Introduction
The insulin receptor is a transmembrane receptor [1] that resides in the plasma membrane and is activated by the binding of insulin. The insulin receptor belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTKs). RTKs are found at the cell surface and have a high affinity for a particular ligand. RTKs are made up of three distinct parts: an extracellular domain with ligand binding sites, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular domain with the tyrosine kinases that initiate intracellular signaling cascades [1]. Downstream signaling from the insulin receptor initiates a variety of cellular pathways including glucose homeostasis, regulation of lipid, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism, gene expression, and even modulation of brain neurotransmitter levels [2]. Amongst RTKs, the insulin receptor is unusual as its undergoes a large conformation change upon insulin binding. Through recent cryo-EM structures of the insulin receptor bound in various conformations, a complete three-dimensional understanding of this conformational changes in finally coming into focus. This page focuses specifically on the insulin receptor's role in glucose homeostasis.
Structural Overview
The insulin receptor is a dimer of heterodimers made of two and two [2]. Within the extracellular ectodomain, there are four potential that can interact with insulin ligands on the extracellular side of the membrane. Binding of insulin initiates a large structural transition from an inactive shape to an active state.
Alpha Subunits
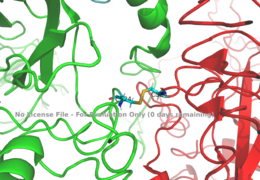
Figure 1: Disulfide bridge (yellow) made of two cysteine residues (blue) that provides a linkage and stability to the two alpha subunits.
PDB 6SOFThe alpha subunits make up the extracellular domain (ectodomain) of the insulin receptor and are the sites of insulin binding. The alpha subunit is comprised of two Leucine rich domains (L1 & L2), a Cysteine rich domain (CR), and a C-terminal alpha helix. The alpha and beta subunits are held together by a disulfide bond at residue C524 of one alpha subunit, and C524 of the other subunit (Figure1). The actual site of insulin binding occurs at the of one of the sites discussed next and is stabilized by the L1 and L2 domains. Two types of insulin binding sites are present in the alpha subunits, Sites 1 and 1' and then Sites 2 and 2'. Due to structural differences in these binding sites, the first two sites, 1 and 1', have much higher affinity than that of sites 2 and 2'. The sites are in pairs because of the heterodimeric nature of the receptor. Each time an insulin ligand binds to sites 1 and 1', it comes in contact with the L1 domain of one protomer and the alpha-CT chain and FnIII-1 loop of another protomer, which is also known as "cross linking". Insulin can also bind at sites 2 and 2', but the location on the back of the beta sheet of the FnIII-1 domain and lower surface area decreases their binding occupancy. [3].
Beta Subunits
The beta subunit spans from the extracellular domain across the transmembrane region and into the intracellular portion of the insulin receptor. The beta subunit is composed of part of fibronectin domain III-2 and all of Fibronectin domain III-3. The beta subunit's FnIII-3 domain has links through the transmembrane region into the intracellular part of the membrane. The conformational change of the extracellular domain of FnIII-3 is transmitted through the entire receptor to induce the T-shape transition. This structural transition will facilitate the autophosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase domain.
Cryo-EM Structural Imaging
Cryo-EM results have displayed clear representations of FnIII-2 and FnIII-3 domains, but lack in high density results for the transmembrane domain and cannot truly model anything past the two fibronectin domains due to the lack of side chain density. Since FnIII-3 is connected to the transmembrane domain and intracellular kinase domains through a short linker, it is suggested that the insulin receptor does extend its T-shape conformation through the cell membrane and into the cell. Therefore, it is expected that the intracellular kinase domains will be in close proximity when this conformation change occurs extracellularly, ultimately allowing for autophosphorylation. The Cryo-EM structure of the extracellular domain of the Insulin Receptor without the presence of insulin bound at its alpha subunit site was established first, and is also known as the apo-form. The shape that it displayed appeared as an upside down V. Then, a subsequent Cryo-EM was established with insulin bound to the alpha subunit binding site, displaying a T shape conformation of the same alpha protomer unit.[3] It is important to note in the overall discussion of the insulin receptor structure that it has only been imaged in pieces, and not as a whole at this point in time. There are proposed structures of the entire molecule based off of the known function of the tyrosine autophosphorylation and downstream activation, but the structure discussed throughout this page only contains part of the Beta subunits through that of the FnIII-3 domain. To analyze work completed on the tyrosine kinase domain of the receptor, [https//www.rcsb.org/structure/1ir3 PDB 1IR3] can be referenced.
Insulin
Insulin is a
peptide hormone produced and secreted from the
islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in response to high blood glucose levels. Insulin is commonly considered the anabolic hormone of the body, and is the an important
ligand in glucose homeostasis. The structure of insulin is fairly simple, it is a monomer composed of two peptide chains linked by an intermolecular disulfide bridge. Insulin initiates the transport of extracellular glucose into the cell where it can be converted into
glycogen for storage and later usage.
