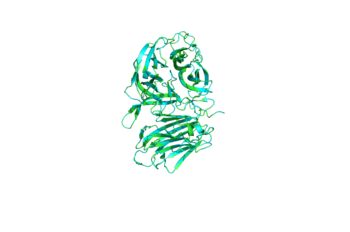
General Description
4EQV is 469 kDa invertase(SInv) isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. SInv catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose into fructose and glucose, thus making it an essential enzyme to plants and other organisms, such as honey bees[1]. Invertase also lends itself to industry and is extensively used fermentation, where yeast are employed to process sugar into ethanol.
Yeast invertase was first isolated in 1860 by Berthelot, but had been alluded to by Dubrunfaut in 1847.[2] Invertase was posited to be an intracellular enzymee, yet de la Fuente and Sols were able to show that invertase can be excreted by the cell, thus it is also extracellular[3]. The intracellular form of the enzyme is not glycosylated, while the extracellular form is extensively glycosylated[1]. The same gene codes for glycosylated and non-glycosylated forms of the enzyme they differ when being transcribed into mRNA, and the extracellular bound SInv is tagged with a signal peptide.[4]
Structure
Though it is an octamer, SInv can be best described as a tetramer of dimers[1]. The illustrates this high degree of symmetry. It should also be pointed out that the A/B and C/D dimers have been dubbed "closed" while the E/F and G/H dimers have been dubbed "open"[1]. This idea of "open" and closed" dimers is explained in more detail in the section titled Open & Closed Assembly.
Catalytic β-propeller Domain
The of 4EQV, shown in crimson, is the catalytic domain of the monomer. The domain is composed mostly of antiparallel β-strands which form five blades, each containing four antiparallel β-strands. The of the β-propeller domain is formed at the axis of the five blades. This catalytic pocket is contains nucleophilic residue Asp22 at its base and is lined with multiple hydrophobic residues, namely Trp48, Phe82, Trp291, Phe296, and Phe388. The of the A/B and C/D chains are rather specific for sucrose. This specificity is due to Gln201, which binds to sucrose and Asp228 conveys an affinity for glucose moiety[5].
The catalytic process, is two-step. First, there is the nucleophilic attack of the anomeric carbon of the fructose moiety by Asp22, to form a covalent enzyme-substrate complex[6]. Glucose the leaving group, is simulaneously protonated by Glu203, which then deprontonates the "acceptor" molecule to activate it as a nucleophile, which then releases fructose[7]. The figure below illustrates this process using a cartoon.
β-sandwich Domain
the of invertase
A formed by chain A and chain B showing how each active site is capped by the β-sandwich Domain.
β-sandwich domains form between residues 343-363.
Open & Closed Assembly
test test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test test
test test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test testtest test test test
the of chain E
Evolutionary Conservation & Related Proteins
Available Structures
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Sainz-Polo MA, Ramirez-Escudero M, Lafraya A, Gonzalez B, Marin-Navarro J, Polaina J, Sanz-Aparicio J. The three-dimensional structure of Saccharomyces invertase: role of a non-catalytic domain in oligomerization and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 21. PMID:23430743 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.446435
- ↑ Sainz-Polo MA, Ramirez-Escudero M, Lafraya A, Gonzalez B, Marin-Navarro J, Polaina J, Sanz-Aparicio J. The three-dimensional structure of Saccharomyces invertase: role of a non-catalytic domain in oligomerization and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 21. PMID:23430743 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.446435
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3002(62)90526-7
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425540
- ↑ Lafraya A, Sanz-Aparicio J, Polaina J, Marin-Navarro J. Fructo-oligosaccharide synthesis by mutant versions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(17):6148-57. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05032-11. Epub , 2011 Jul 15. PMID:21764973 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05032-11
- ↑ Lafraya A, Sanz-Aparicio J, Polaina J, Marin-Navarro J. Fructo-oligosaccharide synthesis by mutant versions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(17):6148-57. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05032-11. Epub , 2011 Jul 15. PMID:21764973 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05032-11
- ↑ Lafraya A, Sanz-Aparicio J, Polaina J, Marin-Navarro J. Fructo-oligosaccharide synthesis by mutant versions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(17):6148-57. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05032-11. Epub , 2011 Jul 15. PMID:21764973 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05032-11