We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Samuel Boyson/Sandbox 900
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| - | BRD7 is a human Bromodomain containing protein that is known to be encoded by the BRD7 gene. The full protein has a molecular weight of around 75 kD, while the Bromodomain itself has a molecular weight of roughly 13 kD. It is categorized as a family IV Bromodomain. While | + | BRD7 is a human Bromodomain containing protein that is known to be encoded by the BRD7 gene. The full protein has a molecular weight of around 75 kD, while the Bromodomain itself has a molecular weight of roughly 13 kD. It is categorized as a family IV Bromodomain. While its function remains largely unidentified, BRD7 is known to recognize acetylated lysine residues on Histones and play role in regulating transcriptional activity(1). It was first discovered in 2000 in Nasal Pharyngeal Cancer (NPC) cells(2) and has been implicated to have a role in NPC, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and other cancer types (3). BRD7 can recognize acetyl lysine residues by using its Bromodomain to bind to Histone tails. Shown in Figure 1 is a 3D rotating image of the apo BRD7 structure (PDB: 2I7K). |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
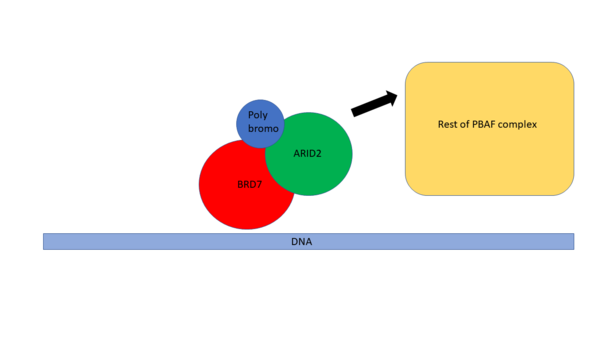
| - | The role of BRD7 in biology is not yet fully understood. It is known however, that BRD7 is part of the PBAF (poly-bromo associated BRG-1 associated factor) complex( | + | The role of BRD7 in biology is not yet fully understood. It is known however, that BRD7 is part of the PBAF (poly-bromo associated BRG-1 associated factor) complex(4). This is a chromatin remodeling complex that is part of the Swi/Snf family. PBAF is a complex that can facilitate transcription of target genes through chromatin remodeling(5). Shown in Figure 2 is a schematic of BRD7 associating with the PBAF complex. BRD7 was found to be in complexed with Poly bromo (Pb) and ARID2 (6) before associating with the rest of the proteins in the PBAF complex. These proteins can then associate with the PBAF complex to assist in the recognition of post translational marks (PTMs) on Histones. |
| + | [[Image:PBAF BD7 schematic.png|600px|center|thumb|Figure2]] | ||
| + | BRD7 also functions as a tumor suppressor gene that can inhibit p53 and is frequently found to be downregulated in Breast Cancer tumor cells containing wild type p53. BRD7 is important for proper p53 mediated transcription of target genes and is a known p53 co-factor. It likely affects acetylation levels at the promoters of target genes allowing for the facilitation of transcription through regulation of chromatin dynamics(7). BRD7 has also been implicated in having function in maintaining male fertility. Although it is still unclear how, BRD7 is involved in spermatogenesis in male mouse models. Knockout of BRD7 during spermatogenesis resulted in complete infertility(8). | ||
== Structural Features == | == Structural Features == | ||
| - | The structure of BRD7 was first solved in 2007 using solution state NMR ( | + | The structure of BRD7 was first solved in 2007 using solution state NMR (9). Like other Bromodomains, BRD7 contains a bundle of 4 left handed antiparallel α-helices. They follow the traditional Bromodomain naming pattern of being called α-Z, α-A, α-B, and α-C in that order from the N-terminal end. In addition to these helices, there are two conserved loops that connect the α-A to the α-Z helix and the α-B to the α-C helix. These are denoted as the ZA and BC loops respectively. To date, two apo structures have been solved for the BRD7 bromodomain using both solution state NMR (9) and X-ray crystallography (10). |
| - | Like other related Bromodomains, BRD7 is also known to bind to acetylated Lysines (Kac) on Histones H3 and H4. Specifically, K9 and K14 on H3 (8). BRD7 has also been shown to recognize a variety of Kac restudies on Histone H4 as well. Although there is no known structure of BRD7 in complex with an acetylated Histone peptide, there is in vitro evidence that supports the interactions between BRD7 and Kac (6). | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:BRD7 with BI9564.png|600px|center|thumb|Figure 2]] | ||
== Comparison to other family IV bromodomains == | == Comparison to other family IV bromodomains == | ||
