This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1627
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | As mentioned in the Introduction, the insulin receptor is relevant to numerous biological functions of the body. In order to address the receptors role in glucose homeostasis, it is important to discuss its relevance in disease. In a healthy, normal-functioning human, each cell's insulin receptors have the ability to bind to an abundance insulin that can get released by the pancreas in response to a rise of blood glucose levels. Without properly functioning insulin receptors that can respond to increases in insulin, and therefore glucose, medical intervention is necessary for survival. | + | As mentioned in the Introduction, the insulin receptor is relevant to numerous biological functions of the body. In order to address the receptors role in glucose homeostasis, it is important to discuss its relevance in disease. In a healthy, normal-functioning human, each cell's insulin receptors have the ability to bind to an abundance of insulin that can get released by the pancreas in response to a rise of blood glucose levels. Without properly functioning insulin receptors that can respond to increases in insulin, and therefore glucose, medical intervention is necessary for survival. |
=== Disease === | === Disease === | ||
One of the most common diseases involving the insulin receptor in regards to glucose uptake and homeostasis is diabetes mellitus. There are two types of diabetes- which are referred to as type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is classified as "insulin dependent" and is characterized by an inability for the body to produce insulin. This is most often the result of damage or insufficiency in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is classified as "insulin independent" and is the result of the body producing insufficient amounts of insulin, or not responding to the insulin. This often occurs because of high blood-glucose levels. Both types of diabetes are often treated with insulin injections, and diet and lifestyle changes. <ref name="Wilcox"> PMID:16278749</ref> <ref name= "Riddle"> PMID: 6351440</ref>. | One of the most common diseases involving the insulin receptor in regards to glucose uptake and homeostasis is diabetes mellitus. There are two types of diabetes- which are referred to as type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is classified as "insulin dependent" and is characterized by an inability for the body to produce insulin. This is most often the result of damage or insufficiency in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is classified as "insulin independent" and is the result of the body producing insufficient amounts of insulin, or not responding to the insulin. This often occurs because of high blood-glucose levels. Both types of diabetes are often treated with insulin injections, and diet and lifestyle changes. <ref name="Wilcox"> PMID:16278749</ref> <ref name= "Riddle"> PMID: 6351440</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 01:03, 30 March 2020
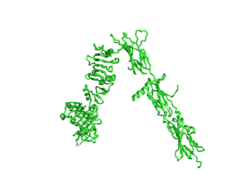
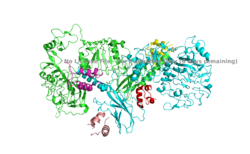
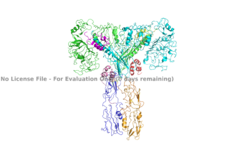
Homo sapiens Insulin Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Tatulian SA. Structural Dynamics of Insulin Receptor and Transmembrane Signaling. Biochemistry. 2015 Sep 15;54(36):5523-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805. Epub , 2015 Sep 3. PMID:26322622 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805
- ↑ Weis F, Menting JG, Margetts MB, Chan SJ, Xu Y, Tennagels N, Wohlfart P, Langer T, Muller CW, Dreyer MK, Lawrence MC. The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 24;9(1):4420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6. PMID:30356040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6
- ↑ Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Wilcox G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005 May;26(2):19-39. PMID:16278749
- ↑ Riddle MC. Treatment of diabetes with insulin. From art to science. West J Med. 1983 Jun;138(6):838-46. PMID:6351440
Student Contributors
- Harrison Smith
- Alyssa Ritter