Function
The insulin receptor's structure is critical to it's function. The receptor begins the signaling pathway that will eventually move glucose transporters to the cell surface which will allow glucose to passively defuse into the cell. The glucose receptor is inactive in the absence of insulin. When there is a surplus of glucose circulating in the blood stream, the production of insulin is upregulated and will bind to many insulin receptors. Upon activation, it undergoes a structural conformation change from the inactive state to the active state. Once activated, the Beta subunits move together to autophosphorylate and initate downstream signaling by the phosphorylation of the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS), eventually resulting in glucose intake.
Conformation Change
Structures of the inactive inverted V conformation only contains a single because the entire inactive alpha subunit dimer has been unable to be photographed because the transition state has yet to be determined in full. In the V-shape, the FnIII-3 domains are separated by about 120Å which keeps the tyrosine kinase domains separated. In the V-shape, autophosphorylation and downstream signaling cannot be initiated. Upon the binding of insulin to either the 1 or 1' site, the conformation change will begin and bring the FnIII-3 domains within 40Å of each other in the T-state conformation. [4] [3] The T shape conformation is well observed in the alpha subunit. It is horizontally composed of L1, CR (including the alpha-CT chain), and L2 domains and vertically composed of the FnIII-1, 2, and 3 domains.
Binding interactions
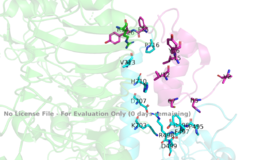
Figure 3: Subunit interactions between the insulin receptor CT-alpha helix (light blue) and insulin (magenta) in one of the binding sites.
PDB 6SOFThe insulin receptor itself is held together by numerous critical disulfide bonds and salt bridges. These bonds maintain a stablized link between the dimers of the receptor, and without them, the conformation change from inactive to active would not be able to occur. One unique interaction within the receptor is known as a tripartite interaction. It occurs between the alpha-CT chain and the FnIII-1 domain region during a conformation chain, and involves the following residues: and the . This duo then interacts with the leucine rich region, L1, that exists on the opposing protomer of the dimer.
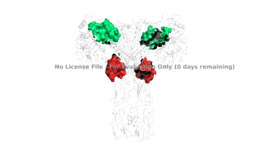
Figure 4: The presence of all four potential binding sides on the active insulin receptor: sites 1 and 1' (green) and sites 2, and 2'(red).
PDB 6SOFIt is generally more common for only one or two insulin molecules to bind to the receptor due to the occurrence of negative affinity at the binding site, as well as the location of the second two binding sites on the back side of the receptor with Beta sheets and the lack of surface area they have. For this reason, studies support that optimal insulin receptor activation requires the binding of ligands to two insulin binding sites. Binding of at least one insulin is required for the activation of the insulin receptor and the change in conformation to the active T state. [5].
Ligand binding interactions are different at and (Figure 4). The interactions at all 4 binding sites are highly hydrophobic, but there are differences between the sites. Binding sites 1 and 1' have two cystines in a disulfide bond linkage along with HIS B5 all from insulin interacting with residues from the FnIII-1 domain. At sites 2 and 2' the interaction with insulin involves more residues than at the first two sites. The FnIII-1 region has - interacting with insulin's resides and numerous locations along its surface.
Relevance
As mentioned in the Introduction, the insulin receptor is relevant to numerous biological functions of the body. In order to address the receptors role in glucose homeostasis, it is important to discuss its relevance in disease. In a healthy, normal-functioning human, each cell's insulin receptors have the ability to bind to an abundance of insulin that can get released by the pancreas in response to a rise of blood glucose levels. Without properly functioning insulin receptors that can respond to increases in insulin, and therefore glucose, medical intervention is necessary for survival.
Disease
One of the most common diseases involving the insulin receptor in regards to glucose uptake and homeostasis is diabetes mellitus. There are two types of diabetes- which are referred to as type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is classified as "insulin dependent" and is characterized by an inability for the body to produce insulin. This is most often the result of damage or insufficiency in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is classified as "insulin independent" and is the result of the body producing insufficient amounts of insulin, or not responding to the insulin. This often occurs because of high blood-glucose levels. Both types of diabetes are often treated with insulin injections, and diet and lifestyle changes. [6] [7].
At the Cellular Level
In the human body, the conformation change from the inactive to active state upon insulin binding has a time constant of six minutes. Once insulin binds and the beta subunits are brought within close proximity, autophosphorylation of the beta subunits begins. Phosphorylation at these sites reaches a maximal level in about one minute, and lasts for approximately six to ten minutes. One insulin receptor substrate has a half-life of 3.5 minutes where it is able to be phosphorylated by the tyrosine kinases of the beta subunit and then act as a central hub to activate further downstream signaling pathways that eventually bring glucose receptors to the surface of the cell to allow for diffusion of glucose into the cell. Once insulin binds to the alpha subunit, the receptor remains active for approximately ten minutes before the insulin is degraded and the receptor returns to its inactive conformation. This time frame puts a perspective on how long it takes for the human body to store excess glucose in their blood stream from a recent meal as glycogen for later use as fuel. [2]




