We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Madison Summers/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Structural highlights and mechanism == | == Structural highlights and mechanism == | ||
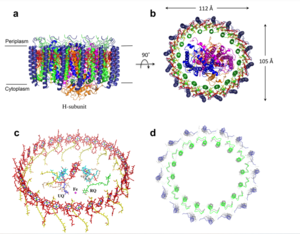
| - | The MCU is a dimer of dimers, described as tetrameric truncated pyramid. The uniporter has only a single strong binding site located in the selectivity pore, near the surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Activity of the uniporter is dependent on membrane potential and calcium concentration. Calcium from the cytoplasm enters the mitochondrial innermemnrane space through the mitochondrial membrane and is passed to the mitochondrial matrix via the MCU. [[Image:structure.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 2]] | + | The MCU is a dimer of dimers, described as tetrameric truncated pyramid. The uniporter has only a single strong binding site located in the selectivity pore with specificity for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium_signaling Calcium], near the surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Activity of the uniporter is dependent on membrane potential and calcium concentration. Calcium from the cytoplasm enters the mitochondrial innermemnrane space through the mitochondrial membrane and is passed to the mitochondrial matrix via the MCU. [[Image:structure.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 2]] |
| + | |||
===Transmembrane Domain=== | ===Transmembrane Domain=== | ||
| - | The | + | |
| + | The transmembrane domain is in the inner mitochondrial membrane open to the inner membrane space. The small pore, highly specific for calcium binding is located in the <scene name='83/837230/Transmembrane_domain/1'>transmembrane domain</scene>, in TM2 (transmembrane 2) while TM 1 (transmembrane 1) surrounds the pore. The transmembrane domain exhibits four fold rotational symmetry. The domain swapping of TM1 of one subunit with the TM2 of the neighboring subunits allows for a tight packing in the transmembrane connectivity. It is important that the selectivity pore is small, allowing only a dehydrated calcium molecule to interact with the 5 ampler wide glutamate ring. | ||
| + | |||
===Coiled coil=== | ===Coiled coil=== | ||
Revision as of 00:00, 2 April 2020
Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter, E. coli
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Yoo J, Wu M, Yin Y, Herzik MA Jr, Lander GC, Lee SY. Cryo-EM structure of a mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Science. 2018 Jun 28. pii: science.aar4056. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4056. PMID:29954988 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aar4056
Student Contributors
- Madison Summers
- Holly Rowe
- Lizzy Ratz