We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Harrison L. Smith/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Image:4 sites highlighted - Harrison.png|thumb|right|260px|Figure 2: The four binding sites of insulin. Sites 1 and 1' are colored green, sites 2 and 2' are colored red. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6SOF PDB 6SOF]]] | [[Image:4 sites highlighted - Harrison.png|thumb|right|260px|Figure 2: The four binding sites of insulin. Sites 1 and 1' are colored green, sites 2 and 2' are colored red. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6SOF PDB 6SOF]]] | ||
===Beta Subunits=== | ===Beta Subunits=== | ||
| - | The beta subunit spans from the extracellular domain across the transmembrane region and into the intracellular portion of the insulin receptor. The beta subunit is composed of part of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibronectin fibronectin] domain III-2 and all of Fibronectin domain III-3. The beta subunit's FnIII-3 domain has links through the transmembrane region into the intracellular part of the membrane.[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_electron_cryomicroscopy Cryo-EM] results have displayed clear representations of FnIII-2 and FnIII-3 domains, but lack in their ability to model the receptor structure throughout the transmembrane region and intracellular region. Although, the FnIII-3 domain is connected to these regions, so it has been proposed that the T-shape conformation extends all the way to the tyrosine kinase domain region. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1IR3 PDB 1IR3] | + | The beta subunit spans from the extracellular domain across the transmembrane region and into the intracellular portion of the insulin receptor. The beta subunit is composed of part of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibronectin fibronectin] domain III-2 and all of Fibronectin domain III-3.<ref name="Scapin">/ The beta subunit's FnIII-3 domain has links through the transmembrane region into the intracellular part of the membrane.[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_electron_cryomicroscopy Cryo-EM] results have displayed clear representations of FnIII-2 and FnIII-3 domains, but lack in their ability to model the receptor structure throughout the transmembrane region and intracellular region. Although, the FnIII-3 domain is connected to these regions, so it has been proposed that the T-shape conformation extends all the way to the tyrosine kinase domain region. [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1IR3 PDB 1IR3] |
== Function== | == Function== | ||
Revision as of 17:05, 19 April 2020
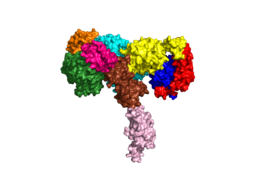
Homo sapiens Insulin Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 De Meyts P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network PMID:27512793
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Tatulian SA. Structural Dynamics of Insulin Receptor and Transmembrane Signaling. Biochemistry. 2015 Sep 15;54(36):5523-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805. Epub , 2015 Sep 3. PMID:26322622 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Scapin G, Dandey VP, Zhang Z, Prosise W, Hruza A, Kelly T, Mayhood T, Strickland C, Potter CS, Carragher B. Structure of the Insulin Receptor-Insulin Complex by Single Particle CryoEM analysis. Nature. 2018 Feb 28. pii: nature26153. doi: 10.1038/nature26153. PMID:29512653 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature26153
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jan 1;6(1). pii: 6/1/a009191. doi:, 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191. PMID:24384568 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009191
- ↑ Wilcox G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005 May;26(2):19-39. PMID:16278749
- ↑ Riddle MC. Treatment of diabetes with insulin. From art to science. West J Med. 1983 Jun;138(6):838-46. PMID:6351440
Student Contributors
- Harrison Smith
- Alyssa Ritter