Sandbox Reserved 1627
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
====Alpha Subunits==== | ====Alpha Subunits==== | ||
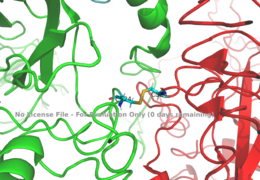
[[Image:Disulfide bridge between alphas.png|thumb|right|260px|Figure 1: Disulfide bridge between the two alpha subunits. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6sof PDB 6SOF]]] | [[Image:Disulfide bridge between alphas.png|thumb|right|260px|Figure 1: Disulfide bridge between the two alpha subunits. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6sof PDB 6SOF]]] | ||
| - | The alpha subunits make up the extracellular domain ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ectodomain ectodomain]) of the insulin receptor and are the sites of insulin binding. The alpha subunit is comprised of two Leucine rich domains (L1 & L2), a Cysteine rich domain (CR), and a C-terminal alpha helix. The two subunits are held together by a disulfide | + | The alpha subunits make up the extracellular domain ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ectodomain ectodomain]) of the insulin receptor and are the sites of insulin binding. The alpha subunit is comprised of two Leucine rich domains (L1 & L2), a Cysteine rich domain (CR), and a C-terminal alpha helix. The two subunits are held together by a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disulfide disulfide bonds] at residue C524 of one alpha subunit, and C524 of the other subunit (Figure1). The actual site of insulin binding occurs at the <scene name='83/832953/Alpha_c_helix/1'>α-CT chain</scene> and is stabilized by the L1 and L2 domains <scene name='83/832953/Inactive_insulin_receptor/2'> Not sure what these are sos</scene>.There are two types of binding sites in the alpha subunits, Sites 1 and 1' and then Sites 2 and 2'. These two types have unique differences from each other, which makes the affinity for the first two sites, 1 and 1', much higher than that of sites 2 and 2'. The sites are in pairs because the receptor is a dimer of heterodimers and contains four protomers of similar structure. Each time an insulin ligand binds to sites 1 and 1', it comes in contact with the L1 domain of one protomer and the alpha-CT chain and FnIII-1 loop of another protomer, which is also known as "cross linking". There is potential for binding at sites 2 and 2', but it is less likely due to the location of the sites on the back of the beta sheet of the FnIII-1 domain on each protomer and the fact that there is a much greater surface area for binding at sites 1 and 1'. <ref name="Uchikawa"> DOI 10.7554/eLife.48630 </ref>. |
===Beta Subunits=== | ===Beta Subunits=== | ||
The beta subunit is part of the extracellular membrane as well, but also spans the membrane region and inserts the intracellular portion of the insulin receptor. This domain is composed of part of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibronectin fibronectin] domain III-2 and all of Fibronectin domain III-3. It is proposed that the beta subunit's FnIII-3 domain has links through the transmembrane region into the intracellular part of the membrane. Due to the fact that it is known that there is a conformation change in the FnIII-3 extracellular part, it is expected that the conformation change follows all the way through to the end of the receptor in order to accomplish the complete T-shape which will ultimately induce the autophosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase domain. | The beta subunit is part of the extracellular membrane as well, but also spans the membrane region and inserts the intracellular portion of the insulin receptor. This domain is composed of part of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibronectin fibronectin] domain III-2 and all of Fibronectin domain III-3. It is proposed that the beta subunit's FnIII-3 domain has links through the transmembrane region into the intracellular part of the membrane. Due to the fact that it is known that there is a conformation change in the FnIII-3 extracellular part, it is expected that the conformation change follows all the way through to the end of the receptor in order to accomplish the complete T-shape which will ultimately induce the autophosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase domain. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Binding interactions=== | ===Binding interactions=== | ||
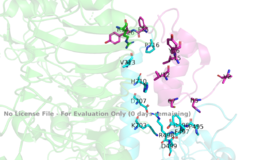
[[Image:Binding site with AA labeled.png|thumb|right|270px|Figure 3: Subunit interactions between the insulin receptor CT-alpha helix (light blue) and insulin (magenta) in one of the binding sites [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6sof PDB 6SOF]]] | [[Image:Binding site with AA labeled.png|thumb|right|270px|Figure 3: Subunit interactions between the insulin receptor CT-alpha helix (light blue) and insulin (magenta) in one of the binding sites [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6sof PDB 6SOF]]] | ||
| - | The insulin receptor itself is held together by numerous critical | + | The insulin receptor itself is held together by numerous critical disulfide bonds and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_(protein_and_supramolecular) salt bridges]. These bonds maintain a stablized link between the dimers of the receptor, and without them, the conformation change from inactive to active would not be able to occur. One unique interaction within the receptor is known as a tripartite interaction. It occurs between the alpha-CT chain and the FnIII-1 domain region during a conformation chain, and involves the following residues:<scene name='83/832953/Alpha_ct_and_fniii-1/2'> ASP496, ARG498, and ASP99 on the FnIII domain</scene> and the <scene name='83/832953/Alpha_ct_and_fniii-1/3'>LYS703, GLU706, and ASP707 on the alpha-CT domain</scene> . This duo then interacts with the leucine rich region, L1, that exists on the opposing protomer of the dimer. |
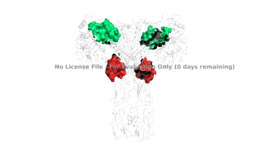
[[Image:4 sites highlighted.png|thumb|right|260px|Figure 4: Sites 1, 1', 2, and 2'. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6sof PDB 6SOF]]] | [[Image:4 sites highlighted.png|thumb|right|260px|Figure 4: Sites 1, 1', 2, and 2'. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6sof PDB 6SOF]]] | ||
It is generally more common for only one or two insulin molecules to bind to the receptor due to the occurrence of negative affinity at the binding site, as well as the location of the second two binding sites on the back side of the receptor with Beta sheets and the lack of surface area they have. For this reason, studies support that optimal insulin receptor activation requires the binding of ligands to two insulin binding sites. Binding of at least one insulin is required for the activation of the insulin receptor and the change in conformation to the active T state. <ref> DOI 10.7554/eLife.48630 </ref>. | It is generally more common for only one or two insulin molecules to bind to the receptor due to the occurrence of negative affinity at the binding site, as well as the location of the second two binding sites on the back side of the receptor with Beta sheets and the lack of surface area they have. For this reason, studies support that optimal insulin receptor activation requires the binding of ligands to two insulin binding sites. Binding of at least one insulin is required for the activation of the insulin receptor and the change in conformation to the active T state. <ref> DOI 10.7554/eLife.48630 </ref>. | ||
Revision as of 01:19, 7 April 2020
Homo sapiens Insulin Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tatulian SA. Structural Dynamics of Insulin Receptor and Transmembrane Signaling. Biochemistry. 2015 Sep 15;54(36):5523-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805. Epub , 2015 Sep 3. PMID:26322622 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Weis F, Menting JG, Margetts MB, Chan SJ, Xu Y, Tennagels N, Wohlfart P, Langer T, Muller CW, Dreyer MK, Lawrence MC. The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 24;9(1):4420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6. PMID:30356040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6
- ↑ Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Wilcox G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005 May;26(2):19-39. PMID:16278749
- ↑ Riddle MC. Treatment of diabetes with insulin. From art to science. West J Med. 1983 Jun;138(6):838-46. PMID:6351440
Student Contributors
- Harrison Smith
- Alyssa Ritter