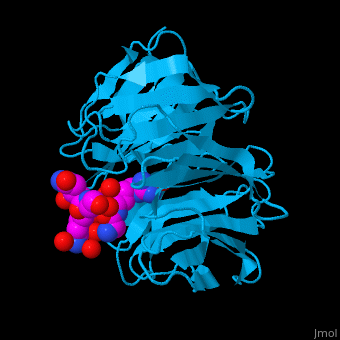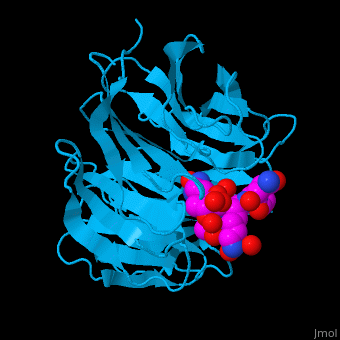
<StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human WD-repeat protein 5 (deepskyblue) complex with histone H3 peptide (magenta) (PDB code [[2h9m]])' scene='70/709459/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human WD-repeat protein 5 (deepskyblue) complex with histone H3 peptide (magenta) (PDB code [[2h9m]])' scene='70/709459/Cv/1'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''WD repeat-containing proteins''' (WDR) contain 4 or more repeating WD units. WD repeats are ca. 40 amino acid long usually bordered by Gly-His and Trp-Asp (WD). All WDRs form a β-propeller structure. WDRs have critical roles in many biological functions like signal transduction, transcription regulation and apoptosis<ref>PMID:11814058</ref>. <br /> | + | '''WD repeat-containing proteins''' or '''ribosome biogenesis protein WDR''' (WDR) contain 4 or more repeating WD units. WD repeats are ca. 40 amino acid long usually bordered by Gly-His and Trp-Asp (WD). All WDRs form a β-propeller structure. WDRs have critical roles in many biological functions like signal transduction, transcription regulation and apoptosis<ref>PMID:11814058</ref>. <br /> |
*'''WD-repeat protein 5''' (WDR5) contains 7 WD repeats. WDR5 contributes to histone modification. It may position the N-terminal of histone H3 for efficient methylation at Lys4. This methylation is implicated in the control of activation of cell lineage genes during embryogenesis. WDR5 interacts with histone-lysine N-methyltransferase (MLL)<ref>PMID:21531708</ref>. <br /> | *'''WD-repeat protein 5''' (WDR5) contains 7 WD repeats. WDR5 contributes to histone modification. It may position the N-terminal of histone H3 for efficient methylation at Lys4. This methylation is implicated in the control of activation of cell lineage genes during embryogenesis. WDR5 interacts with histone-lysine N-methyltransferase (MLL)<ref>PMID:21531708</ref>. <br /> | ||
*'''WD repeat-containing protein 48 and 20''' act as regulators of deubiquinating complexes. | *'''WD repeat-containing protein 48 and 20''' act as regulators of deubiquinating complexes. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
**[[3mxx]], [[3n0d]], [[3n0e]] – hWDR5 (mutant)<br /> | **[[3mxx]], [[3n0d]], [[3n0e]] – hWDR5 (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[3smr]], [[3ur4]], [[4ia9]], [[4qqe]], [[4ql1]], [[5eal]], [[5eam]], [[5eap]], [[5ear]] – hWDR5 + piperazine derivative<br /> | **[[3smr]], [[3ur4]], [[4ia9]], [[4qqe]], [[4ql1]], [[5eal]], [[5eam]], [[5eap]], [[5ear]] – hWDR5 + piperazine derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6u5m]], [[6u5y]], [[6u6w]], [[6u80]], [[6u8b]], [[6u8l]], [[6u8o]] – hWDR5 + sulfonamide inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ufx]], [[6ucs]], [[6pg3]], [[6pg4]], [[6pg5]], [[6pg6]], [[6pg7]], [[6pg8]], [[6pg9]], [[6pga]], [[6pgb]], [[6pgc]], [[6pgd]], [[6pge]], [[6pgf]], [[5vfc]], [[6dar]], [[6das]], [[6d9x]], [[6dai]], [[6dak]], [[6e1z]], [[6e1y]], [[6e22]], [[6e23]] – hWDR5 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[2cnx]], [[2co0]], [[2h6k]], [[2h6n]], [[2h6q]], [[2h13]], [[2h9m]], [[2h9n]], [[2h9p]], [[2g99]], [[2g9a]], [[2o9k]], [[3psl]], [[4a7j]] – hWDR5 + histone H3 peptide<br /> | **[[2cnx]], [[2co0]], [[2h6k]], [[2h6n]], [[2h6q]], [[2h13]], [[2h9m]], [[2h9n]], [[2h9p]], [[2g99]], [[2g9a]], [[2o9k]], [[3psl]], [[4a7j]] – hWDR5 + histone H3 peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5vfc]], [[6dar]], [[6das]], [[6d9x]], [[6dai]], [[6dak]] – hWDR5 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[4gm3]], [[4gm8]], [[4gm9]], [[4gmb]] – hWDR5 + peptide inhibitor<br /> | **[[4gm3]], [[4gm8]], [[4gm9]], [[4gmb]] – hWDR5 + peptide inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[2xl2]], [[2xl3]] – hWDR5 + retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 peptide<br /> | **[[2xl2]], [[2xl3]] – hWDR5 + retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 peptide<br /> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
**[[3eg6]], [[3emh]], [[3uvk]], [[3uvl]], [[3uvm]], [[3uvn]], [[3uvo]], [[4erq]], [[4ery]], [[4es0]], [[4esg]], [[4ewr]], [[5sxm]] – hWDR5 + MLL peptide<br /> | **[[3eg6]], [[3emh]], [[3uvk]], [[3uvl]], [[3uvm]], [[3uvn]], [[3uvo]], [[4erq]], [[4ery]], [[4es0]], [[4esg]], [[4ewr]], [[5sxm]] – hWDR5 + MLL peptide<br /> | ||
**[[4erz]] – hWDR5 + MLL4<br /> | **[[4erz]] – hWDR5 + MLL4<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6kiv]], [[6kiz]], [[6kiu]], [[6kix]] – hWDR5 in MLL1-ubNCP complex - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6kiw]] – hWDR5 in MLL3-ubNCP complex - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6pww]], [[6pwv]] – hWDR5 + MLL1 + RbBP5 + histones - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6byn]] – hWDR5 + monobody<br /> | **[[6byn]] – hWDR5 + monobody<br /> | ||
**[[3p4f]] – hWDR5 + retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 peptide + MLL peptide<br /> | **[[3p4f]] – hWDR5 + retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 peptide + MLL peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6iam]] – hWDR5 + small ubiquitin-related modifier 5<br /> | ||
*WDR9 | *WDR9 | ||
**[[2q2e]] – hWDR9 residues 1310-1430<br /> | **[[2q2e]] – hWDR9 residues 1310-1430<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *WDR12 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6p0q]] – hWDR12 UBL domain residues 1-87<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6n31]] – hWDR12 residues 90-422<br /> | ||
*WDR20 | *WDR20 | ||
**[[5k19]] – hWDR20<br /> | **[[5k19]] – hWDR20<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *WDR33 or pre-mRNA 3' end processing protein WDR33 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6f9n]] – hWDR33 residues 35-410 + CPSF160<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6urg]] – hWDR33 + CPSF160 + CPSF30 + CPSF100 - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6fbs]], [[6fuw]], [[6uro]] – hWDR33 + CPSF160 + CPSF30 + PAS motif - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
*WDR48 | *WDR48 | ||
| Line 50: | Line 66: | ||
**[[5l8w]], [[5cvn]], [[5cvo]] – hWDR48 + ubiquitin + ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase<br /> | **[[5l8w]], [[5cvn]], [[5cvo]] – hWDR48 + ubiquitin + ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase<br /> | ||
**[[5k1a]], [[5k1b]] – hWDR48 + ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase<br /> | **[[5k1a]], [[5k1b]] – hWDR48 + ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5k1c]] – hWDR48 + WDR20 + ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase<br /> | + | **[[5k1c]], [[6jlq]] – hWDR48 + WDR20 + ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | *WDR60 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6rlb]], [[6sc2]] – hWDR60 + WDR34 + dynein + O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyktransferase - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
*WDR61 | *WDR61 | ||
**[[3ow8]] – hWDR61<br /> | **[[3ow8]] – hWDR61<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *WDR91 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6vyc]] – hWDR91 residues 392-747<br /> | ||
*WDR92 | *WDR92 | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[3i2n]] – hWDR92<br /> |
*WDR SLP1 | *WDR SLP1 | ||
Revision as of 09:38, 28 March 2020
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of WD-repeat protein
Updated on 28-March-2020
References
- ↑ Li D, Roberts R. WD-repeat proteins: structure characteristics, biological function, and their involvement in human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 Dec;58(14):2085-97. PMID:11814058
- ↑ Gan Q, Thiebaud P, Theze N, Jin L, Xu G, Grant P, Owens GK. WD repeat-containing protein 5, a ubiquitously expressed histone methyltransferase adaptor protein, regulates smooth muscle cell-selective gene activation through interaction with pituitary homeobox 2. J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21853-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.233098. Epub, 2011 Apr 28. PMID:21531708 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.233098
- ↑ Tullio-Pelet A, Salomon R, Hadj-Rabia S, Mugnier C, de Laet MH, Chaouachi B, Bakiri F, Brottier P, Cattolico L, Penet C, Begeot M, Naville D, Nicolino M, Chaussain JL, Weissenbach J, Munnich A, Lyonnet S. Mutant WD-repeat protein in triple-A syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000 Nov;26(3):332-5. PMID:11062474 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/81642
- ↑ Schuetz A, Allali-Hassani A, Martin F, Loppnau P, Vedadi M, Bochkarev A, Plotnikov AN, Arrowsmith CH, Min J. Structural basis for molecular recognition and presentation of histone H3 by WDR5. EMBO J. 2006 Sep 20;25(18):4245-52. Epub 2006 Aug 31. PMID:16946699
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky