This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Vm24 Scorpion Toxin
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
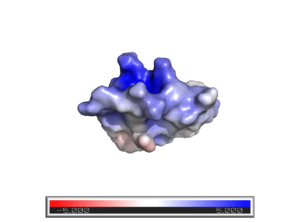
<Structure load='2k9o' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Vm24 Scorpion Toxin [[2k9o]]' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='2k9o' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Vm24 Scorpion Toxin [[2k9o]]' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
==Protein Source== | ==Protein Source== | ||
| - | Gurolla G.B et al ***link*** isolated the peptide components of ''Vaejovis mexicanus smithi | + | Gurolla G.B et al ***link*** isolated the peptide components of ''Vaejovis mexicanus smithi'' venom using high-performance liquid chromatography. Over 200 components were identified. The structure of Vm24 was determined by solution NMR spectroscopy, and it was sequenced via trypsin digestion. The a synthetic Vm24 gene was created and artificially translated to produce the synthetic Vm24 toxin displayed. |
Revision as of 19:01, 24 April 2020
Introduction
Vm24 synthetic scorpion toxin is a peptide toxin isolated from Vaejovis mexicanus scorpion venom. It is a potent inhibitor of Kv1.3 potassium channels of human T lymphocytes. Its high affinity and specificity for human lymphocytes makes it a candidate for the treatment of several autoimmune disorders.
|
Protein Source
Gurolla G.B et al ***link*** isolated the peptide components of Vaejovis mexicanus smithi venom using high-performance liquid chromatography. Over 200 components were identified. The structure of Vm24 was determined by solution NMR spectroscopy, and it was sequenced via trypsin digestion. The a synthetic Vm24 gene was created and artificially translated to produce the synthetic Vm24 toxin displayed.