| - | BRD has a similar sequence to other Bromodomains contained within family IV. The other proteins in family IV are: BRD9, BRPF3, BRPF1, BRPF1B, BRD1, ATAD2, and ATAD2B. Shown in Figure 3 is a sequence alignment between BRD7 and its closest related member of family IV, BRD9. The bromodomain sequence is 70 residues long for BRD7 and BRD9. For BRD7, the bromodomain sequence ranges from residue 148-218 while in BRD9 the sequence ranges from 153-223. Despite being the two most closely related bromodomains in family IV, | + | BRD has a similar sequence to other Bromodomains contained within family IV. The other proteins in family IV are: BRD9, BRPF3, BRPF1, BRPF1B, BRD1, ATAD2, and ATAD2B. Shown in Figure 3 is a sequence alignment between BRD7 and its closest related member of family IV, BRD9. The bromodomain sequence alignment is 70 residues long for BRD7 and BRD9. For BRD7, the bromodomain sequence ranges from residue 148-218 while in BRD9 the sequence ranges from 153-223. Despite being the two most closely related bromodomains in family IV, these two sequences only share 71.83% sequence identity in the conserved bromodomain region. Amino acid differences with little chemical similarity are highlighted in yellow. |
[[Image:BRD7 BRD9 sequence alignment.png|600px|center|thumb|Figure 3]] | [[Image:BRD7 BRD9 sequence alignment.png|600px|center|thumb|Figure 3]] | ||
| + | ==Interactions with Ligands and inhibitors== | ||
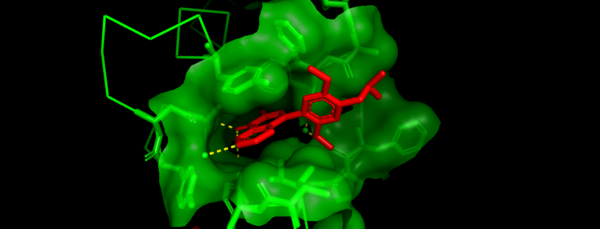
| + | Like other related Bromodomains, BRD7 is also known to bind to acetylated Lysines (Kac) on Histones H3 and H4 (1). Although there is no known structure of BRD7 in complex with an acetylated Histone peptide, there is in vitro evidence that supports the interactions between BRD7 and acetylated Histones (9). Currently the only published structures of BRD7 bound to a ligand has shown it in complex with a variety of well characterized bromodomain inhibitors including BI9564 and BI7273 (9,10). These inhibitors are often competitive inhibitors that will bind the active site of the bromodomain and prevent acetyl lysine binding(11). Shown in Figure 4 is a zoomed in image of BRD7 (green) in complex with bromodomain inhibitor BI9564 (red)(10). BI9564 fits tightly into the acetyl lysine binding pocket of this protein with the main interacting residues being TYR217, ASN211, TYR210, ILE164, PHE158, PHE156, and PHE155(10). Specific mutations in the binding pocket of BRD7 can prevent acetyl lysine recognition as well. Due to its implication in a variety of cancers, and its association with transcriptional regulation BRD7 has become a drug target for therapeutic inhibitors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:BRD7 with BI9564.png|600px|center|thumb|Figure 3]] | ||
== Implications in disease== | == Implications in disease== | ||
| - | BRD7 along with many other Bromodomains has been widely implicated in a variety of diseases like Cancer. There is increasing evidence that BRD7 is highly downregulated in a variety of human cancers | + | BRD7 along with many other Bromodomains has been widely implicated in a variety of diseases like Cancer(12-14). There is increasing evidence that BRD7 is highly downregulated in a variety of human cancers and BRD7 is known to act as a crucial component of both the p53 and BRCA1 oncogenic pathways(3). BRD7 is most notably associated with NPC. In NPC cells, it is frequently found that BRD7 is under expressed, which may play a large role in NPC development and progression(15). When BRD7 is overexpressed, it slows the growth of NPC cells through transcriptional regulation and inhibits the G1 to S phase cell cycle transition (1). |
| + | BRD7 has also been widely studied in breast cancer (13). It is a known binding partner of BRCA1 and has been found to be essential to expression of the Estrogen receptor on breast cancer cells. Inhibition of BRD7 in these cells has been shown to prevent Estrogen receptor expression causing the cancer cells to become more resistant to treatment(13). BRD7 was also found to be frequently deleted or downregulated in breast cancer cells suggesting its importance in the formation or sustainability of these cell lines (12). | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 16:42, 28 April 2020
Bromodomain Containing Protein 7 (BRD7)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644